OTTER project
Basic information
Project Title
OTTER project
Full project title
OTTER project
Category
Reconnecting with nature
Project Description
OTTER is a project that aims to spark young people’s interest in science and environmental sustainability with the help of Education Outside the Classroom (EOC) tools and methods, and to assess how these can help improve the sophisticated consumption and scientific citizenship of kids, as well as the transferability of cognitive, affective, social and behavioural skills through the implementation of EOC Labs across Europe.
Geographical Scope
Cross-border/international
Project Region
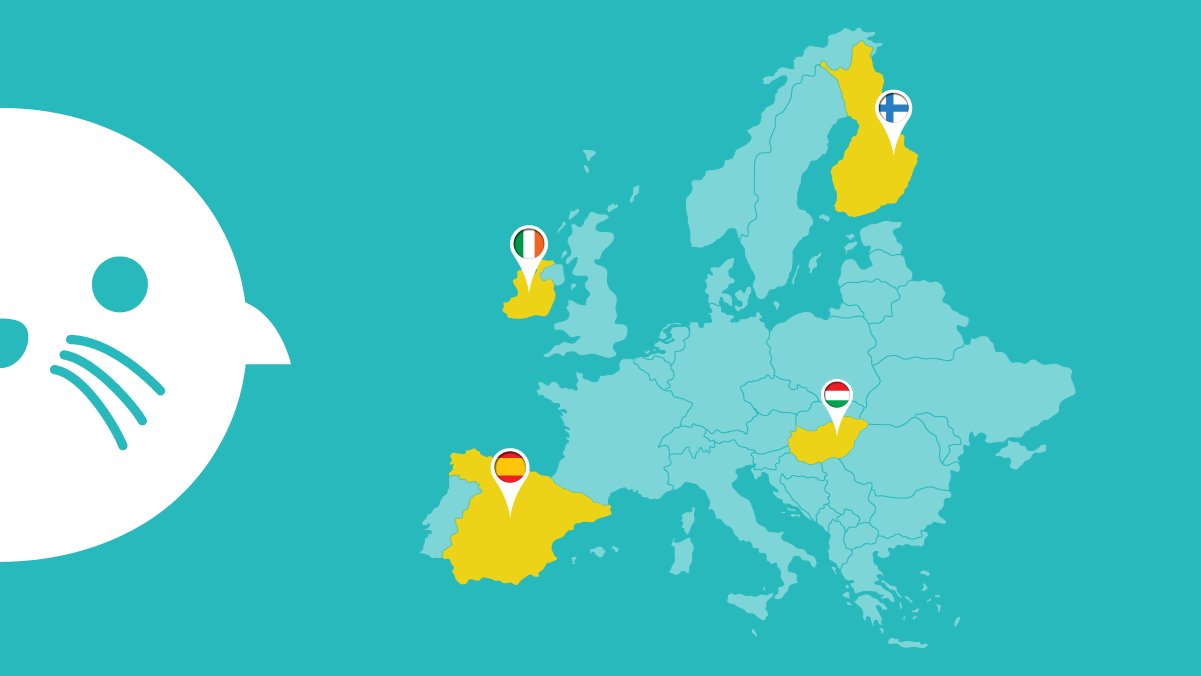
CROSS-BORDER/INTERNATIONAL: Hungary, Ireland
Urban or rural issues
Mainly urban
Physical or other transformations
It refers to other types of transformations (soft investment)
EU Programme or fund
Yes
Which funds
Horizon2020 / Horizon Europe
Description of the project
Summary
OUR MISSION:
OTTER is an EU-funded project that aims to spark young people’s interest in science and environmental sustainability with the help of Education Outside the Classroom tools and methodologies.
WHY OTTER?
Current global challenges and crises have highlighted the need for scientists and scientifically literate people in our societies. However, recent studies have shown that interest in scientific topics among young people is in decline, with fewer people wanting to pursue careers as scientists. In response to this, educators and researchers came up with an innovative concept: Education Outside the Classroom, a highly effective approach that promotes out-of-school science learning to make the educational process more engaging.
OUR ACTIVITIES:
- We connect educators, scientists, and creatives through the Hub (Finland, Ireland, Hungary, Spain) to co-design new Education Outside the Classroom experiences and exchange best practices and insights.
- We develop toolkits, guidelines, and materials to include on the Learning Platform that is designed to help educators become acquainted with Education Outside the Classroom.
