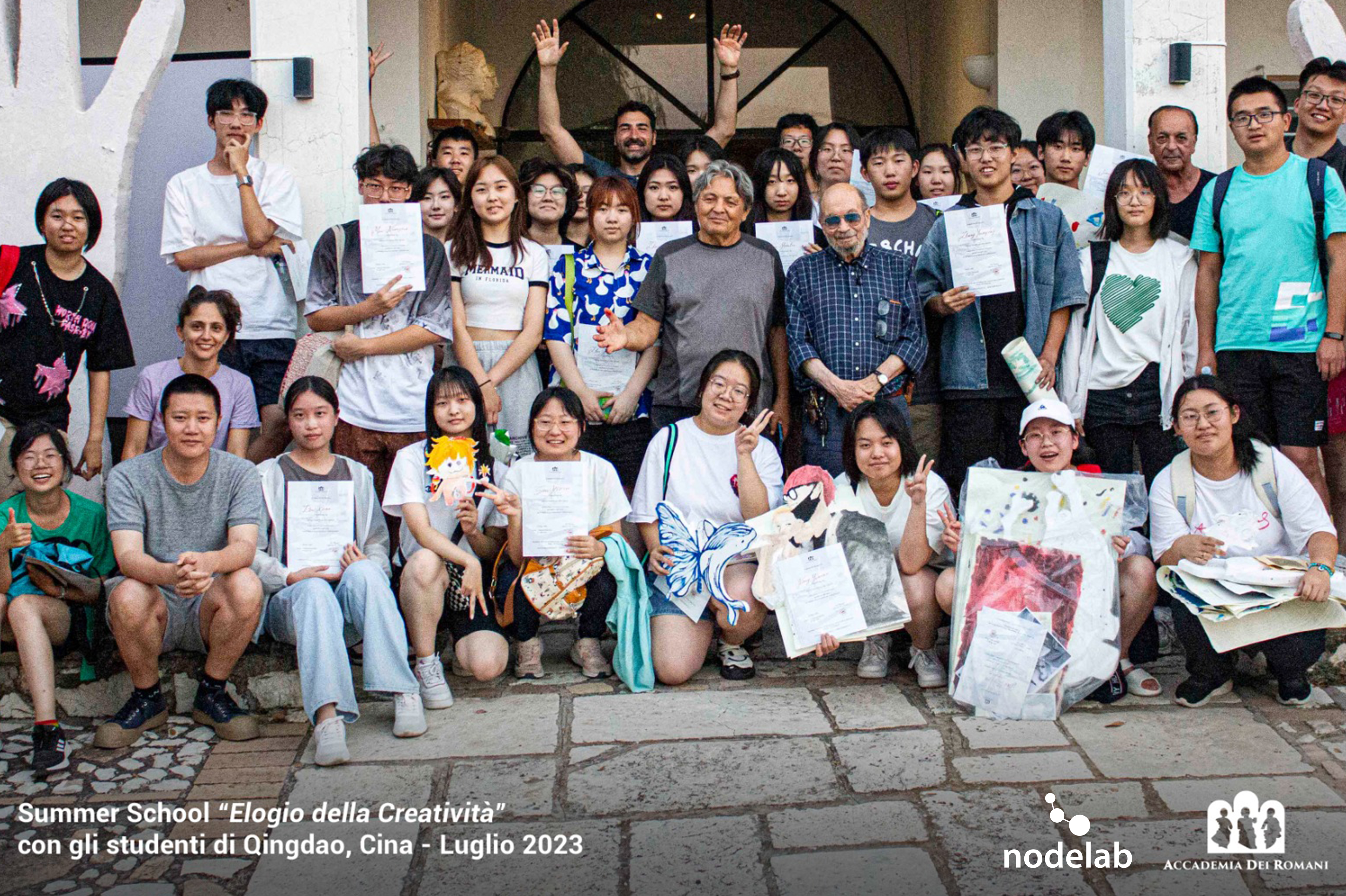
Regaining a sense of belonging
nodelab
nodelab | art, sustainability, new technologies
Connecting Urban Innovation with Rural Sustainability
NL bridges urban-rural linkages through education 5.0, digital fabrication, and sustainability. Operating in two key nodes—Guidonia Montecelio and Magliano Sabina—it fosters innovation, creativity, and community well-being. By empowering individuals with future-ready skills, Nodelab promotes healthier, smarter, and more resilient environments, connecting people, ideas, and territories across diverse contexts.
NL bridges urban-rural linkages through education 5.0, digital fabrication, and sustainability. Operating in two key nodes—Guidonia Montecelio and Magliano Sabina—it fosters innovation, creativity, and community well-being. By empowering individuals with future-ready skills, Nodelab promotes healthier, smarter, and more resilient environments, connecting people, ideas, and territories across diverse contexts.
Italy
Regional
Lazio
It addresses urban-rural linkages
It refers to a physical transformation of the built environment (hard investment)
Yes
2024-12-31
Yes
NGEU – Next Generation EU
No
Yes
Yes
Yes
As an individual
Nodelab is an innovative project designed to strengthen urban-rural linkages through the integration of education 5.0, digital fabrication, and sustainable development practices. Operating in Guidonia Montecelio (urban context) and Magliano Sabina (rural setting), Nodelab creates a dynamic ecosystem where technology, creativity, and community well-being converge.
The project aims to empower communities by fostering inclusive education, technological innovation, and environmental sustainability. Nodelab inspires a new generation of change-makers capable of addressing contemporary challenges through hands-on learning and collaboration.
Target groups include students and young people interested in STEAM, educators seeking innovative methodologies aligned with Education 5.0, local communities promoting social cohesion, and entrepreneurs interested in digital fabrication.
