Taranto Circolare
Basic information
Project Title
Taranto Circolare
Full project title
Taranto Circolare: the circular transition begins in Taranto
Category
Shaping a circular industrial ecosystem and supporting life-cycle thinking
Project Description
Embark on a journey of sustainability and innovation with the Taranto Circolare Project—an inspiring initiative reshaping the city of Taranto into a vibrant hub of circular living. Join us in reimagining waste as a resource, fostering community engagement, and creating a greener, more resilient tomorrow for Taranto. Let's turn the circle of possibilities into a reality.
Geographical Scope
Local
Project Region
Taranto, Italy
Urban or rural issues
Mainly urban
Physical or other transformations
It refers to other types of transformations (soft investment)
EU Programme or fund
Yes
Which funds
Other
Other Funds
NextGenerationEU<br />
Grants to micro and small enterprises, third sector entities and organisations operating in the cultural and creative sectors to promote innovation and green design - Capacity building for cultural operators to manage the digital and green transition;<br />
year: 2023
Description of the project
Summary
The 'Taranto Circolare' project is promoted by the Tondo organisation with the aim of enhancing the circular economy in the area of Taranto, Apulia, southern Italy. The project aims to guide Taranto's ecological transformation towards a circular model, becoming a point of reference and coordination.
The three main phases of the project include the analysis of the city's flows and business models, the creation of a Digital Portal and the promotion and design of new circular initiatives. The analysis identifies key sectors and the potential for implementing circularity. The platform digitises material and energy flows, connects actors, and provides tools for analysis and collaboration. The third phase develops projects to increase circularity.
Beneficiaries include Taranto civil society, local companies, institutions and citizens.
The Apulia region, which is particularly involved in the challenges of European cohesion, finds support in Taranto Circolare to address the socio-economic costs of the climate transition, as the project encourages the shift to sustainable practices, promotes collaboration, creates a local network and supports new initiatives, with the final aim of incresing the circularity level of Taranto.
An analysis has been developed on the material and energy flows of the city in Taranto. The analysis includes explanations about the current state of the city’s circularity and identifies the prossible projects to be developed to increase the circularity level of the city. In addition, the most relevant projects on circular economy of the city have been mapped, and involved within the digital platform.
The project integrates and promotes New European Bauhaus values and working principles, since it wants to promote the ecological and circular transition, working towards the reduction of the media-environmental impact, always keeping the focus on culture-related issues, with an eye on inclusivity.
The three main phases of the project include the analysis of the city's flows and business models, the creation of a Digital Portal and the promotion and design of new circular initiatives. The analysis identifies key sectors and the potential for implementing circularity. The platform digitises material and energy flows, connects actors, and provides tools for analysis and collaboration. The third phase develops projects to increase circularity.
Beneficiaries include Taranto civil society, local companies, institutions and citizens.
The Apulia region, which is particularly involved in the challenges of European cohesion, finds support in Taranto Circolare to address the socio-economic costs of the climate transition, as the project encourages the shift to sustainable practices, promotes collaboration, creates a local network and supports new initiatives, with the final aim of incresing the circularity level of Taranto.
An analysis has been developed on the material and energy flows of the city in Taranto. The analysis includes explanations about the current state of the city’s circularity and identifies the prossible projects to be developed to increase the circularity level of the city. In addition, the most relevant projects on circular economy of the city have been mapped, and involved within the digital platform.
The project integrates and promotes New European Bauhaus values and working principles, since it wants to promote the ecological and circular transition, working towards the reduction of the media-environmental impact, always keeping the focus on culture-related issues, with an eye on inclusivity.
Key objectives for sustainability
Taranto Circolare contributes to the transformation of local ecosystems in favour of more sustainable practices in a spirit of circularity. It mainly acts as an active researcher, collector and stimulator of good practices of the circular economy in Taranto and the territorial activities that have an influence on it, generating a positive impact on the entire city, as a stimulus to start working within this new economic, environmental and social paradigm aimed at promoting sustainability and the achievement of circularity.
New stimuli and ideas proposed through the Digital Portal are serving to accelerate the ecological and circular transition, creating new jobs, improving the quality of life of people and the surrounding environment, and having a positive economic impact.
At the economic and industrial level, the objectives of the project activities were to create new programmes and initiatives that implement the principles of the circular economy and that can support the optimisation of local resource management and the generation of products that give new life to waste, as well as the creation of collaborative processes between companies towards industrial symbiosis at all levels.
