Biomimetic Architecture
Basic information
Project Title
Full project title
Category
Project Description
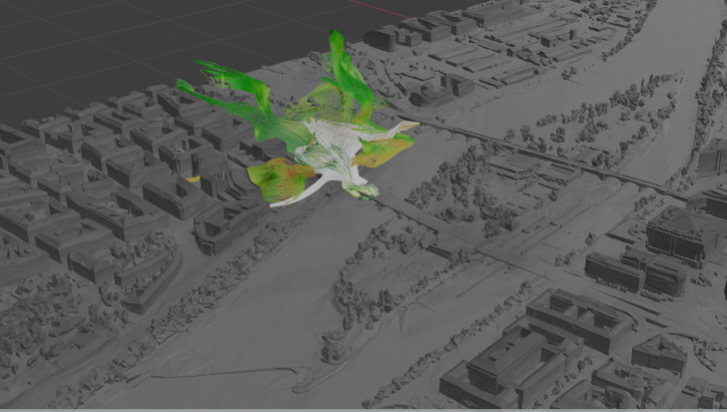
The project proposes a new strategy for creating biomimetic architectural structures based on the idea of adaptation to a dynamically changing environment and with the use of advanced machine learning and AI methods. The biomimetic architecture uses physical and virtual processes that are transformed and assembled into structures based on environmental properties and behaviour. The project investigates a living dynamic system as a complex set of natural and cultural sub-processes.
Project Region
EU Programme or fund
Description of the project
Summary
The project proposes a new strategy for creating biomimetic architectural structures based on the idea of adaptation to a dynamically changing environment and with the use of advanced machine learning and AI methods. The biomimetic architecture uses physical and virtual processes that are transformed and assembled into structures based on environmental properties and behaviour. The project investigates a living dynamic system as a complex set of natural and cultural sub-processes in which each of the interacting entities and systems creates complex aggregates. It deals with natural processes, communication flows, information networks, dense noise masses of data, a large group of agents and their spatial interactions in the environment. By significantly expanding existing research, the project creates a model useful for testing various aspects of adaptation to a complex dynamic environment. This refers to the difficulty of designing artificial agents that can intelligently respond to evolving complex processes.
In our view, urban and architectural structures are complex multi-dimensional structures in which natural processes and interactions of large groups of agents, communication flows, information networks, and others are intertwined. The above structures undergo continuous transformations. A dynamic environment is any space that surrounds us and the structure of which changes over time or is modified by groups of agents. There are closed spaces with relatively well-defined boundaries and others that do not have well-defined boundaries, which we can call open spaces. These environments are usually rich, complex and can generate significant "noisy" data, unstructured and sometimes very dynamic changes.
Key objectives for sustainability
Biomimetic architecture uses the features of natural design processes and relies on dynamic adaptation to environmental changes. The analogies of evolving architecture should be understood not only in terms of the applied natural processes of development of forms through natural selection, but also in the restless tendencies towards optimization and self-organisation that significantly improve the efficiency and power of diverse prototyping. Architecture is designing for survival, designing for life, and emphasizes the need for a responsible approach to the transformation and formation of The project proposes a new strategy for creating biomimetic architectural structures based on the idea of adaptation to a dynamically changing environment and with the use of advanced machine learning and AI methods. The biomimetic architecture uses physical and virtual processes that are transformed and assembled into structures based on environmental properties and behaviour. The project investigates a living dynamic system as a complex set of natural and cultural sub-processes in which each of the interacting entities and systems creates complex aggregates. It deals with natural processes, communication flows, information networks, dense noise masses of data, a large group of agents and their spatial interactions in the environment. By significantly expanding existing research, the project creates a model useful for testing various aspects of adaptation to a complex dynamic environment. This refers to the difficulty of designing artificial agents that can intelligently respond to evolving complex processes.energy and materials.