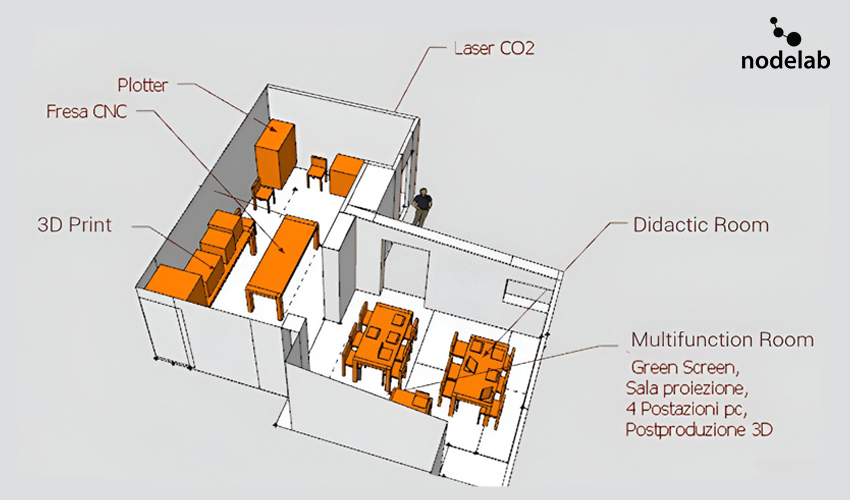
Specific objectives are to establish a Fablab 5.0 at the ex-Monastery of Santa Croce in Magliano Sabina, replicating the Guidonia fablab model, develop educational programs focused on sustainability and technology, promote environmental awareness, and stimulate local economies through entrepreneurship support.
Achieved outcomes include the creation of an operational Fablab 5.0, delivery of educational programs, active community participation, strengthened urban-rural connections, and promotion of sustainable development practices for healthier, resilient environments. In this way, the project, center the NEB key points programm.
The project aims to empower communities by fostering inclusive education, technological innovation, and environmental sustainability. Nodelab inspires a new generation of change-makers capable of addressing contemporary challenges through hands-on learning and collaboration.
Target groups include students and young people interested in STEAM, educators seeking innovative methodologies aligned with Education 5.0, local communities promoting social cohesion, and entrepreneurs interested in digital fabrication.
Specific objectives are to establish a Fablab 5.0 at the ex-Monastery of Santa Croce in Magliano Sabina, replicating the Guidonia fablab model, develop educational programs focused on sustainability and technology, promote environmental awareness, and stimulate local economies through entrepreneurship support.
Achieved outcomes include the creation of an operational Fablab 5.0, delivery of educational programs, active community participation, strengthened urban-rural connections, and promotion of sustainable development practices for healthier, resilient environments. In this way, the project, center the NEB key points programm.
Education 5.0
Digital Fabrication
Sustainability
Urban-Rural Linkages
Community Empowerment
The Nodelab project promotes sustainability through an innovative 5.0 education model focused on environmental, social, and economic resilience. By integrating advanced technologies with sustainability principles, Nodelab fosters responsible practices that strengthen urban-rural connections, creating lasting impacts in both Guidonia Montecelio and Magliano Sabina.
Key Sustainability Objectives:
1. Environmental Sustainability:
- Promote eco-friendly digital fabrication using sustainable materials and energy-efficient technologies within the FabLab 5.0.
- Apply circular economy principles, such as recycling, upcycling, and waste reduction during prototyping and production activities.
2. Social Sustainability:
- Rebuild a sense of community belonging through shared learning spaces and collaborative projects, enhancing community cohesion.
- Promote inclusive education, engaging young people, local communities, and underrepresented groups.
3. Economic Sustainability:
- Support local entrepreneurship by providing skills for green business development and digital innovation.
- Foster competencies for the green economy, creating new job opportunities linked to sustainability.
How These Objectives Have Been Met:
- Implementation of training programs focused on sustainability, digital fabrication, and eco-design.
- Establishment of a FabLab 5.0 as a hub for sustainable innovation, equipped with tools that minimize environmental impact.
- Active community engagement through workshops and educational activities that promote sustainability awareness and practices.
Exemplary Aspects of Nodelab:
Exemplary Aspects of Nodelab:
Nodelab shows how education 5.0 can support sustainable development by combining technology with environmental responsibility. It offers a replicable model for fostering resilient, eco-conscious communities through strong urban-rural linkages.
Key Sustainability Objectives:
1. Environmental Sustainability:
- Promote eco-friendly digital fabrication using sustainable materials and energy-efficient technologies within the FabLab 5.0.
- Apply circular economy principles, such as recycling, upcycling, and waste reduction during prototyping and production activities.
2. Social Sustainability:
- Rebuild a sense of community belonging through shared learning spaces and collaborative projects, enhancing community cohesion.
- Promote inclusive education, engaging young people, local communities, and underrepresented groups.
3. Economic Sustainability:
- Support local entrepreneurship by providing skills for green business development and digital innovation.
- Foster competencies for the green economy, creating new job opportunities linked to sustainability.
How These Objectives Have Been Met:
- Implementation of training programs focused on sustainability, digital fabrication, and eco-design.
- Establishment of a FabLab 5.0 as a hub for sustainable innovation, equipped with tools that minimize environmental impact.
- Active community engagement through workshops and educational activities that promote sustainability awareness and practices.
Exemplary Aspects of Nodelab:
Exemplary Aspects of Nodelab:
Nodelab shows how education 5.0 can support sustainable development by combining technology with environmental responsibility. It offers a replicable model for fostering resilient, eco-conscious communities through strong urban-rural linkages.
