Reconnecting with nature
Conservation of wildlife populations
Analysis of wildlife stress resistance and its improvement
Preserving wildlife populations is a very important task, as the loss of species diversity will trigger the destruction of the ecosystem as a whole. One of the dangerous factors affecting wild animals is stress. Every animal lives in a certain ecosystem, which is destroyed by human actions. The animal is forced to migrate and look for new habitats, which causes stress, which later causes its death.
Ukraine
National
It addresses urban-rural linkages
It refers to other types of transformations (soft investment)
Early concept
No
No
As an individual
The aim of the project is to develop methods to counteract the negative effects of stress on wildlife, which will be ensured by increasing their stress resistance through the use of nanopreparations. The target groups include specialists who ensure the role of wildlife control and conservation authorities and target groups of people concerned about the current state of wildlife. Among the results achieved, a scheme was developed to assess the stress state of the following groups of animals, namely ruminants, pigs and poultry. A large amount of statistical data was analyzed to improve their metabolism for better adaptation of their organism to the environment.
Stress
Wild animals
Stress resistance
Nanopreparations
Ecosystem
The project involves studying the stressful state of wild animals and developing methods to increase their stress resistance. The implementation of these points will help to preserve the life of these animals and the possibility of their further reproduction. To give you an example, hares live in a certain local area, which they have studied in detail and know where they can feed and rest. Let's imagine that this is a large group of animals. And at some point in time, a stressful factor arises in their habitat that makes it impossible for these animals to stay in the area of their permanent localization. Animals are forced to migrate to a safer habitat, and they spend a considerable amount of time and effort to do so. Not every animal in this period of stress can adapt and find a solution to this problem. A significant concentration of negative effects of stress accumulates in its body. The first thing that occurs is a decrease or lack of desire to eat, then the animal begins to lose weight significantly, and so on with serious consequences. Secondly, animals that have migrated in a considerable panic from their previous place of residence are exposed to significant metabolic disorders and neurohumoral shifts in their own bodies, which will negatively affect their health. Also, one of the main problems is the development of infertility in the population of these animals, which will disrupt the sustainability of the ecosystem and its closed food chain. This will further affect other animals. Therefore, addressing the issue of stress is quite an urgent issue.
The development and implementation of this project will help to preserve the population of animals in the wild, as well as animals placed in artificially created conditions for their existence and reproduction. It is worth noting that the habitat of animals in each country is diverse and unique. Therefore, we must do everything possible to pass on this unique nature to future generations and teach them how to properly protect the nature handed down to them. After all, many well-known and widespread species of animals in the past are increasingly becoming known only on the pages of books and museum shelves. And attempts by scientists to reproduce wild animals in artificial conditions do not always achieve the hopes and expectations. Therefore, obtaining a new tool to help preserve wildlife populations is important for many countries.
This project is multifaceted in its implementation, so the application of wildlife analysis is not limited to their sustainable habitat. Artificially created habitats for wildlife can also be considered. Artificially created habitats for wild animals have better access to monitoring the condition of animals and providing them with food, i.e., placing appropriate feeders with food content controlled by humans. Such artificial conditions help to develop a model of work for this project and train a wide range of people in various manipulative actions. For example, people with little experience and skills can help feed the necessary medicines to wild animals. This is not difficult because we envisage administering these drugs with food, not by injection, which minimizes the impact of humans as a stress factor. And given the fact that the drug belongs to nano-acquahelates, it is needed in small doses, and its introduction into the feed is provided by the aerosol method, which makes it possible for a wide range of people who want to preserve nature and help wild animals, but due to certain limitations are not able to do it themselves, to participate in the project. Therefore, this project is flexible enough for each person.
The involvement of civil society was ensured through small financial payments and the willingness of people who wanted to participate in the project.
This project was of interest to forestries in Kyiv and Poltava regions, which began to face the problem of declining animal populations as a result of severe stress factors, including explosions and shock waves from military weapons.
The project relates to the fields of knowledge such as Biology and Veterinary Medicine, and disciplines such as Physiology, Chemistry and Biochemistry.
The innovation of this project is to develop a new method of counteracting the effects of stress on the body of wild animals through the use of minerals that will affect the decay time of the hormone cortisol, which will reduce its level in the body of animals and improve their adaptation to stress factors and increase the overall stress resistance of the body.