Key objectives for aesthetics and quality
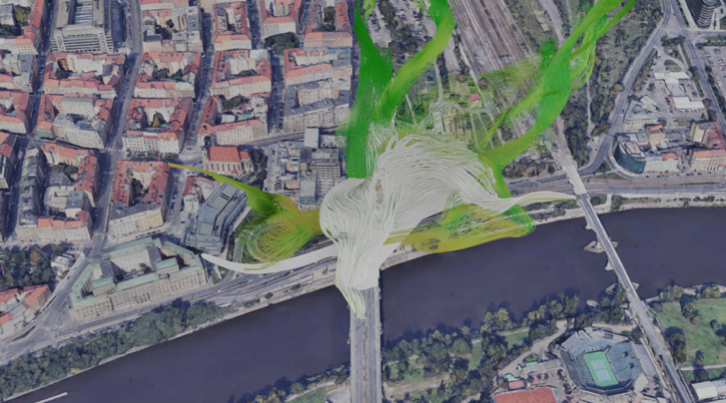
he project proposes a new strategy for creating biomimetic architectural structures based on the idea of adaptation to a dynamically changing environment and with the use of advanced machine learning and AI methods. The biomimetic architecture uses physical and virtual processes that are transformed and assembled into structures based on environmental properties and behaviour. The project investigates a living dynamic system as a complex set of natural and cultural sub-processes in which each of the interacting entities and systems creates complex aggregates. It deals with natural processes, communication flows, information networks, dense noise masses of data, a large group of agents and their spatial interactions in the environment. By significantly expanding existing research, the project creates a model useful for testing various aspects of adaptation to a complex dynamic environment. We used selected data that describes behaviour of citizens of Prague or Karsruhe /with consultancy with experts from department of Architecture Czech Technical University. We used data that express transforming processes as movement and communication flow during Covid pandemia change. We compare and analyze changes of behaviour of city citizens.
Key objectives for inclusion
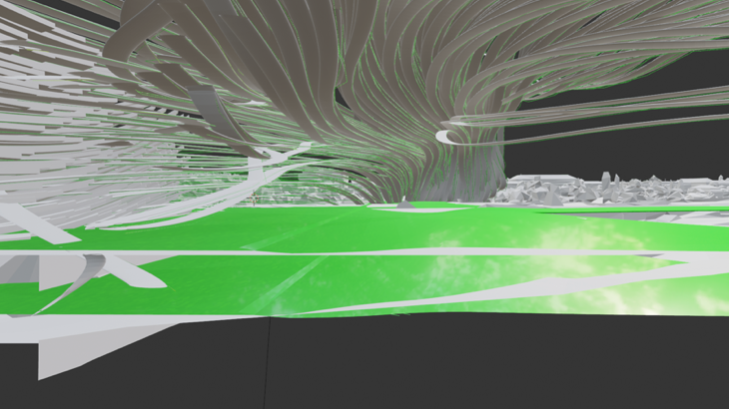
Working with large data sets obtained from a changing environment requires advanced machine learning methods. We tested various AI methods for modeling and generating new architectural forms. In particular, we use Transformers that work by using convolutional neural networks together with attention models, making them much more efficient than previous models. We have previously tested recurrent neural networks RNN, long short term memory networks LSTM and VAE variational autoencoders (Lisek 2020). The transformer model is a seq2seq model which uses attention in the encoder as well as the decoder. Transformers have been used for many (conditional) sequence generation tasks, such as machine translation, constituency parsing, protein sequence generation and can be used for architecture design. Transformer models consist of an Encoder and a Decoder. The Encoder takes the input sequence and maps it into a higher dimensional space (n-dimensional vector). That abstract vector is fed into the Decoder which turns it into an output sequence. The output sequence can be in any sequence of numbers, symbols, etc. The attention-mechanism looks at an input sequence and decides at each step which other parts of the sequence are important. Self-attention, is an attention mechanism relating different positions of a single sequence in order to compute a representation of the sequence. Self-attention can be intuitively explained using a text example, when reading this text, you are temporarily focusing on the word being read, but at the same time your mind still keeps the important keywords of the text to provide context. In our research we worked with sequences of numbers that represent 3d object as positions of its particles/elements and velocity.