The Nodelab project aims to create inclusive, inspiring, and culturally enriching environments that foster creativity, collaboration, and community engagement. By blending innovative design with cultural heritage, Nodelab enhances both physical spaces and lived experiences within urban and rural communities, thanks to the transformative potential of the Digital Lab 5.0.
Key objectives for aesthetics and quality of experience include:
1. Revitalization of Historical Spaces:
- Transform the ex-Monastery of Santa Croce and urban spaces in Guidonia Montecelio into vibrant hubs that celebrate historical identity and contemporary design.
- Integrate modern elements with cultural heritage, enhancing aesthetics while respecting historical context.
2. Human-Centered Design:
- Create 5.0 spaces that are engaging, accessible, and foster a sense of belonging.
- Prioritize comfort, well-being, and inclusivity through thoughtful layouts, natural lighting, and sustainable materials.
3. Cultural and Artistic Integration:
- Promote artistic expression through workshops and creative labs supported by the Digital Lab 5.0, involving local artists, students, and residents.
- Blend traditional crafts with digital arts, enriching the cultural landscape.
These objectives have been met through:
- Designing multifunctional spaces that balance functionality with aesthetic value, inspiring creativity.
- Involving the community in co-design processes to reflect cultural identity and needs.
- Incorporating public art projects and interactive installations via the Digital Lab 5.0, merging tradition with modern design.
Exemplary aspects of Nodelab:
Nodelab shows how design and culture can create transformative spaces. Its approach merges heritage with contemporary aesthetics, fostering civic pride. By leveraging the Digital Lab 5.0, Nodelab serves as a replicable model for sustainable cultural development across Europe.
Key objectives for aesthetics and quality of experience include:
1. Revitalization of Historical Spaces:
- Transform the ex-Monastery of Santa Croce and urban spaces in Guidonia Montecelio into vibrant hubs that celebrate historical identity and contemporary design.
- Integrate modern elements with cultural heritage, enhancing aesthetics while respecting historical context.
2. Human-Centered Design:
- Create 5.0 spaces that are engaging, accessible, and foster a sense of belonging.
- Prioritize comfort, well-being, and inclusivity through thoughtful layouts, natural lighting, and sustainable materials.
3. Cultural and Artistic Integration:
- Promote artistic expression through workshops and creative labs supported by the Digital Lab 5.0, involving local artists, students, and residents.
- Blend traditional crafts with digital arts, enriching the cultural landscape.
These objectives have been met through:
- Designing multifunctional spaces that balance functionality with aesthetic value, inspiring creativity.
- Involving the community in co-design processes to reflect cultural identity and needs.
- Incorporating public art projects and interactive installations via the Digital Lab 5.0, merging tradition with modern design.
Exemplary aspects of Nodelab:
Nodelab shows how design and culture can create transformative spaces. Its approach merges heritage with contemporary aesthetics, fostering civic pride. By leveraging the Digital Lab 5.0, Nodelab serves as a replicable model for sustainable cultural development across Europe.
The Nodelab project promotes inclusion by creating accessible, affordable, and participatory environments that foster equal opportunities for all. Through education 5.0 and the Digital Lab 5.0, Nodelab supports diversity, accessibility, and community involvement in both urban and rural contexts.
Key objectives for inclusion include:
1. Accessibility for All:
- Ensure that educational programs and spaces are accessible, with courses open to everyone, including individuals with disabilities.
- Design environments following universal design principles to eliminate barriers and promote equal participation.
2. Affordability and Equal Opportunities:
- Provide affordable training programs to reduce educational inequalities, ensuring access for economically disadvantaged groups.
- Foster digital literacy and skills to bridge gaps between different social groups.
3. Inclusive Governance and Community Participation:
- Encourage participatory decision-making where local communities are actively involved in planning activities.
- Promote social cohesion through collaborative projects connecting diverse groups in urban and rural areas.
These objectives have been met through:
- Implementing inclusive educational programs with adaptive methods for people with disabilities.
- Creating multifunctional spaces with accessibility features for all participants.
- Engaging communities in co-design workshops, fostering shared ownership and inclusive governance.
Exemplary aspects of Nodelab:
Nodelab shows how inclusion can be integrated into education and community spaces. Its approach blends accessibility, affordability, and participatory governance, creating environments where everyone can thrive. With the Digital Lab 5.0, Nodelab offers a replicable model for inclusive practices, promoting social innovation and equity across communities.
Key objectives for inclusion include:
1. Accessibility for All:
- Ensure that educational programs and spaces are accessible, with courses open to everyone, including individuals with disabilities.
- Design environments following universal design principles to eliminate barriers and promote equal participation.
2. Affordability and Equal Opportunities:
- Provide affordable training programs to reduce educational inequalities, ensuring access for economically disadvantaged groups.
- Foster digital literacy and skills to bridge gaps between different social groups.
3. Inclusive Governance and Community Participation:
- Encourage participatory decision-making where local communities are actively involved in planning activities.
- Promote social cohesion through collaborative projects connecting diverse groups in urban and rural areas.
These objectives have been met through:
- Implementing inclusive educational programs with adaptive methods for people with disabilities.
- Creating multifunctional spaces with accessibility features for all participants.
- Engaging communities in co-design workshops, fostering shared ownership and inclusive governance.
Exemplary aspects of Nodelab:
Nodelab shows how inclusion can be integrated into education and community spaces. Its approach blends accessibility, affordability, and participatory governance, creating environments where everyone can thrive. With the Digital Lab 5.0, Nodelab offers a replicable model for inclusive practices, promoting social innovation and equity across communities.
The Nodelab project actively involves citizens and civil society to ensure it meets the real needs of local communities in Guidonia Montecelio and Magliano Sabina. This participation strengthens the project’s impact and fosters a strong connection with the territories it serves.