At the environmental level, the project's objective was to understand which areas are the most relevant, where there is the most waste and where waste could be better utilised, as well as to recognise which areas could be valuable and where circularity principles could be implemented. In fact, the project has served to understand the main ongoing projects on the circular economy and also proposes what could be potential additional projects to be developed to improve the level of circularity in the area.
At the social level, the project's objective was to raise the awareness of the Taranto community on circular economy issues, so that they can include the necessary tools to enable the ecological transition in their daily lives.
New stimuli and ideas proposed through the Digital Portal are serving to accelerate the ecological and circular transition, creating new jobs, improving the quality of life of people and the surrounding environment, and having a positive economic impact.
At the economic and industrial level, the objectives of the project activities were to create new programmes and initiatives that implement the principles of the circular economy and that can support the optimisation of local resource management and the generation of products that give new life to waste, as well as the creation of collaborative processes between companies towards industrial symbiosis at all levels.
At the environmental level, the project's objective was to understand which areas are the most relevant, where there is the most waste and where waste could be better utilised, as well as to recognise which areas could be valuable and where circularity principles could be implemented. In fact, the project has served to understand the main ongoing projects on the circular economy and also proposes what could be potential additional projects to be developed to improve the level of circularity in the area.
At the social level, the project's objective was to raise the awareness of the Taranto community on circular economy issues, so that they can include the necessary tools to enable the ecological transition in their daily lives.
Key objectives for aesthetics and quality
The Taranto Circolare project helps to relaunch the city of Taranto nationally and internationally, as it aims to improve the city's image and the consequent development of tourism in the area. The Digital Portal promotes the city's good practices, generating attractions for investors, new partners and tourists.
The project also contributes to supporting and enhancing the productive and cultural supply chains of Taranto, which will thus benefit from a positive promotion of its image, positioning itself as a point of reference, meeting and experimentation of new circular business strategies and coordination of the innovation ecosystem.
The project aims to make the Digital Portal and the proposed activities a space for the creation of new social relations, encouraging a sense of belonging through new experiences and the integration and promotion of new lasting cultural values.
Through Taranto Crea funding (Invitalia programme to create and develop entrepreneurial initiatives in the cultural-tourism and non-profit industry in Southern Italy), Tondo has implemented the project in close relationship with the actors of Old City of Taranto, the city's historical and cultural centre: among these are the Municipality of Taranto, the University of Bari "Aldo Moro", the Polytechnic of Bari, various associations operating in the Old City (such as the Jonian Dolphin Conservation), realities aimed at the promotion and preservation of Taranto culture at local, regional and national levels.
The project also contributes to supporting and enhancing the productive and cultural supply chains of Taranto, which will thus benefit from a positive promotion of its image, positioning itself as a point of reference, meeting and experimentation of new circular business strategies and coordination of the innovation ecosystem.
The project aims to make the Digital Portal and the proposed activities a space for the creation of new social relations, encouraging a sense of belonging through new experiences and the integration and promotion of new lasting cultural values.
Through Taranto Crea funding (Invitalia programme to create and develop entrepreneurial initiatives in the cultural-tourism and non-profit industry in Southern Italy), Tondo has implemented the project in close relationship with the actors of Old City of Taranto, the city's historical and cultural centre: among these are the Municipality of Taranto, the University of Bari "Aldo Moro", the Polytechnic of Bari, various associations operating in the Old City (such as the Jonian Dolphin Conservation), realities aimed at the promotion and preservation of Taranto culture at local, regional and national levels.
Key objectives for inclusion
Taranto Circolare aims to be an inclusive, participatory and accessible project for all. Inclusiveness in this project was key to ensuring that the transition to a circular economy benefits all stakeholders, including local residents and the community involved.
The main objectives in terms of inclusiveness were:
Involving local communities: to ensure inclusiveness, the project actively involved the local communities of Taranto from the early stages of the decision-making process. Residents' voices, local companies and civil society have been heard, and their needs and concerns have been taken into account in project design and implementation.
Involving stakeholders: Inclusiveness also extended to stakeholders, such as local businesses, associations and public institutions. Collaboration between all these actors helped develop solutions that took into account a wide range of perspectives.
In addition, we are convinced that over time, Taranto Circolare could also create local employment opportunities: the implementation of a circular economy could lead to new employment opportunities, for example in waste collection, recycling and management. These employment opportunities could be accessible to the local population, particularly those who may have been adversely affected by the previous economic situation in Taranto.
