New Sources
Basic information
Project Title
Full project title
Category
Project Description
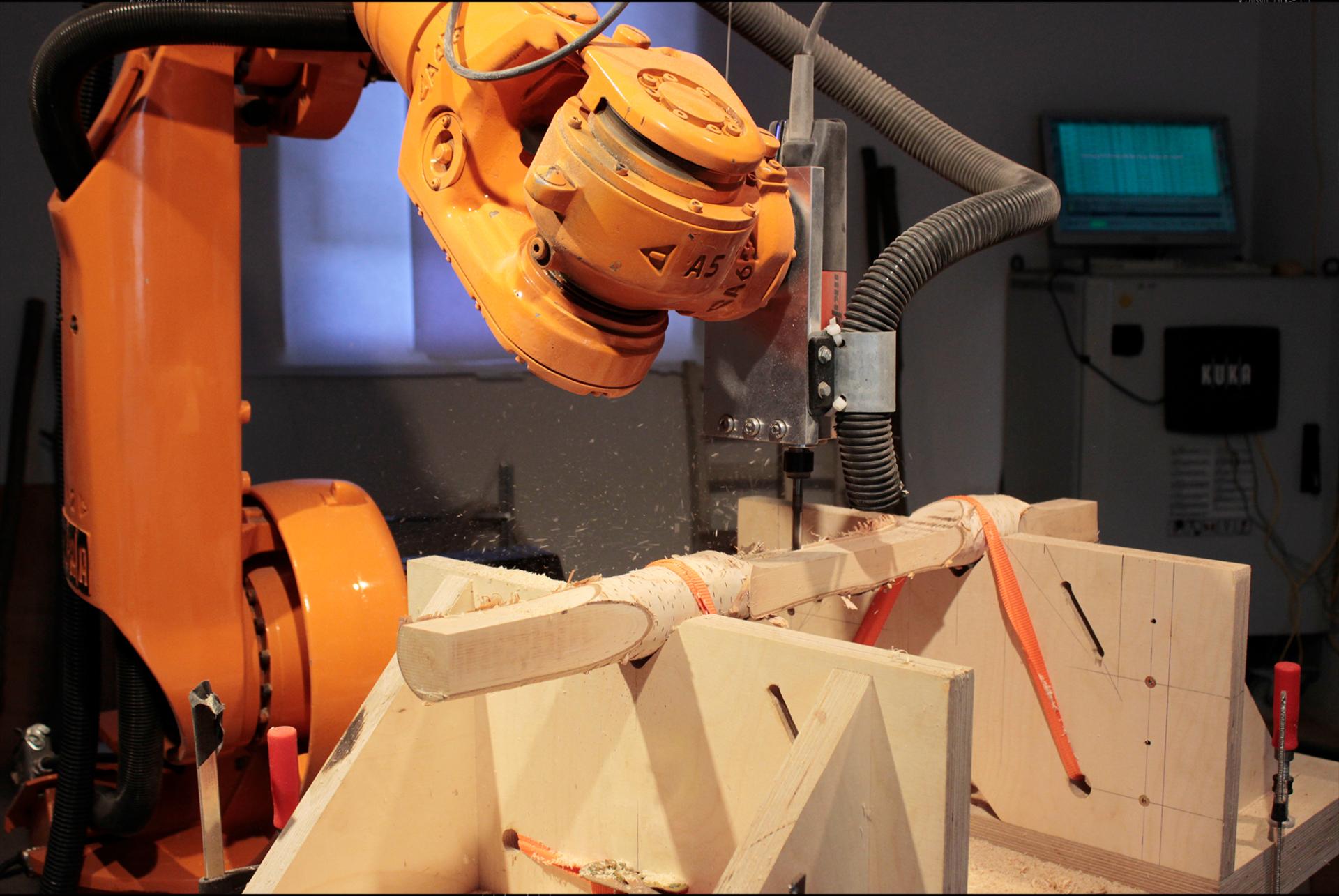
Deforestation will be a major topic in our future lives. New Sources tackles this phenomenon and provides a new solution for a sustainable production of everyday objects without wasting valuable material. Through an interconnection of 3D-scanning, computational design and robotic fabrication it is possible to use leftover materials from the wood industry in a serially production process. Branches that have no direct application so far are transformed by algorithms into domestic objects.