Citizens and civil society have been engaged through:
1. Participatory Co-Design:
Local residents, students, educators, and community organizations contribute through workshops where they share ideas, identify community needs, and influence the design of educational programs and 5.0 spaces.
2. Community-Led Activities:
Nodelab organizes cultural events, sustainability workshops, and educational activities co-created with local stakeholders, ensuring relevance to the social and cultural context.
3. Feedback Mechanisms:
Surveys, consultations, and focus groups are regularly conducted to gather feedback, allowing the project to adapt and evolve based on community input.
The impact of this involvement has been significant:
- Sense of Ownership:
Active participation has created a strong sense of belonging, motivating people to contribute to the project’s growth and sustainability.
- Tailored Solutions:
Community feedback ensures that Nodelab’s initiatives are inclusive and aligned with local needs, particularly in education and digital literacy.
- Social Cohesion:
The project connects diverse groups, strengthening relationships and fostering resilience through shared goals and experiences.
Nodelab showcases how citizen involvement can turn a project into a dynamic, community-driven initiative, ensuring long-term sustainability and positive social impact.
Citizens and civil society have been engaged through:
1. Participatory Co-Design:
Local residents, students, educators, and community organizations contribute through workshops where they share ideas, identify community needs, and influence the design of educational programs and 5.0 spaces.
2. Community-Led Activities:
Nodelab organizes cultural events, sustainability workshops, and educational activities co-created with local stakeholders, ensuring relevance to the social and cultural context.
3. Feedback Mechanisms:
Surveys, consultations, and focus groups are regularly conducted to gather feedback, allowing the project to adapt and evolve based on community input.
The impact of this involvement has been significant:
- Sense of Ownership:
Active participation has created a strong sense of belonging, motivating people to contribute to the project’s growth and sustainability.
- Tailored Solutions:
Community feedback ensures that Nodelab’s initiatives are inclusive and aligned with local needs, particularly in education and digital literacy.
- Social Cohesion:
The project connects diverse groups, strengthening relationships and fostering resilience through shared goals and experiences.
Nodelab showcases how citizen involvement can turn a project into a dynamic, community-driven initiative, ensuring long-term sustainability and positive social impact.
The Nodelab project engages stakeholders at local, regional, national, and European levels to ensure a comprehensive and impactful approach to its design and implementation. Their involvement has been crucial in shaping the project’s objectives, expanding its reach, and enhancing its sustainability.
At the local level, community members, schools, local associations, and municipal authorities in Guidonia Montecelio and Magliano Sabina have actively participated in co-design workshops, educational program development, and the creation of 5.0 spaces. Their direct input has ensured that the project addresses real community needs and fosters local ownership.
At the regional level, partnerships with educational institutions, cultural organizations, and regional development agencies have helped align Nodelab with broader policies on education, sustainability, and innovation. These stakeholders have provided expertise, resources, and strategic guidance to enhance the project’s impact within the Lazio region.
At the national level, collaborations with governmental bodies and research institutions have supported the dissemination of best practices, provided access to funding opportunities, and facilitated policy alignment with national education and sustainability goals.
At the European level, Nodelab engages with networks, projects, and initiatives that promote education 5.0, digital innovation, and sustainability. This connection has allowed for the exchange of knowledge, exposure to diverse practices, and participation in European programs that strengthen the project’s visibility and influence.
The added value of this multi-level engagement lies in the integration of diverse perspectives, the creation of strong partnerships, and the ability to adapt and scale the project across different contexts, making Nodelab a model of collaborative and sustainable development.
At the local level, community members, schools, local associations, and municipal authorities in Guidonia Montecelio and Magliano Sabina have actively participated in co-design workshops, educational program development, and the creation of 5.0 spaces. Their direct input has ensured that the project addresses real community needs and fosters local ownership.
At the regional level, partnerships with educational institutions, cultural organizations, and regional development agencies have helped align Nodelab with broader policies on education, sustainability, and innovation. These stakeholders have provided expertise, resources, and strategic guidance to enhance the project’s impact within the Lazio region.
At the national level, collaborations with governmental bodies and research institutions have supported the dissemination of best practices, provided access to funding opportunities, and facilitated policy alignment with national education and sustainability goals.
At the European level, Nodelab engages with networks, projects, and initiatives that promote education 5.0, digital innovation, and sustainability. This connection has allowed for the exchange of knowledge, exposure to diverse practices, and participation in European programs that strengthen the project’s visibility and influence.
The added value of this multi-level engagement lies in the integration of diverse perspectives, the creation of strong partnerships, and the ability to adapt and scale the project across different contexts, making Nodelab a model of collaborative and sustainable development.
The Nodelab project integrates multiple disciplines to create an innovative and inclusive learning environment. The project reflects a combination of fields, including education, digital technologies, sustainability, arts, social sciences, and urban planning, all contributing to its design and implementation.
Education forms the foundation, focusing on inclusive and adaptive learning methods that support diverse needs. Digital technologies, through the Digital Lab 5.0, provide tools for digital fabrication, coding, and design, fostering hands-on learning and innovation. Sustainability is embedded in all activities, promoting environmental awareness, circular economy principles, and eco-friendly practices. The arts enhance cultural expression and creativity, offering new ways to engage with local heritage and identity. Social sciences contribute insights into community dynamics, inclusion strategies, and participatory governance, ensuring the project reflects social realities. Urban planning ensures that the design of learning spaces is functional, accessible, and aesthetically pleasing.
These disciplines interacted through collaborative workshops, co-design sessions, and interdisciplinary working groups. Educators worked with technologists, sustainability experts, artists, and urban planners to co-create educational programs, design learning environments, and develop community projects. This interaction fostered the exchange of ideas and knowledge, allowing for the development of innovative solutions that reflect a broad range of perspectives.