The main objectives in terms of inclusiveness were:
Involving local communities: to ensure inclusiveness, the project actively involved the local communities of Taranto from the early stages of the decision-making process. Residents' voices, local companies and civil society have been heard, and their needs and concerns have been taken into account in project design and implementation.
Involving stakeholders: Inclusiveness also extended to stakeholders, such as local businesses, associations and public institutions. Collaboration between all these actors helped develop solutions that took into account a wide range of perspectives.
In addition, we are convinced that over time, Taranto Circolare could also create local employment opportunities: the implementation of a circular economy could lead to new employment opportunities, for example in waste collection, recycling and management. These employment opportunities could be accessible to the local population, particularly those who may have been adversely affected by the previous economic situation in Taranto.
Results in relation to category
The Taranto Circular Project is proposing, stimulating and collecting good practices of circular economy, starting from the Old City of Taranto and involving territorial activities that positively influence the whole city. It is playing a crucial role in initiating and accelerating the ecological and circular transition.
To date, we have achieved two important results:
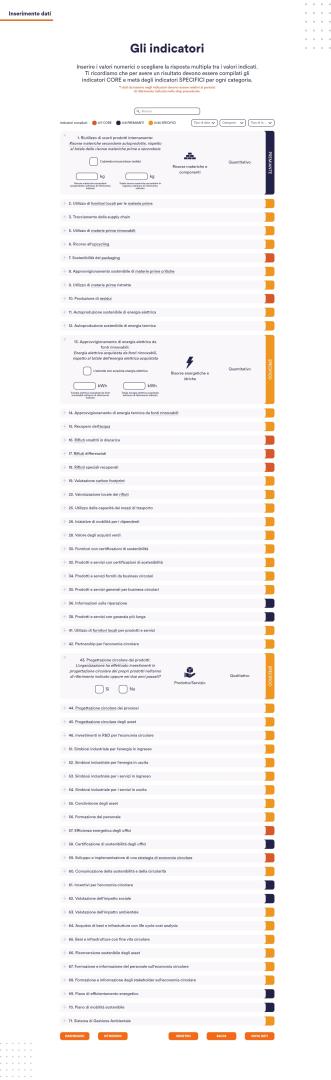
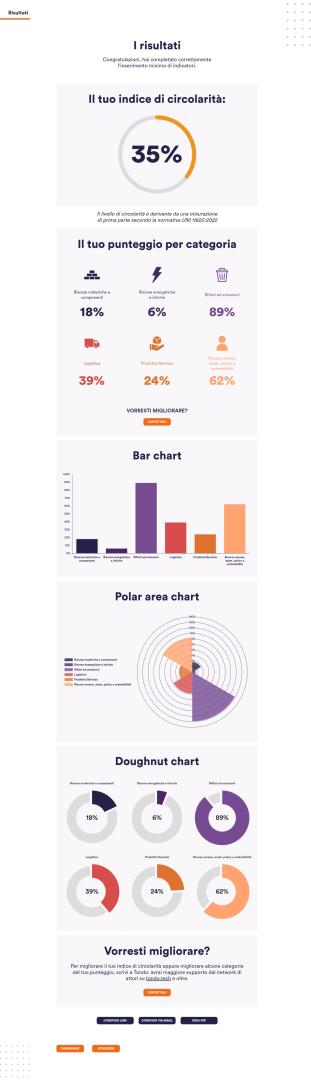
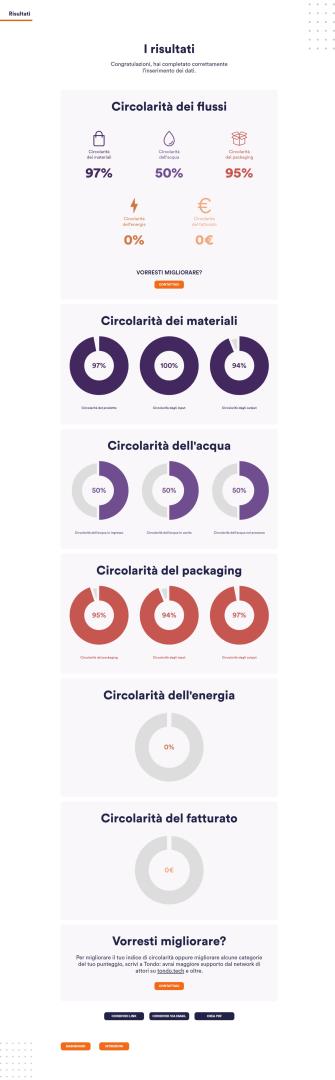
- We have concluded a Report in which we report the results of the analysis of the city's material and energy flows and the business models of Taranto's economic actors applying the principles of the circular economy. The aim of the study is to measure, in collaboration with local universities, the current state of circularity and identify the best business opportunities.