Geographical Scope
Project Region
Urban or rural issues
Physical or other transformations
EU Programme or fund
Which funds
Description of the project
Summary
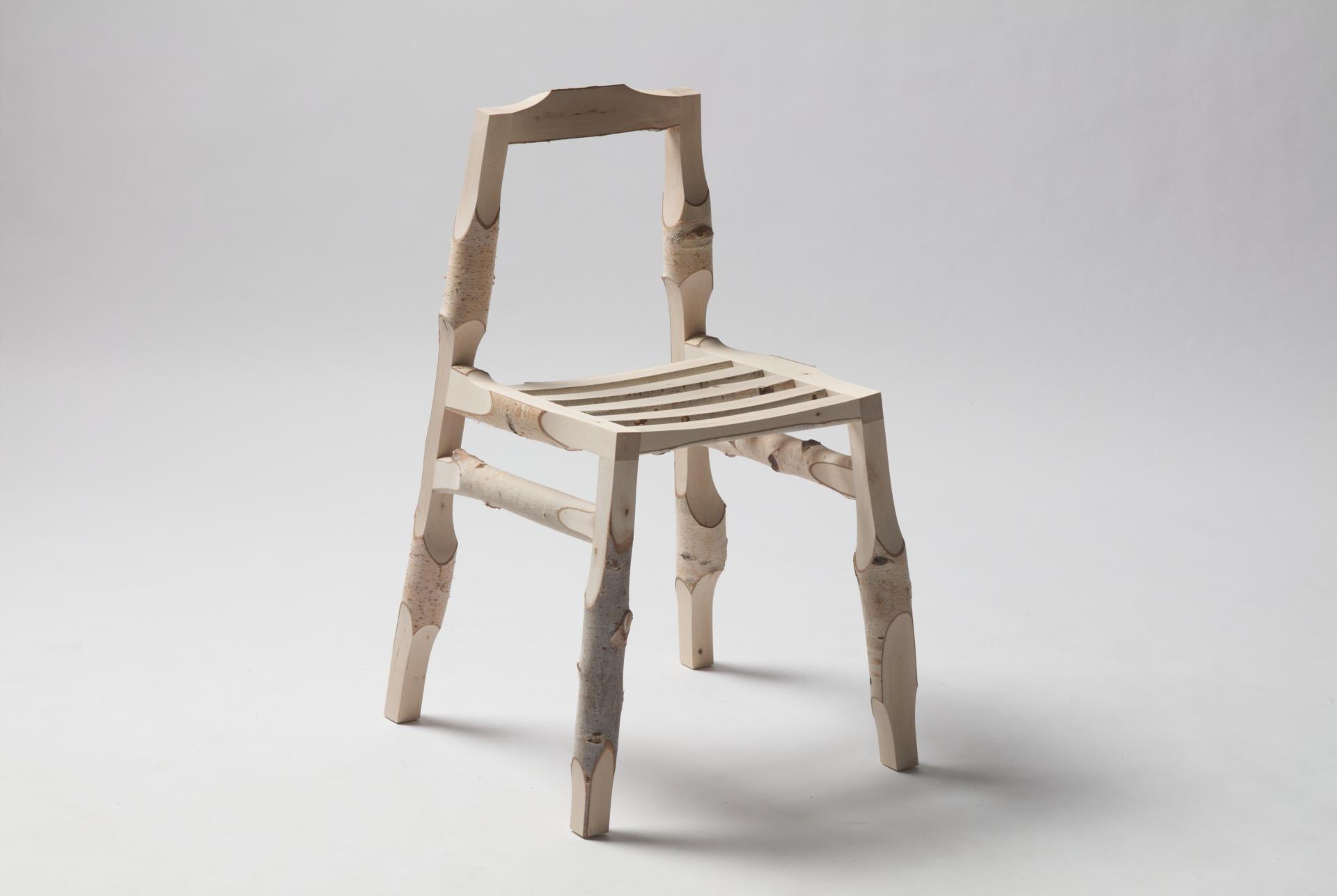
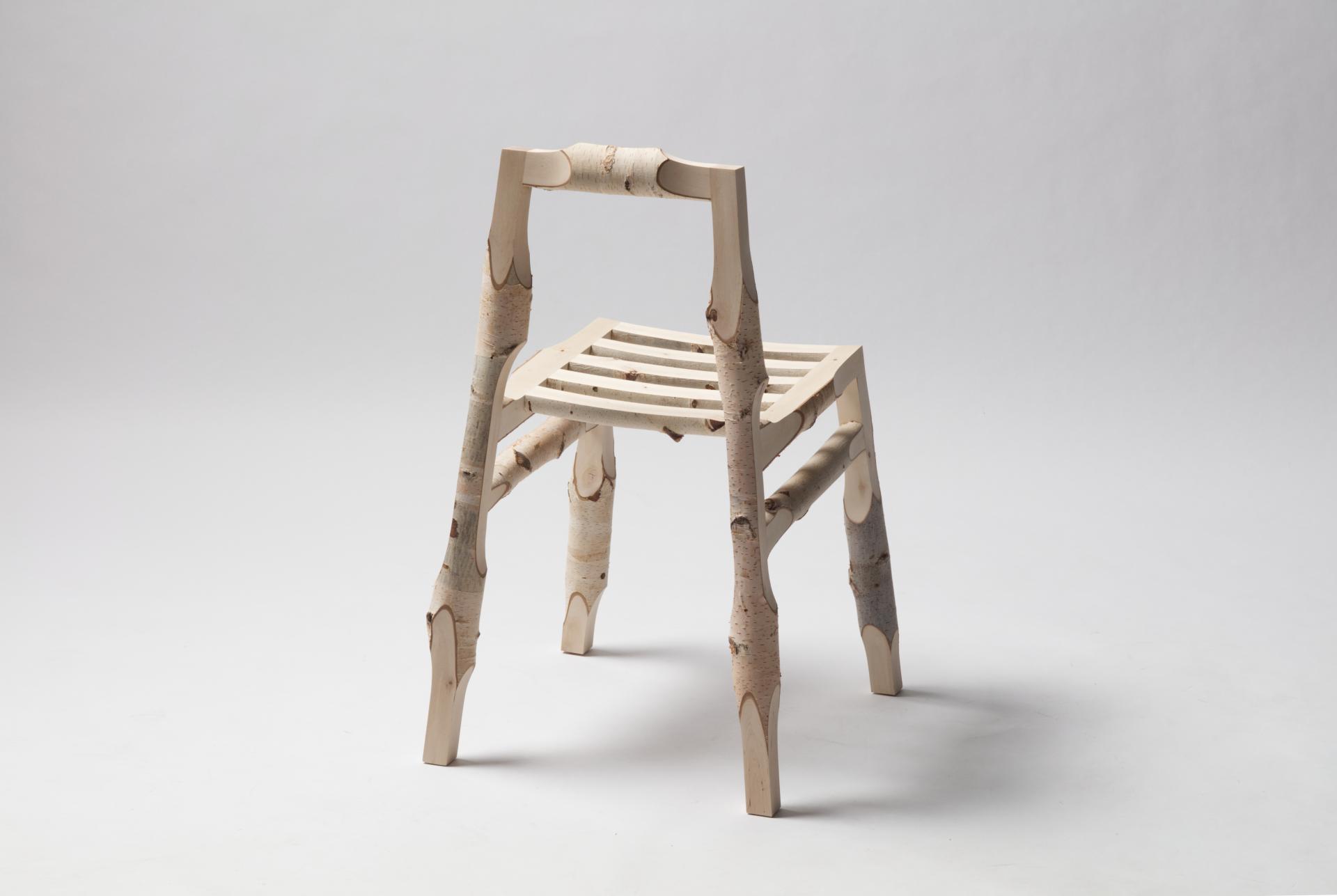
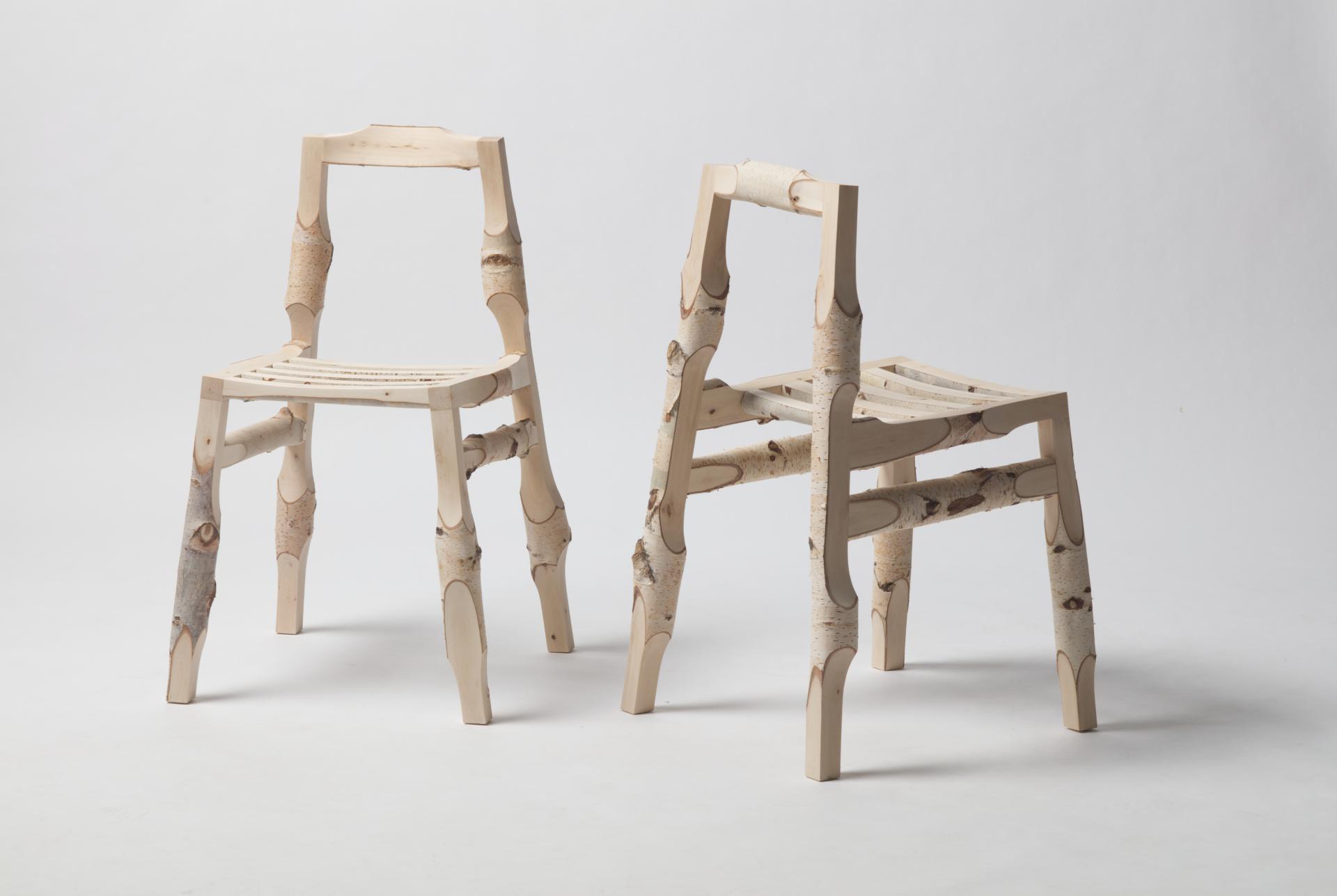
Deforestation will be a major topic in our future lives. Every year tree cover loss increases faster then ever through wood industry, agriculture and natural disasters like bushfires or heavy storms. The World Bank estimates that about 10 million square km of forest have been lost since the beginning of the 20th century. In the past 25 years, forests shrank by 1.3 million square km. To counteract this trend more sustainable models are needed. New Sources is a case study that shows the possibilities of contemporary technologies towards a more sustainable future. The interconnection of 3D-scanning, computational design and robotic manufacturing creates a serial production process for using wooden left over materials. Raw branches are 3D-scanned and then virtually processed by algorithms to constantly recalculate all production data for each individual part of an object. Due to the irregularity of the material every object becomes a unique piece. The Computational Log Chair is the first object of the series. Precisely milled surfaces and edges appear all around the object stand in contrast to the raw branch surface and display the intersection between nature and technology. Birch bark partly remains and becomes a natural ornament. It keeps the original character of the material alive. The project criticizes global material consumption and questions the standardization of natural grown materials in our domestic environment.