Results in relation to category
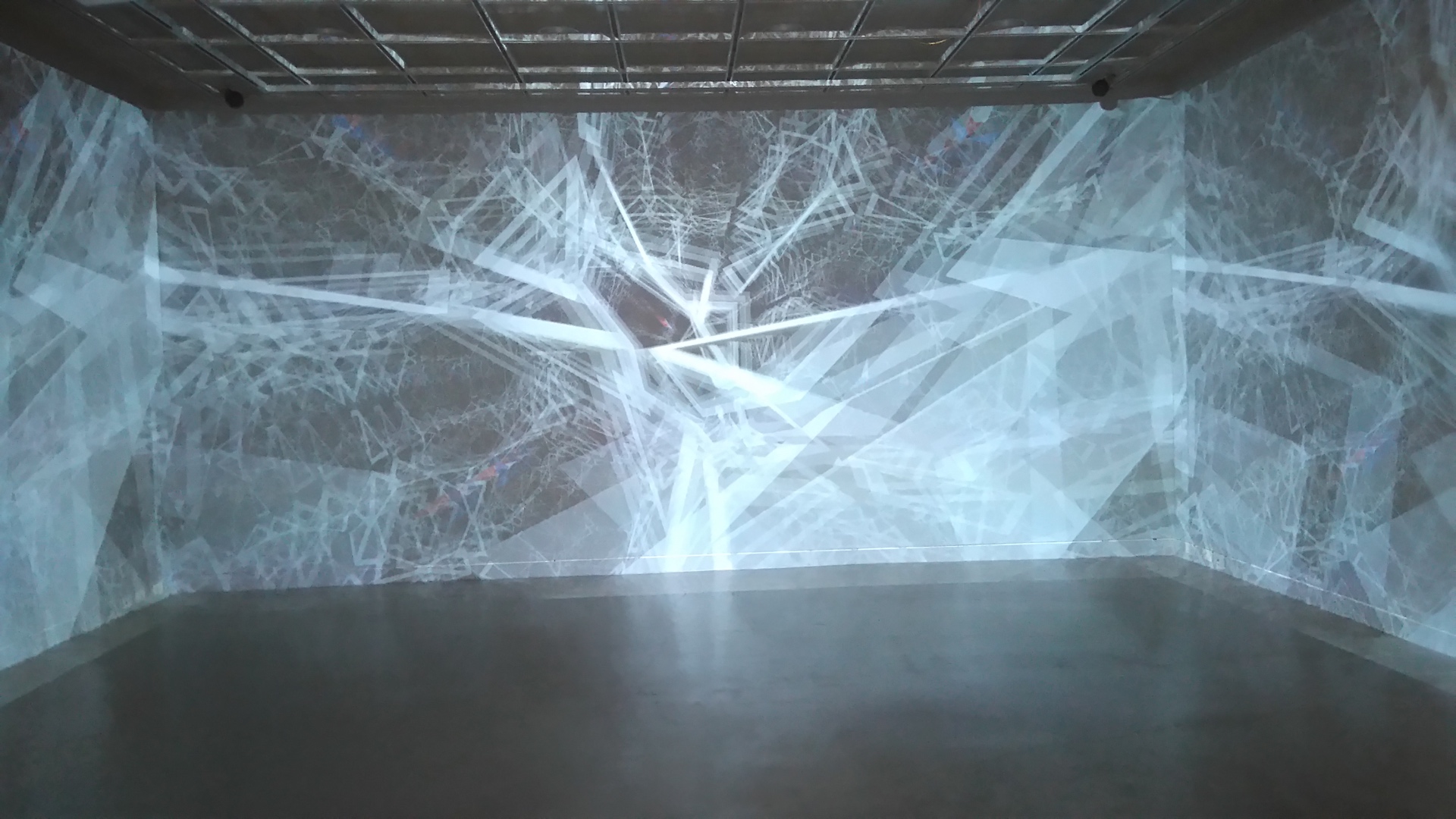
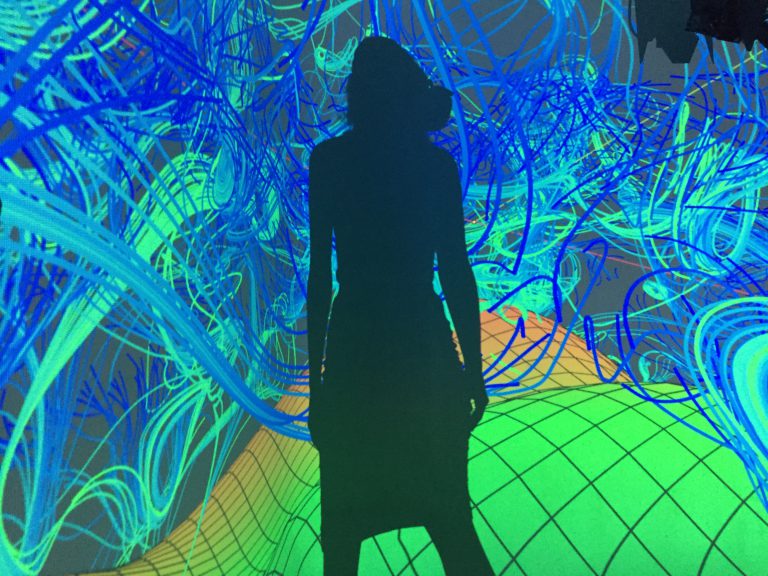
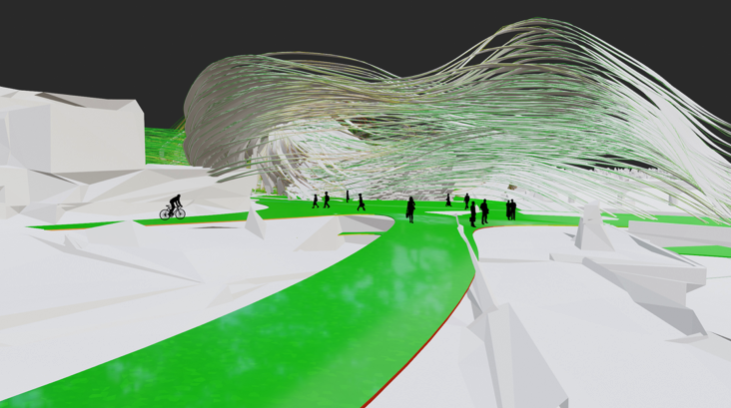
An interesting direction of research on modern architecture is related to the problem of immersion, creating virtual environments and sound spatialisation. Virtual environments also provide an excellent space for testing machine learning methods. Restrictions introduced during the pandemic motivated me to research potential of AI and virtual architecture for the evolution of society. Our research was focused on a roles of Presence, Flow, Immersion, and Interactivity. We was particularly interested in the problem of presence and flow in VE. Presence is defined as the subjective experience of being in one place or environment, even when one is physically situated in another. Presence is a normal awareness phenomenon that requires directed attention and is based in the interaction between sensory stimulation, environmental factors that encourage and enable immersion. Flow is a state of experience where someone is completely absorbed and immersed in an activity. We researched relations between presence, adaptation and interactivity, e.g. how interactivity and adaptation improves experience of presence. We tested our meta-learning approach in virtual environment. We studied how various new methods of operation in virtual architecture can influence future social structures. We created immersive architectural installations that were presented during Siggraph Asia 2020 and at Institute of Electronic Arts.
How Citizens benefit
The goal was to create new support tools in the form of software for researching and developing evolutionary architecture. The above research is fundamental to an architecture of the future that will be well adapted, in particular a flexible safe architecture that accommodates mass migrations and crisis situations such as pandemics. It is also necessary to create large groups of researchers, architects and urban planners that change and adapt the architecture of our cities and suburban to the new needs of their inhabitants.