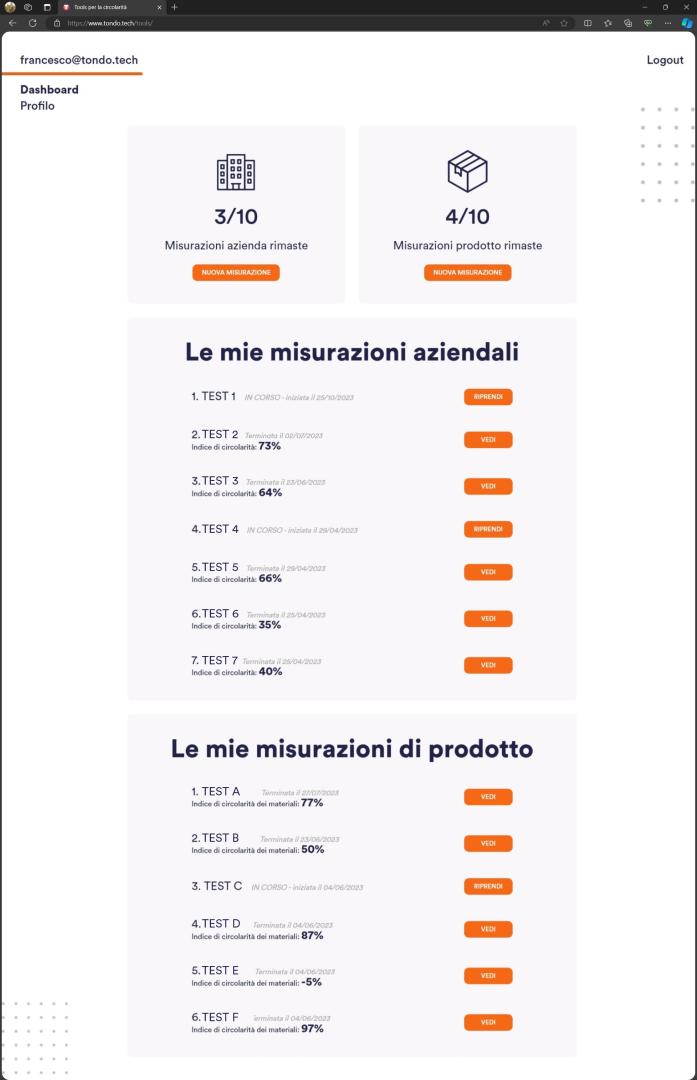
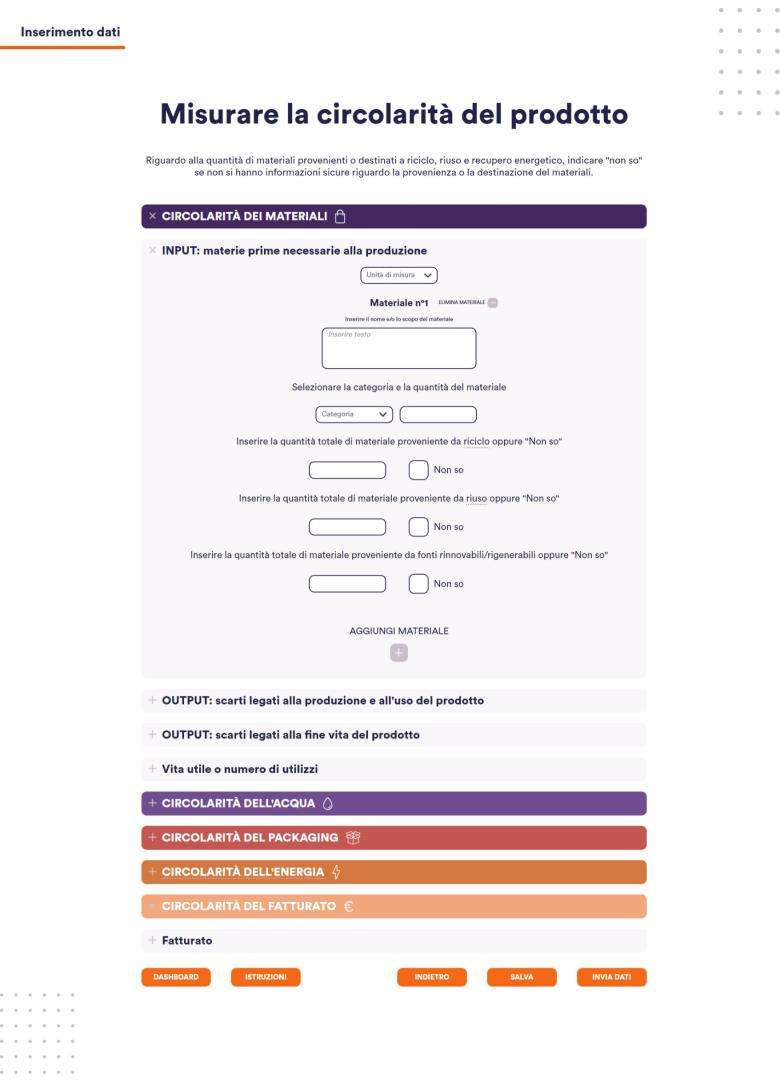
- We have created the Taranto Circular Digital Portal: like a showcase, the platform will promote businesses, organisations and activities that look at sustainability as an opportunity. The portal will provide tools for institutions to analyse material, energy and emission flows; it will connect actors to foster new collaborations and give an overview of available calls for proposals that can help sustainable planning.
In addition, the external communication of Taranto Circular is improving the city's image in terms of narrative, branding and attractiveness.
To date, we have achieved two important results:
- We have concluded a Report in which we report the results of the analysis of the city's material and energy flows and the business models of Taranto's economic actors applying the principles of the circular economy. The aim of the study is to measure, in collaboration with local universities, the current state of circularity and identify the best business opportunities.
- We have created the Taranto Circular Digital Portal: like a showcase, the platform will promote businesses, organisations and activities that look at sustainability as an opportunity. The portal will provide tools for institutions to analyse material, energy and emission flows; it will connect actors to foster new collaborations and give an overview of available calls for proposals that can help sustainable planning.
In addition, the external communication of Taranto Circular is improving the city's image in terms of narrative, branding and attractiveness.
How Citizens benefit
Apulia, a region facing challenges in securing living standards, universal access to services, addressing unemployment, and retaining talent, is a focus of the EU's cohesion policy. Taranto, significantly impacted by socio-economic costs of climate transition, is supported by the EU's Just Transition Fund.
Taranto Circolare aims to address local issues by allowing citizens to benefit from circular economy projects present on the Digital Portal. The project promotes circular economy principles, supporting companies, associations, and organizations in the micro and macro territory engaged in sustainable projects. It creates a local ecosystem for the circular economy, environmental sustainability, and green transition, aiming to make Taranto a symbol of change, innovation, and sustainability.