Key objectives for sustainability
Just the main stemm of a straight grown tree is usually used for timber. The top of the tree and all branches are cut off and not used. This left over material is then burned or shredded and pressed into chipboards that are most of the time mixed with harmful binders like formaldehyde. After using them once they end up in landfills or waste incinerators. Reduce, Reuse, Recycle are the core principles of the project New Sources. The innovative production process makes it possible to use these left overs before their final exploitation. Through a scalable process branches can be used to construct everyday objects or even small architectural structures without using new materials. Single branches are connected through traditional wood joinery and doesn´t require any environmental harmful chemicals to connect them with each other. After use or in case of a damage the material can still go into its final cycle. Next to the wood industry there are many material streams in our built environment for example in parks or along roads. These areas are usually trimmed twice a year and this material could also be used to build domestic objects instead of wasting it. Furthermore heavy storms appear more often in the last decade and break down branches or even whole trees. By using just these materials and the industries left overs the project is a sustainable and future orientated approach for wood working and furniture production. A big advantage of using algorithm based production is to be able to locally produce on demand. Looking more into the future whole trees could be scanned by drones through photogrammetry before even cutting them down and planing ahead with the entire material of a tree becomes possible.
Key objectives for aesthetics and quality
Due to the irregularity of the material every object becomes a unique piece even if it was serially produced. Visually no chair is identical to another one but provides exactly the same comfort while sitting. The precisely milled surfaces and edges look like they would have been carved by hand at first glance. By coming closer you understand that its precisely machine made. The milled surfaces stand in contrast to the raw branch surfaces and display the intersection of nature and technology. The bark partly remains and works as a natural ornament to keep the original character of the material alive. Unlike standardized material, you get a sense about the materials origin that leads to a return to nature. Usually unique furniture pieces are really expensive and are found in galleries or the art context. This new production process makes it possible to serially produce unique pieces for an affordable price, without wasting valuable material.
Key objectives for inclusion
One of New Sources key ambitions is to make sustainable design affordable and accessible to more people, across all levels of society. Design products and especially unique furniture pieces are usually perceived as not affordable by the average European consumer due to their high-cost and their limited availability. With the project New Sources I developed a sustainable production process, that is capable to mass produce unique pieces for an affordable price because of low material costs and automatized production processes based on algorithmic programming. Another aim I want to tackle with the project is the participation of local communities. Forests are not the only source for wood. There is also the built environment where material can be sourced. Without taking the timber industry into account, several tons of material accumulate every year in cities, gardens and along roads. Instead of burning this material or let it rot on ground ponies single people or whole communities could collaborate with production facilities to build their own objects and environments. Due to the support of intelligent, AI based software it will be much easier in the future to use these machines without being a specialist. This is where co-design processes can start. Its already a trend that production facilities and digital tools become more and more accessible through Fablabs or community workshops.
Physical or other transformations
Innovative character
New Sources explores the possibilities of contemporary production methods for unique and sustainable everyday objects. On the one hand using waste materials and automated production processes these objects become accessible to a large target group and are not limited to a wealthy and cultural upper class any more. On the other hand it is a sustainable way to produce objects without wasting new material sources. Technology and algorithms transform these materials into raw-looking objects, to embracing nature as a pillar of one’s home. In an increasingly digital society it will me more important than ever to ground yourself and get back to nature.