The added value of this multidisciplinary approach lies in its ability to address complex challenges holistically. By integrating different fields, Nodelab combines technological innovation with cultural, social, and environmental dimensions. This has enhanced the project’s impact, making it a replicable model for sustainable, community-centered development that fosters creativity, inclusion, and resilience.
Education forms the foundation, focusing on inclusive and adaptive learning methods that support diverse needs. Digital technologies, through the Digital Lab 5.0, provide tools for digital fabrication, coding, and design, fostering hands-on learning and innovation. Sustainability is embedded in all activities, promoting environmental awareness, circular economy principles, and eco-friendly practices. The arts enhance cultural expression and creativity, offering new ways to engage with local heritage and identity. Social sciences contribute insights into community dynamics, inclusion strategies, and participatory governance, ensuring the project reflects social realities. Urban planning ensures that the design of learning spaces is functional, accessible, and aesthetically pleasing.
These disciplines interacted through collaborative workshops, co-design sessions, and interdisciplinary working groups. Educators worked with technologists, sustainability experts, artists, and urban planners to co-create educational programs, design learning environments, and develop community projects. This interaction fostered the exchange of ideas and knowledge, allowing for the development of innovative solutions that reflect a broad range of perspectives.
The added value of this multidisciplinary approach lies in its ability to address complex challenges holistically. By integrating different fields, Nodelab combines technological innovation with cultural, social, and environmental dimensions. This has enhanced the project’s impact, making it a replicable model for sustainable, community-centered development that fosters creativity, inclusion, and resilience.
The NL project stands out for its innovative character, offering a unique approach compared to mainstream actions in education, community development, and sustainability. While traditional projects often focus on isolated disciplines or standardized learning models, Nodelab integrates education 5.0, digital technologies, sustainability, and community engagement into a cohesive and dynamic framework.
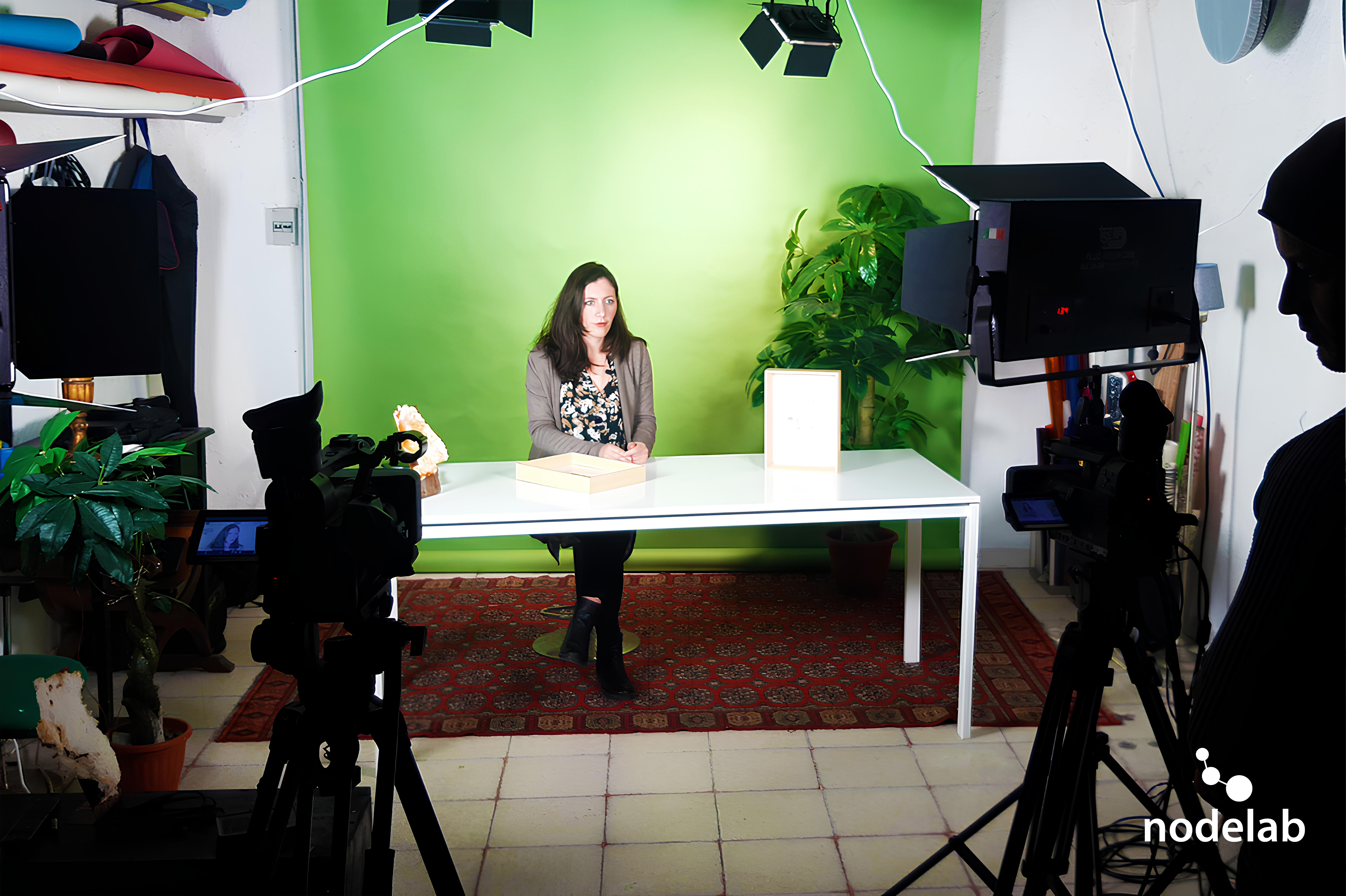
Unlike conventional educational programs, Nodelab shifts from passive learning to active, experiential education through hands-on activities in the Digital Lab 5.0. This lab fosters creativity, problem-solving, and digital literacy by providing access to advanced technologies such as digital fabrication tools, which are typically limited to specialized institutions.