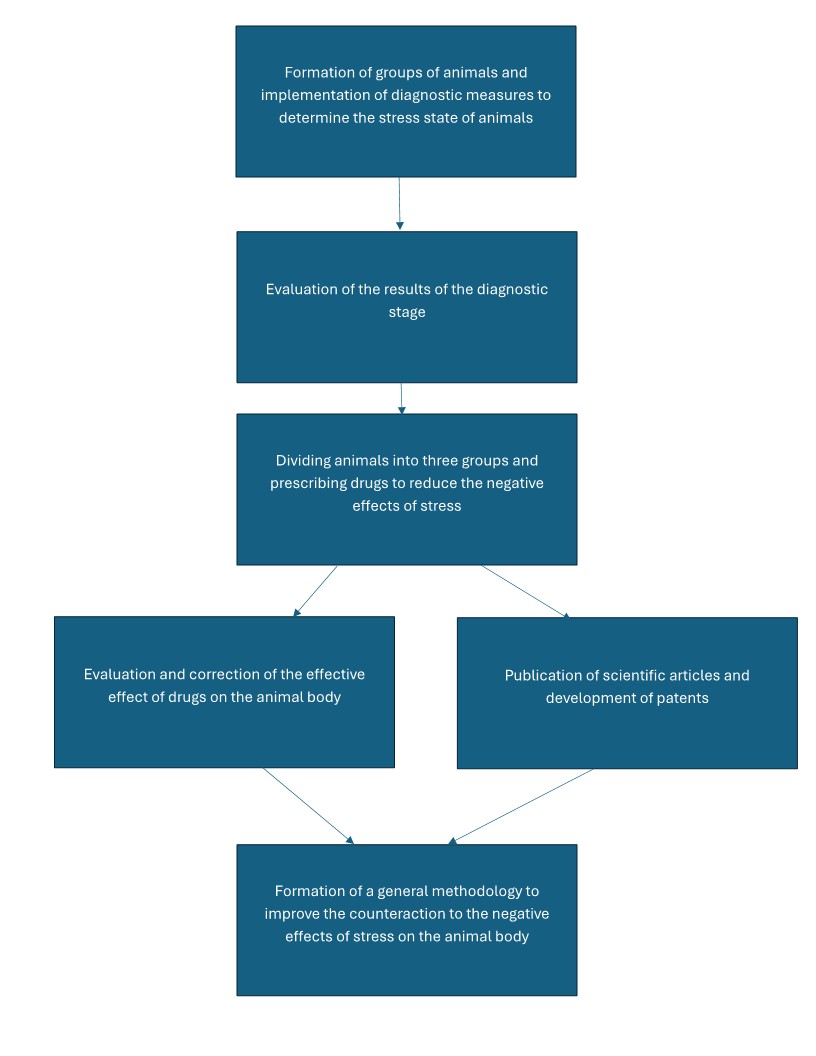
The main principle of this project is to implement it in two stages. The first is to assess the stressful state of animals, which will be carried out by analyzing their mental state using the developed methodology for studying the nervous system and assessing the level of hormones in the animal's body, primarily the concentration of the hormone cortisol, high levels of which indicate significant stress in the animal. The second stage involves the use of mineral supplements to improve the animal's condition by influencing the concentration of this hormone and counteracting its significant increase in the future. Mineral additives will be combined with feed mixtures, which minimizes the complexity of the drug's prescription, and will be used as an additional food additive.
The project has a high percentage of reproducibility and low complexity in implementation. The study of the stressful state of animals is carried out by assessing the activity of the nervous system using an electrocardiogram and the activity of hormone levels in the blood of animals. Having received this data, it is possible to form a certain understanding of the animal's health status. After that, using mineral supplements in combination with food, the animal consumes this drug and accumulates the necessary level of these micro and macro elements that will help the animal's body reduce the negative effects of stress.
Global challenges include the creation of a multifaceted mechanism for assessing the stressful state of animals and the use of a well-established step-by-step solution to the negative effects of stress on the animal's body to preserve them and improve their general condition.
This project will be submitted this year for participation in the state funding competition, and the project plan will be additionally submitted to Ukrainian companies engaged in livestock farming in February this year and participate in the grant. After that, we received funding to purchase the necessary reagents and launch a scientific process to address this issue. Subsequently, publishing scientific articles and obtaining patents.