- We implement the Outdoor Labs in primary and secondary schools in Finland, Ireland, Hungary, and Spain, based on the knowledge we’ve gained from the previous activities, and we monitor the impact.
- We produce the eTraining in which we explain how we can become more environmentally friendly.
In summary:
OTTER will leverage the power of Education Outside the Classroom methods to improve STEAM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, Mathematics) learning among young people and raise awareness of today’s environmental problems. At the same time, OTTER will aim for the recognition, validation, and accreditation of Education Outside the Classroom across Europe.
WE EMPOWER YOUNGSTERS TO ACKNOWLEDGE THEIR POWER, BECOME BETTER CITIZENS, AND FIGHT FOR A MORE SUSTAINABLE PLANET.
OTTER is an EU-funded project that aims to spark young people’s interest in science and environmental sustainability with the help of Education Outside the Classroom tools and methodologies.
WHY OTTER?
Current global challenges and crises have highlighted the need for scientists and scientifically literate people in our societies. However, recent studies have shown that interest in scientific topics among young people is in decline, with fewer people wanting to pursue careers as scientists. In response to this, educators and researchers came up with an innovative concept: Education Outside the Classroom, a highly effective approach that promotes out-of-school science learning to make the educational process more engaging.
OUR ACTIVITIES:
- We connect educators, scientists, and creatives through the Hub (Finland, Ireland, Hungary, Spain) to co-design new Education Outside the Classroom experiences and exchange best practices and insights.
- We develop toolkits, guidelines, and materials to include on the Learning Platform that is designed to help educators become acquainted with Education Outside the Classroom.
- We implement the Outdoor Labs in primary and secondary schools in Finland, Ireland, Hungary, and Spain, based on the knowledge we’ve gained from the previous activities, and we monitor the impact.
- We produce the eTraining in which we explain how we can become more environmentally friendly.
In summary:
OTTER will leverage the power of Education Outside the Classroom methods to improve STEAM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, Mathematics) learning among young people and raise awareness of today’s environmental problems. At the same time, OTTER will aim for the recognition, validation, and accreditation of Education Outside the Classroom across Europe.
WE EMPOWER YOUNGSTERS TO ACKNOWLEDGE THEIR POWER, BECOME BETTER CITIZENS, AND FIGHT FOR A MORE SUSTAINABLE PLANET.
Key objectives for sustainability
Amid urgent educational and environmental challenges and a need for increased sophisticated consumerism and scientific citizenship within Europe, and amid the relationship between STEAM subjects and the kind of workforce required to tackle the environmental issues, OTTER project will specifically focus in the field of environmental sustainability and the reduction of plastic waste in the Education Outside the Classroom methods and pedagogies to be developed, as well as on the assessment of the acquisition of scientific knowledge and transferable skills in students. Furthermore, an e-learning specifically on sustainability will be developed for teachers to learn from an easy, intermediate to and advanced level on sustainability and on how to apply it as a topic to EOC methods for kids.
Key objectives for aesthetics and quality
Education Outside the Classroom focuses on the out-of-school opportunities for learning that goes away from traditional methods. Its design is centred around the learning experience of the student so it is done in a way that sparks their interest and calls for familiarity. The OTTER labs are to be structured in four parts based on the experienced aimed at each stage:
- OBSERVE & INQUIRE: During this first day students will be exposed to a topic related to sustainability and linked to their academic curriculum.
- DISCOVER!: Students will visit companies, factories, or NGOs that deal with sustainability and plastic waste. By the end of the day, they will work in groups on the issue discussed, and present their solutions to a jury of teachers, local experts and even students.
- ENERGIZE: Students will get involved in local activities to reduce plastic waste and learn the advantages of living in a clean and less polluted environment.
- REFLECT: The last day is dedicated to thinking about the previous days. Open sessions and debates will prompt students’ critical thinking and their role within a circular economy and their experience based on their geographical and cultural background.
- OBSERVE & INQUIRE: During this first day students will be exposed to a topic related to sustainability and linked to their academic curriculum.
- DISCOVER!: Students will visit companies, factories, or NGOs that deal with sustainability and plastic waste. By the end of the day, they will work in groups on the issue discussed, and present their solutions to a jury of teachers, local experts and even students.
- ENERGIZE: Students will get involved in local activities to reduce plastic waste and learn the advantages of living in a clean and less polluted environment.