Throughout the project, local actors, including the municipality, universities, small and medium-sized enterprises, foundations, and civil society, actively participated. The first phase involved collaboration with Local Universities to analyze material and energy flows in Taranto's old city. Subsequently, Tondo came into contact with the local population: public events such as "Re Think Circular Economy Taranto 2022" have strengthened the dialogue with local actors (local companies and associations) and citizens, culminating in a platform launch event in December 2022. The success of launch events and presentations at local and regional levels encouraged numerous entities in Taranto's circularity sector to contact Tondo for platform inclusion.
In addition, several workshops were organized to involve local actors and cities, and have their point of view on the design and implementation of the project. Even during the third phase of the project (planning of new ideas) the local population is strongly involved: their ideas and proposals are heard, with the intention of being then transformed into concrete projects.
Taranto Circolare aims to address local issues by allowing citizens to benefit from circular economy projects present on the Digital Portal. The project promotes circular economy principles, supporting companies, associations, and organizations in the micro and macro territory engaged in sustainable projects. It creates a local ecosystem for the circular economy, environmental sustainability, and green transition, aiming to make Taranto a symbol of change, innovation, and sustainability.
Throughout the project, local actors, including the municipality, universities, small and medium-sized enterprises, foundations, and civil society, actively participated. The first phase involved collaboration with Local Universities to analyze material and energy flows in Taranto's old city. Subsequently, Tondo came into contact with the local population: public events such as "Re Think Circular Economy Taranto 2022" have strengthened the dialogue with local actors (local companies and associations) and citizens, culminating in a platform launch event in December 2022. The success of launch events and presentations at local and regional levels encouraged numerous entities in Taranto's circularity sector to contact Tondo for platform inclusion.