In terms of community development, mainstream projects often separate urban and rural initiatives. Nodelab bridges this gap by creating strong urban-rural linkages, connecting Guidonia Montecelio and Magliano Sabina through shared projects and knowledge exchange. This dual focus promotes regional cohesion, encouraging collaboration between diverse communities
Nodelab’s commitment to inclusion and accessibility also sets it apart. Courses are open to everyone, including individuals with disabilities, and designed following universal design principles. This inclusive approach is embedded not only in the content but also in the governance model, where local communities actively participate in decision-making, co-design, and project implementation.
Finally, Nodelab’s focus on sustainability through education is a key innovation. Rather than treating sustainability as a separate topic, it is integrated into all activities, fostering a culture of environmental responsibility. This holistic, cross-disciplinary model redefines how education, technology, and community development can work together for lasting impact, making Nodelab a replicable example of future-oriented learning and social transformation.
Unlike conventional educational programs, Nodelab shifts from passive learning to active, experiential education through hands-on activities in the Digital Lab 5.0. This lab fosters creativity, problem-solving, and digital literacy by providing access to advanced technologies such as digital fabrication tools, which are typically limited to specialized institutions.
In terms of community development, mainstream projects often separate urban and rural initiatives. Nodelab bridges this gap by creating strong urban-rural linkages, connecting Guidonia Montecelio and Magliano Sabina through shared projects and knowledge exchange. This dual focus promotes regional cohesion, encouraging collaboration between diverse communities
Nodelab’s commitment to inclusion and accessibility also sets it apart. Courses are open to everyone, including individuals with disabilities, and designed following universal design principles. This inclusive approach is embedded not only in the content but also in the governance model, where local communities actively participate in decision-making, co-design, and project implementation.
Finally, Nodelab’s focus on sustainability through education is a key innovation. Rather than treating sustainability as a separate topic, it is integrated into all activities, fostering a culture of environmental responsibility. This holistic, cross-disciplinary model redefines how education, technology, and community development can work together for lasting impact, making Nodelab a replicable example of future-oriented learning and social transformation.
The Nodelab project adopts a multidisciplinary and participatory methodology that integrates education 5.0, digital innovation, and sustainability to foster community development and social inclusion. The approach is based on active learning, co-creation, and the promotion of urban-rural linkages, ensuring that all stakeholders are engaged in the project’s design and implementation.
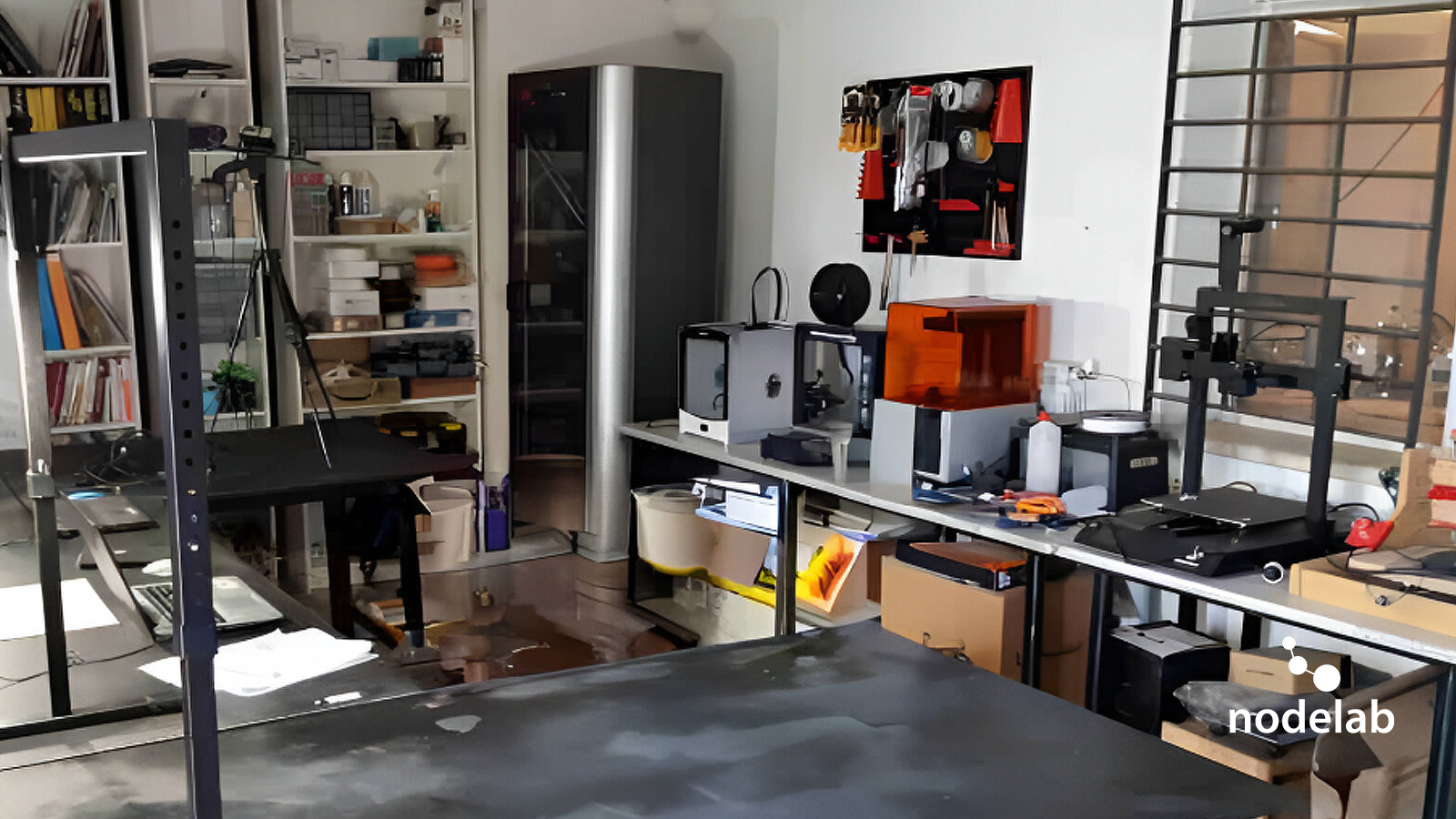
At its core, NL uses an experiential learning model, where knowledge is acquired through hands-on activities, practical workshops, and real-world problem-solving. The Digital Lab 5.0 plays a central role in this process, providing access to advanced technologies such as digital fabrication tools, 3D printing, and coding platforms. This environment encourages creativity, experimentation, and innovation, empowering participants to develop technical skills while addressing real community challenges.