- REFLECT: The last day is dedicated to thinking about the previous days. Open sessions and debates will prompt students’ critical thinking and their role within a circular economy and their experience based on their geographical and cultural background.
Key objectives for inclusion
It is paramount of OTTER closing the gender and geographical gaps in STEAM through promoting educational activities, as well as increasing awareness of the gender and geographical gaps in education outside the classroom and in STEAM, their causes and ways of closing these gaps among stakeholders in Europe. A dedicated part of the project will target the intersectional aspects relevant for building an inclusive education ecosystem. OTTER aims to address goals related to inclusive education, by addressing the education for disadvantaged groups, such as prospective female scientists, or students from different geographical areas. Finally, by addressing the thematic of plastic waste, OTTER will bring appropriate answers to the goals fixed up for the sustainable development as inclusion needs to be thought beyond humanity.
Results in relation to category
We have created the 4 different channels for the OTTER Hub (for Spain, for Hungary, for Ireland and the International Hub), and we have been holding conversations with practitioners to develop and shape the OTTER methodology that we will use in the Labs for the different age groups. In parallel, we started developing the OTTER Platform that will count with an e-learning on sustainability, a teachers training, a practitioners toolkit and accreditation guidelines, for anyone to use across Europe willing to replicate OTTERs methodology. Next year we will start carrying out the 4 OTTER Labs in the 4 pilot countries, followed by the assessment of the methodology. We already have all the school members that will participate in our OTTER Labs and we can{t wait to start working with the kids!
How Citizens benefit
OTTER LABS: Kids from some primary and secondary schools from Hungary, Ireland, Spain and Finland (ages 6-18) will benefit from the labs by learning STEAM in a more fun and engaging way, by developing transversal skills and by becoming scientific citizens capable of making informed decisions, and sophisticated consumers that consider environmental impacts and the ethicality of the production process of products before buying them.
OTTER HUB: Opened for teachers, parents and practitioners of education outside the classroom approaches. The benefits of joining the hub includes being part of a growing community of change-leaders, developing Education Outside the Classroom activities, training materials and guidelines adapted to each user's reality, and working together towards the accreditation guidelines for Education Outside the Classroom methods in Europe.
- OTTER PLATFORM: For anyone wanting to implement education outside the classroom activities, the platform will have toolkits, guidelines and materials available for use for free.
OTTER HUB: Opened for teachers, parents and practitioners of education outside the classroom approaches. The benefits of joining the hub includes being part of a growing community of change-leaders, developing Education Outside the Classroom activities, training materials and guidelines adapted to each user's reality, and working together towards the accreditation guidelines for Education Outside the Classroom methods in Europe.
- OTTER PLATFORM: For anyone wanting to implement education outside the classroom activities, the platform will have toolkits, guidelines and materials available for use for free.
Physical or other transformations
It refers to other types of transformations (soft investment)
Innovative character
EOC has many benefits for the cognitive, physical, and affective development of children through different ways of learning:
1. Lifelong learning: teaching and learning activities in EOC contexts involve learners of different age (children and teachers) not only helpping pupils during their childhood, but also equip them with transferable skills they will need throughout their lives.
2. Integral learning: EOC promotes all kinds of development: intellectual, social, moral, affective, religious, sportive, artistic, musical, etc. This holistic approach combines complementary learning to acquire more knowledge and develop diverse skills.
3. Regular learning: It is more productive to distribute learning contents in small parcels several times than once in longer training sequences as we need time to assimilate and integrate new information and to use it as a foundation for further learning. EOC must be regular and frequent.
4. Natural learning: by being in direct contact with the natural environment and getting familiar with our surroundings, students will develop a special relationship with their environment and learn to preserve it.
5. Challenging learning: EOC activities allow children to take responsibilities and initiative, to have courage and to investigate more deeply the world around them.
6. Tailored learning: Most of the time, EOC focuses on alternative pedagogies and learner-based approach, where students and teachers learn from each other, enrich their knowledge, and develop their skills. Teachers are trained and encouraged to identify the learning needs of the children and to propose to them the most appropriate activities, the ones that foster motivation, curiosity, and the joy of learning.
7. Community-based learning: education is best offered in a community so that children feel have a sense of belonging and a desire to make a positive contribution. EOC offers the opportunity of collaboration and mutual learning with those around you.