In addition, several workshops were organized to involve local actors and cities, and have their point of view on the design and implementation of the project. Even during the third phase of the project (planning of new ideas) the local population is strongly involved: their ideas and proposals are heard, with the intention of being then transformed into concrete projects.
Physical or other transformations
It refers to other types of transformations (soft investment)
Innovative character
The Taranto Circolare Project's innovation lies in its comprehensive and forward-looking strategy, incorporating digital solutions, circular economy principles, collaborative platforms, and an outward-facing approach to sustainable development.
The project was born from the idea that a digital portal that served as a showcase to promote businesses, organizations and activities focused on the circular economy has not yet been implemented in Italy, and its impact can be crucial in inspiring different stakeholders to undertake circular transformation paths. It also addresses the need to revitalise and coordinate the innovation ecosystem by embracing the benefits of the circular economy at local and national/international levels.
The innovation of our initiative consists in introducing a new product, a virtual portal to promote, create awareness and guide citizens and businesses in the circular economy sector in the Taranto area. The portal presents local initiatives and proposes pathways for ecological and circular transformation supported by the project.It provides analysis tools for the city and businesses, assess the circularity and impact of linear production processes and alternative circular opportunities.
In the realm of public policy, the project innovatively supports the city in aligning with European directives and Italian policy strategies on the circular economy. It aligns with policies such as the Circular Economy Action Plan 2020 and the Urban Agenda for the EU, specifically focusing on the "Better Knowledge" axis and preparing a blueprint for a circular city portal. The initiative also aligns with the National Strategy for the Circular Economy 2021 of the Ministry for Ecological Transition.
The project was born from the idea that a digital portal that served as a showcase to promote businesses, organizations and activities focused on the circular economy has not yet been implemented in Italy, and its impact can be crucial in inspiring different stakeholders to undertake circular transformation paths. It also addresses the need to revitalise and coordinate the innovation ecosystem by embracing the benefits of the circular economy at local and national/international levels.
The innovation of our initiative consists in introducing a new product, a virtual portal to promote, create awareness and guide citizens and businesses in the circular economy sector in the Taranto area. The portal presents local initiatives and proposes pathways for ecological and circular transformation supported by the project.It provides analysis tools for the city and businesses, assess the circularity and impact of linear production processes and alternative circular opportunities.
In the realm of public policy, the project innovatively supports the city in aligning with European directives and Italian policy strategies on the circular economy. It aligns with policies such as the Circular Economy Action Plan 2020 and the Urban Agenda for the EU, specifically focusing on the "Better Knowledge" axis and preparing a blueprint for a circular city portal. The initiative also aligns with the National Strategy for the Circular Economy 2021 of the Ministry for Ecological Transition.
Disciplines/knowledge reflected
The Taranto Circular initiative saw the collaboration of experts from various disciplines and fields of knowledge.
Especially for the first phase of the project, we relied on the theory of urban metabolism. For the second and third phases, we were inspired by the themes of interconnection and digital transition.
Taking inspiration from successful models like Groninger, Umea, Valladolid, Rotterdam, and Brussels, as well as Rotterdam Circulair, also our platform aims to promote, support, and disseminate circular economy principles within the Taranto region. The platform includes a section for collecting and presenting tenders and funding opportunities at national and international levels for circular projects, similar to Circular Glasgow. It also aims to enhance awareness and support the birth of new local projects by sharing scientific materials and real case studies on the circular economy.
For the second part of the project (development of the digital platform), we mostly used the study of interconnection theories and principles of digital transformation.
For the third part (development of new proposals), we focused on the principles of community participation.
Especially for the first phase of the project, we relied on the theory of urban metabolism. For the second and third phases, we were inspired by the themes of interconnection and digital transition.
Taking inspiration from successful models like Groninger, Umea, Valladolid, Rotterdam, and Brussels, as well as Rotterdam Circulair, also our platform aims to promote, support, and disseminate circular economy principles within the Taranto region. The platform includes a section for collecting and presenting tenders and funding opportunities at national and international levels for circular projects, similar to Circular Glasgow. It also aims to enhance awareness and support the birth of new local projects by sharing scientific materials and real case studies on the circular economy.
For the second part of the project (development of the digital platform), we mostly used the study of interconnection theories and principles of digital transformation.
For the third part (development of new proposals), we focused on the principles of community participation.