The project also applies participatory design methodologies, involving local residents, educators, students, and civil society in co-design sessions. This inclusive process ensures that the project reflects the specific needs and aspirations of the communities in Guidonia Montecelio and Magliano Sabina. By fostering dialogue and collaboration, Nodelab creates a sense of ownership and belonging among participants.
Sustainability is embedded across all activities through the integration of environmental education and circular economy principles. Rather than being treated as a standalone topic, sustainability is woven into every aspect of the curriculum and project activities, promoting environmentally responsible behaviors and practices.
Finally, NL’s methodology emphasizes interdisciplinary collaboration, bringing together experts from diverse fields such as education, technology, arts, urban planning, and social sciences. This cross-sector approach enriches the learning experience, promotes holistic problem-solving, and ensures the project’s relevance and impact in different contex
At its core, NL uses an experiential learning model, where knowledge is acquired through hands-on activities, practical workshops, and real-world problem-solving. The Digital Lab 5.0 plays a central role in this process, providing access to advanced technologies such as digital fabrication tools, 3D printing, and coding platforms. This environment encourages creativity, experimentation, and innovation, empowering participants to develop technical skills while addressing real community challenges.
The project also applies participatory design methodologies, involving local residents, educators, students, and civil society in co-design sessions. This inclusive process ensures that the project reflects the specific needs and aspirations of the communities in Guidonia Montecelio and Magliano Sabina. By fostering dialogue and collaboration, Nodelab creates a sense of ownership and belonging among participants.
Sustainability is embedded across all activities through the integration of environmental education and circular economy principles. Rather than being treated as a standalone topic, sustainability is woven into every aspect of the curriculum and project activities, promoting environmentally responsible behaviors and practices.
Finally, NL’s methodology emphasizes interdisciplinary collaboration, bringing together experts from diverse fields such as education, technology, arts, urban planning, and social sciences. This cross-sector approach enriches the learning experience, promotes holistic problem-solving, and ensures the project’s relevance and impact in different contex
The NL project incorporates several elements that can be easily replicated or transferred to other places, groups of beneficiaries, and diverse contexts. Its flexible structure, multidisciplinary approach, and focus on education 5.0 make it adaptable to various environments, whether urban or rural.
One of the most transferable elements is the experiential learning methodology. The active, hands-on approach, centered on practical workshops and real-world problem-solving, can be applied in different educational settings, from schools and universities to community centers. This model encourages critical thinking, creativity, and collaboration, making it effective across diverse learning environments.
The Digital Lab 5.0 is another key element that can be replicated. Its modular structure allows for the integration of digital fabrication technologies, such as 3D printing, laser cutting, and coding platforms, which can be tailored to the resources and needs of different communities. This technology fosters innovation, technical skills development, and entrepreneurial opportunities, particularly in underserved areas.
The participatory design process used in Nodelab is highly adaptable. By involving local communities in co-design sessions, decision-making, and project implementation, the approach ensures that initiatives are context-specific and community-driven. This model of engagement can be transferred to other projects aiming to strengthen civic participation and social cohesion.
Sustainability practices integrated into the project, such as circular economy principles, environmental education, and resource-efficient technologies, can also be applied in other contexts. These practices promote long-term environmental responsibility and can be adapted to various cultural and geographical settings.
Finally, NL’s interdisciplinary collaboration model, which brings together educators, technologists, artists, urban planners, and social scientists, can be repli
One of the most transferable elements is the experiential learning methodology. The active, hands-on approach, centered on practical workshops and real-world problem-solving, can be applied in different educational settings, from schools and universities to community centers. This model encourages critical thinking, creativity, and collaboration, making it effective across diverse learning environments.
The Digital Lab 5.0 is another key element that can be replicated. Its modular structure allows for the integration of digital fabrication technologies, such as 3D printing, laser cutting, and coding platforms, which can be tailored to the resources and needs of different communities. This technology fosters innovation, technical skills development, and entrepreneurial opportunities, particularly in underserved areas.
The participatory design process used in Nodelab is highly adaptable. By involving local communities in co-design sessions, decision-making, and project implementation, the approach ensures that initiatives are context-specific and community-driven. This model of engagement can be transferred to other projects aiming to strengthen civic participation and social cohesion.
Sustainability practices integrated into the project, such as circular economy principles, environmental education, and resource-efficient technologies, can also be applied in other contexts. These practices promote long-term environmental responsibility and can be adapted to various cultural and geographical settings.