In our view, urban and architectural structures are complex multi-dimensional structures in which natural processes and interactions of large groups of agents, communication flows, information networks, and others are intertwined. The above structures undergo continuous transformations. A dynamic environment is any space that surrounds us and the structure of which changes over time or is modified by groups of agents. There are closed spaces with relatively well-defined boundaries and others that do not have well-defined boundaries, which we can call open spaces. Examples of confined spaces include homes, offices, hospitals, classrooms, and cars. Examples of open spaces are: streets, bridges and parking lots, fields (in agriculture), air (in the case of airplanes) and the sea (for underwater pollution measurements and tsunami early warning system). These environments are usually rich, complex, unpredictable, and can generate significant "noisy" data, unstructured and sometimes very dynamic changes.
Innovative character
Our approach for analyzing and creating evolving architecture is based on meta-learning. Meta-learning is the next generation of artificial intelligence systems. Meta-learning goes by many different names: learning to learn, multi-task learning, transfer learning, zero shot learning, etc. People easily transfer knowledge acquired in solving one task to another more general task. This means that we naturally recognize and apply previously acquired knowledge to new tasks. The more the new task is related to our previous experience, the easier we can master it. In contrast, popular machine learning algorithms deal with individual tasks and problems. Transfer learning attempts to change this by developing methods to transfer knowledge acquired in one or more source tasks and using them to improve learning in a related target task. The goal of transfer learning is to improve learning in the target task by using knowledge from the source task. Techniques enabling knowledge transfer will constitute significant progress in AI and and architecture.
We used more flexible and general algorithms that adopt to many tasks (Liquid Time-constant Networks architecture). Usually, a neural network’s parameters are locked into place after training. In contrast, in a liquid neural network LTCN, the parameters are allowed to continue changing over time and with experience. The resulting models represent dynamical systems with varying (i.e.,liquid) time-constants coupled to their hidden state, with outputs being computed by numerical differential equation solvers.