1. Lifelong learning: teaching and learning activities in EOC contexts involve learners of different age (children and teachers) not only helpping pupils during their childhood, but also equip them with transferable skills they will need throughout their lives.
2. Integral learning: EOC promotes all kinds of development: intellectual, social, moral, affective, religious, sportive, artistic, musical, etc. This holistic approach combines complementary learning to acquire more knowledge and develop diverse skills.
3. Regular learning: It is more productive to distribute learning contents in small parcels several times than once in longer training sequences as we need time to assimilate and integrate new information and to use it as a foundation for further learning. EOC must be regular and frequent.
4. Natural learning: by being in direct contact with the natural environment and getting familiar with our surroundings, students will develop a special relationship with their environment and learn to preserve it.
5. Challenging learning: EOC activities allow children to take responsibilities and initiative, to have courage and to investigate more deeply the world around them.
6. Tailored learning: Most of the time, EOC focuses on alternative pedagogies and learner-based approach, where students and teachers learn from each other, enrich their knowledge, and develop their skills. Teachers are trained and encouraged to identify the learning needs of the children and to propose to them the most appropriate activities, the ones that foster motivation, curiosity, and the joy of learning.
7. Community-based learning: education is best offered in a community so that children feel have a sense of belonging and a desire to make a positive contribution. EOC offers the opportunity of collaboration and mutual learning with those around you.
Disciplines/knowledge reflected
- environmental sciences
- science education and communication
- stem professors
- scientists
- circus and performing arts
- project managers
- communicators
- science education and communication
- stem professors
- scientists
- circus and performing arts
- project managers
- communicators
Methodology used
OTTER is theoretically framed within the Contextual Model of Learning, a well-established framework for studying the complexities of learning within free-choice settings. Drawing upon constructivist, cognitive, and sociocultural theories of learning, this model exemplifies the contextually driven processes of interactions and interplay between a person’s personal, sociocultural, and physical contexts. The personal context represents an individual’s personal history (e.g., prior knowledge and experiences) , the sociocultural context refers to the fact that museum learning is socioculturally situated given that individuals are defined by their social relationships and culture, and the physical context refers to the museum spaces and their characteristics. Analysing and understanding the type of EOC activities and the impact they have on students, will help us sharpen the available knowledge, provide us valuable feedback for the selection of activities to be immersed in the EOC programme, and later on, to test through the OTTER Outdoor Lab, if those activities indeed impact the students as reported. The use of both quantitative and qualitative research strategies, also known as mixed methods research, draws on the strengths of both approaches by using complementary assessment methods.
How stakeholders are engaged
- At a local level, we are working with teachers from primary and secondary schools to implement OTTER labs with their students and carry out educational activities outside the classroom focused on STEAM learning and environmental sustainability.
- At a national level, we opened the Hubs (one per pilot country: Spain, Ireland, Hungary and Finland) to discuss national-relevant issues about EOC accreditation, experiences about EOC implementation and exchange knowledge and ideas.
- At an Europen level, we will share the tools in the platform, we count with one international Hub opened for all countries that are not the pilot case studies, and we will share guidelines for pushing for the accreditation of EOC activities in Europe.
- At a national level, we opened the Hubs (one per pilot country: Spain, Ireland, Hungary and Finland) to discuss national-relevant issues about EOC accreditation, experiences about EOC implementation and exchange knowledge and ideas.
- At an Europen level, we will share the tools in the platform, we count with one international Hub opened for all countries that are not the pilot case studies, and we will share guidelines for pushing for the accreditation of EOC activities in Europe.
Global challenges
The main global challenge addressed in OTTER is achieving sustainability. The way we will approach it is by adapting each OTTER Lab to its local context. In day 2 "Discover!" the lab centres in visiting local NGOs or companies that deal with sustainability and plastic waste. The aim is that kids see first hand how STEAM is applied in tangible actions addressing local issues. By the end of the day, they will work in groups on the issue discussed, and present their solutions to a jury of teachers, local experts and other students.
Learning transferred to other parties
Our content will be divided by age groups so all the resources on activities, methods and pedagogies can be replicated in any context. We will also provide guidelines and an e-training. The idea is to easily be able to carry out Education Outside the Classroom activities for steam learning in a sustainable future context, all across Europe and for kids of different ages.
Keywords
STEAM
Education Outside the Classroom
Sustainable future
Kids
Plastic Waste