Finally, NL’s interdisciplinary collaboration model, which brings together educators, technologists, artists, urban planners, and social scientists, can be repli
The NL project addresses several global challenges by providing innovative local solutions that foster sustainability, inclusion, and community resilience. Its approach is rooted in creating connections between urban and rural environments, bridging gaps in education, technology, and social cohesion.
One of the key global challenges Nodelab tackles is climate change and environmental degradation. By integrating sustainability into every aspect of its activities, Nodelab promotes environmental awareness, resource efficiency, and circular economy principles. Local solutions include hands-on workshops on eco-design, sustainable digital fabrication, and environmental education, encouraging communities to adopt environmentally responsible practices that can be scaled globally.
Another critical challenge is the growing digital divide, which affects access to education and technology, particularly in rural and underserved areas. Nodelab addresses this by establishing Digital Lab 5.0 spaces equipped with advanced technologies, providing digital literacy training, and fostering skills in digital fabrication, coding, and innovative problem-solving. This helps reduce inequalities and empowers individuals with the competencies needed in the digital age.
Social fragmentation and the loss of community identity are also global issues that Nodelab seeks to address. The project rebuilds a sense of belonging through participatory design, inclusive educational programs, and the revitalization of cultural spaces like the ex-Monastery of Santa Croce. By engaging local communities in co-creation processes, Nodelab strengthens social bonds, promotes civic participation, and fosters cultural heritage preservation.
Finally, NL responds to the global challenge of educational inequality by offering inclusive, adaptive learning opportunities open to all, including individuals with disabilities. Its education 5.0 approach emphasizes creativity, critical thinking, and lifelong lear
One of the key global challenges Nodelab tackles is climate change and environmental degradation. By integrating sustainability into every aspect of its activities, Nodelab promotes environmental awareness, resource efficiency, and circular economy principles. Local solutions include hands-on workshops on eco-design, sustainable digital fabrication, and environmental education, encouraging communities to adopt environmentally responsible practices that can be scaled globally.
Another critical challenge is the growing digital divide, which affects access to education and technology, particularly in rural and underserved areas. Nodelab addresses this by establishing Digital Lab 5.0 spaces equipped with advanced technologies, providing digital literacy training, and fostering skills in digital fabrication, coding, and innovative problem-solving. This helps reduce inequalities and empowers individuals with the competencies needed in the digital age.
Social fragmentation and the loss of community identity are also global issues that Nodelab seeks to address. The project rebuilds a sense of belonging through participatory design, inclusive educational programs, and the revitalization of cultural spaces like the ex-Monastery of Santa Croce. By engaging local communities in co-creation processes, Nodelab strengthens social bonds, promotes civic participation, and fosters cultural heritage preservation.
Finally, NL responds to the global challenge of educational inequality by offering inclusive, adaptive learning opportunities open to all, including individuals with disabilities. Its education 5.0 approach emphasizes creativity, critical thinking, and lifelong lear
The NL project has achieved significant results, outcomes, and impacts aligned with its focus on sustainability, inclusion, and community development. By bridging urban-rural connections and integrating education 5.0 with digital innovation and sustainability practices, Nodelab has delivered measurable benefits for both direct and indirect beneficiaries.
The project’s key results include the successful establishment of Digital Lab 5.0 spaces in Guidonia Montecelio and Magliano Sabina. These hubs provide access to advanced technologies such as digital fabrication tools, fostering creativity, technical skills, and innovative thinking among participants. Nodelab has implemented inclusive educational programs, reaching diverse groups including students, educators, entrepreneurs, and individuals with disabilities, ensuring equal access to quality learning opportunities.
One of the most impactful outcomes has been the revitalization of local spaces, such as the ex-Monastery of Santa Croce, transforming them into vibrant centers for cultural and educational activities. This has strengthened the sense of community belonging, encouraged civic participation, and promoted the preservation of cultural heritage. The participatory design process has empowered local residents, giving them an active role in shaping the project, which has increased community engagement and ownership.
For direct beneficiaries, such as students and educators, NL has provided hands-on learning experiences, digital literacy skills, and exposure to sustainable practices. This has improved their employability, entrepreneurial potential, and capacity for innovation. Indirect beneficiaries include local communities who benefit from enhanced social cohesion, economic opportunities through the promotion of local entrepreneurship, and the creation of environmentally sustainable practices that improve the quality of life.
In summary, Nodelab’s impact extends beyond educational outcomes, fostering
The project’s key results include the successful establishment of Digital Lab 5.0 spaces in Guidonia Montecelio and Magliano Sabina. These hubs provide access to advanced technologies such as digital fabrication tools, fostering creativity, technical skills, and innovative thinking among participants. Nodelab has implemented inclusive educational programs, reaching diverse groups including students, educators, entrepreneurs, and individuals with disabilities, ensuring equal access to quality learning opportunities.
One of the most impactful outcomes has been the revitalization of local spaces, such as the ex-Monastery of Santa Croce, transforming them into vibrant centers for cultural and educational activities. This has strengthened the sense of community belonging, encouraged civic participation, and promoted the preservation of cultural heritage. The participatory design process has empowered local residents, giving them an active role in shaping the project, which has increased community engagement and ownership.
For direct beneficiaries, such as students and educators, NL has provided hands-on learning experiences, digital literacy skills, and exposure to sustainable practices. This has improved their employability, entrepreneurial potential, and capacity for innovation. Indirect beneficiaries include local communities who benefit from enhanced social cohesion, economic opportunities through the promotion of local entrepreneurship, and the creation of environmentally sustainable practices that improve the quality of life.
In summary, Nodelab’s impact extends beyond educational outcomes, fostering