Methodology used
The methodology used in the first phase of the project (analysis of the city's material and energy flows and the business models of Taranto's economic actors that apply the principles of circularity, with the aim of measuring, thanks to collaboration with the area's universities, the current state of circularity and identifying the best business opportunities) was as follows:
We identified some major macro-sectors in the province of Taranto based on economic importance, raw material use, energy consumption and waste production (manufacturing, construction, agribusiness, energy and waste)
We used Exiobase to make an initial macro-estimation of material input in the province of Taranto.
We analysed the main companies in the area through sustainability reports to adjust the initial estimate of material input (e.g. ex Ilva, Eni, Italcave, Serveco, Irigom).
We analysed data on waste production and management in the area through ISPRA and the Taranto Chamber of Commerce to identify the waste produced and how it is managed.
During the second phase of the project, we created a digital platform to connect stakeholders, facilitate communication and information sharing, and provide tools for data analysis and the promotion of circular practices. We launched initiatives to promote circular practices among local businesses, organisations and the community.
During the third phase of the project, together with local stakeholders, we proposed new ideas, using the digital platform to connect stakeholders and stimulate the creation of new collaborative projects.
We identified some major macro-sectors in the province of Taranto based on economic importance, raw material use, energy consumption and waste production (manufacturing, construction, agribusiness, energy and waste)
We used Exiobase to make an initial macro-estimation of material input in the province of Taranto.
We analysed the main companies in the area through sustainability reports to adjust the initial estimate of material input (e.g. ex Ilva, Eni, Italcave, Serveco, Irigom).
We analysed data on waste production and management in the area through ISPRA and the Taranto Chamber of Commerce to identify the waste produced and how it is managed.
During the second phase of the project, we created a digital platform to connect stakeholders, facilitate communication and information sharing, and provide tools for data analysis and the promotion of circular practices. We launched initiatives to promote circular practices among local businesses, organisations and the community.
During the third phase of the project, together with local stakeholders, we proposed new ideas, using the digital platform to connect stakeholders and stimulate the creation of new collaborative projects.
How stakeholders are engaged
For the full implementation of the project, Tondo collaborated with several stakeholders at various level:
- Universities of the Italian Region Apulia: Bari Polytechnic and the University of Bari Aldo Moro. Their involvement was planned for the first phase of the project (research and data analysis to measure the level of circularity in Taranto) and for the third phase of promotion and design of the digital portal.
- With Eni, the Main Partner of Taranto Circular that with its technical skills and technology provided support in the development of new projects on the territory.
- With The Municipality of Taranto, as a partner in the launch event of the platform held in December 2022.
- With several Italian and European project funders: Taranto City Council, Bank of Italy, Invitalia, European Union.
- With several local companies and associations that have decided to register on the digital platform, such as B&B La Nassa, Nasse Animation Studio, Bioenutra, Jonian Dolphin Conservation, Masseria Fruttirossi, Ionian, Distilleria Bartin, Preinvel, Cyrkl Srl, Il Club dei Cerca Cose, Havanaeco, Ho.gu srl, Sherwood, Terra delle Gravine. Through the digital portal they promote their projects, creating new synergies , promoting new networks and learning more about the circular economy.
- With local Confindustria and Confapi
- With the Italian Order of engineers
- Universities of the Italian Region Apulia: Bari Polytechnic and the University of Bari Aldo Moro. Their involvement was planned for the first phase of the project (research and data analysis to measure the level of circularity in Taranto) and for the third phase of promotion and design of the digital portal.
- With Eni, the Main Partner of Taranto Circular that with its technical skills and technology provided support in the development of new projects on the territory.
- With The Municipality of Taranto, as a partner in the launch event of the platform held in December 2022.
- With several Italian and European project funders: Taranto City Council, Bank of Italy, Invitalia, European Union.
- With several local companies and associations that have decided to register on the digital platform, such as B&B La Nassa, Nasse Animation Studio, Bioenutra, Jonian Dolphin Conservation, Masseria Fruttirossi, Ionian, Distilleria Bartin, Preinvel, Cyrkl Srl, Il Club dei Cerca Cose, Havanaeco, Ho.gu srl, Sherwood, Terra delle Gravine. Through the digital portal they promote their projects, creating new synergies , promoting new networks and learning more about the circular economy.
- With local Confindustria and Confapi
- With the Italian Order of engineers
Global challenges
Taranto Circolare tackles global challenges through localized strategies, addressing key issues such as climate change, biodiversity loss, unemployment, Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), social and economic disparities, and EU Cohesion Policy.
Climate Change and Environmental Sustainability:
The project addresses the socio-economic costs of climate transition in Taranto, aligning with global efforts to mitigate climate change.
By promoting circular economy projects, it aims to reduce environmental impact, minimize waste, and foster sustainable practices, contributing to global environmental sustainability goals.
Biodiversity Loss:
Loss of biodiversity is a global concern affecting ecosystems worldwide.
Taranto Circolare advocates environmental sustainability principles, potentially preserving local biodiversity through eco-friendly practices and circular initiatives.
Unemployment and Economic Opportunities:
Unemployment is a common global challenge, with regions struggling to create sustainable economic opportunities.
The project addresses unemployment by promoting circular economy projects, creating jobs, and supporting the development of a sustainable local economy.
Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs):
Achieving UN SDGs requires concerted efforts at the local level.
Taranto Circolare aligns with various SDGs, including responsible consumption, climate action, decent work, and economic growth, contributing to the global objectives.
Social and Economic Disparities:
Global disparities in living standards and access to basic services are pervasive.
The project aims to secure good living standards, addressing local socio-economic challenges and serving as a potential model for regions facing similar disparities.
EU Cohesion Policy:
Achieving cohesion and economic convergence among EU regions is a key challenge.
Taranto Circolare contributes to the EU's cohesion policy by fostering collaboration among local actors.
Climate Change and Environmental Sustainability:
The project addresses the socio-economic costs of climate transition in Taranto, aligning with global efforts to mitigate climate change.
By promoting circular economy projects, it aims to reduce environmental impact, minimize waste, and foster sustainable practices, contributing to global environmental sustainability goals.
Biodiversity Loss:
Loss of biodiversity is a global concern affecting ecosystems worldwide.
Taranto Circolare advocates environmental sustainability principles, potentially preserving local biodiversity through eco-friendly practices and circular initiatives.
Unemployment and Economic Opportunities:
Unemployment is a common global challenge, with regions struggling to create sustainable economic opportunities.
The project addresses unemployment by promoting circular economy projects, creating jobs, and supporting the development of a sustainable local economy.
Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs):
Achieving UN SDGs requires concerted efforts at the local level.
Taranto Circolare aligns with various SDGs, including responsible consumption, climate action, decent work, and economic growth, contributing to the global objectives.
Social and Economic Disparities:
Global disparities in living standards and access to basic services are pervasive.
The project aims to secure good living standards, addressing local socio-economic challenges and serving as a potential model for regions facing similar disparities.
EU Cohesion Policy:
Achieving cohesion and economic convergence among EU regions is a key challenge.
Taranto Circolare contributes to the EU's cohesion policy by fostering collaboration among local actors.
Learning transferred to other parties
The project combines elements of research, digital tools, and circular transformation activities, and we believe it can become an example of how to analyze the circularity of cities, find development opportunities, create a dialogue between actors, and stimulate ecological transition. We built a model that can be replicated over several cities and adapted to smaller territories.
The replicability of the project can produce positive externalities for Taranto, both in terms of visibility and reputation, and in terms of utility, thanks to the connections that can be created between territories that apply the same platforms and methodologies. Economic-financial sustainability would represent another positive externality as it would make the entire organizational structure more stable and effective.
We are conviced that exponentiality is guaranteed by the methodologies and tools that are the foundations of this project. The impact to which we aspire is also that Taranto Circolare could be a springboard for new projects, processes and services. The latter will arise thanks to a greater knowledge of the needs and potentialities of the territory and of all the relations between the subjects reactivated thanks to this project, faced with an increasingly clear orientation given by the context of European and Italian public policies and the drive of the private sector towards an increasingly circular economy.
The replicability of the project can produce positive externalities for Taranto, both in terms of visibility and reputation, and in terms of utility, thanks to the connections that can be created between territories that apply the same platforms and methodologies. Economic-financial sustainability would represent another positive externality as it would make the entire organizational structure more stable and effective.
We are conviced that exponentiality is guaranteed by the methodologies and tools that are the foundations of this project. The impact to which we aspire is also that Taranto Circolare could be a springboard for new projects, processes and services. The latter will arise thanks to a greater knowledge of the needs and potentialities of the territory and of all the relations between the subjects reactivated thanks to this project, faced with an increasingly clear orientation given by the context of European and Italian public policies and the drive of the private sector towards an increasingly circular economy.
Keywords
Circular Cities
Local Development
Community Participation
Interdisciplinarity
Digital Transformation