Urban Regeneration Strategy
Urban Regeneration Strategy "Between City and Countryside. For a Diffused Urbanity"
We are redeveloping the heart of Campogalliano, transforming forgotten areas into public spaces
for everyone: from Parco della Bilancia, a green oasis for young and old, to the new Senior Center, a
place for meeting and socializing. New housing for vulnerable people and an eye to the future with
energy-efficient buildings. A more connected, sustainable, and welcoming town thanks to gentle
mobility, more nature and culture in the city.
for everyone: from Parco della Bilancia, a green oasis for young and old, to the new Senior Center, a
place for meeting and socializing. New housing for vulnerable people and an eye to the future with
energy-efficient buildings. A more connected, sustainable, and welcoming town thanks to gentle
mobility, more nature and culture in the city.
Italy
{Empty}
Prototype level
Yes
Yes
No
No
No
036003: Campogalliano (IT)
The project is part of the Urban Regeneration Strategy "Between City and Countryside. For a Diffused Urbanity", promoted by the Municipality of Campogalliano and co-funded by the Emilia-Romagna Region. The goal is to transform underutilized urban areas into vibrant public spaces, improving urban quality, connectivity, and social integration through architectural and urban interventions.
Target Groups
• Residents of Campogalliano: Beneficiaries of improved public spaces and new infrastructure.
• Elderly people: Creation of a Senior Center for social interaction.
• Vulnerable population: Dedicated residences for fragile categories.
• Merchants and economic operators: Revitalization of the commercial fabric.
• Visitors and tourists: Improved accessibility and enhancement of cultural heritage.
Expected Specific Objectives
• Urban regeneration and architectural redevelopment: Transformation of Parco della Bilancia and adjacent public areas into functional and accessible spaces.
• Social inclusion and functional mix: Creation of gathering spaces and new residences for the vulnerable population.
• Improvement of sustainable mobility: Development of safe pedestrian and cycling paths.
• Environmental sustainability: Use of NZEB (Nearly Zero Energy Building) standards for low-energy-impact buildings.
• Enhancement of cultural heritage: Expansion of the Museo della Bilancia and the creation of a "diffused museum".
The intervention aims to redefine the concept of public space, enhancing the quality of life and creating a more connected and sustainable urban environment
Target Groups
• Residents of Campogalliano: Beneficiaries of improved public spaces and new infrastructure.
• Elderly people: Creation of a Senior Center for social interaction.
• Vulnerable population: Dedicated residences for fragile categories.
• Merchants and economic operators: Revitalization of the commercial fabric.
• Visitors and tourists: Improved accessibility and enhancement of cultural heritage.
Expected Specific Objectives
• Urban regeneration and architectural redevelopment: Transformation of Parco della Bilancia and adjacent public areas into functional and accessible spaces.
• Social inclusion and functional mix: Creation of gathering spaces and new residences for the vulnerable population.
• Improvement of sustainable mobility: Development of safe pedestrian and cycling paths.
• Environmental sustainability: Use of NZEB (Nearly Zero Energy Building) standards for low-energy-impact buildings.
• Enhancement of cultural heritage: Expansion of the Museo della Bilancia and the creation of a "diffused museum".
The intervention aims to redefine the concept of public space, enhancing the quality of life and creating a more connected and sustainable urban environment
Urban regeneration
Social inclusion
Sustainability
Cultural Heritage
Community Engagement
The urban redevelopment initiative in Campogalliano integrates advanced principles of environmental, social, and economic sustainability, representing an innovative model of urban regeneration.
1. Energy Efficiency and Environmental Impact Reduction
• The planned buildings, including the Senior Center and Social Residences, will be constructed following the NZEB (Nearly Zero Energy Building) standard, ensuring low energy consumption and optimized use of natural resources.
• Energy-saving technologies will be implemented, including photovoltaic systems, solutions for hygrothermal comfort, and high-performance insulating materials.
• Public and building lighting will use high-efficiency LED systems, reducing electricity consumption.
2. Sustainable Mobility and Emissions Reduction
• The initiative includes the creation of a network of safe pedestrian and cycling paths, promoting slow mobility and reducing car use.
• Public transport stops will be reconfigured to improve accessibility, encouraging greater use of public transport.
• Architectural barriers will be removed to ensure full accessibility to the redeveloped urban spaces.
3. Urban Green Redevelopment and Landscape Enhancement
• Parco della Bilancia will be enhanced with new green areas, educational trails, and interactive elements related to the theme of the diffused museum.
• An urban reforestation program will be implemented, maintaining and strengthening existing trees.
• "Desealing" policies will be adopted to reduce impermeable surfaces and improve rainwater management.
4. Social Inclusion and Community-Centered Approach
• The initiative integrates a participatory approach, involving citizens in the co-design of public spaces.
• The project aims to strengthen the sense of community through the creation of shared spaces for different age groups and social categories.
1. Energy Efficiency and Environmental Impact Reduction
• The planned buildings, including the Senior Center and Social Residences, will be constructed following the NZEB (Nearly Zero Energy Building) standard, ensuring low energy consumption and optimized use of natural resources.
• Energy-saving technologies will be implemented, including photovoltaic systems, solutions for hygrothermal comfort, and high-performance insulating materials.
• Public and building lighting will use high-efficiency LED systems, reducing electricity consumption.
2. Sustainable Mobility and Emissions Reduction
• The initiative includes the creation of a network of safe pedestrian and cycling paths, promoting slow mobility and reducing car use.
• Public transport stops will be reconfigured to improve accessibility, encouraging greater use of public transport.
• Architectural barriers will be removed to ensure full accessibility to the redeveloped urban spaces.
3. Urban Green Redevelopment and Landscape Enhancement
• Parco della Bilancia will be enhanced with new green areas, educational trails, and interactive elements related to the theme of the diffused museum.
• An urban reforestation program will be implemented, maintaining and strengthening existing trees.
• "Desealing" policies will be adopted to reduce impermeable surfaces and improve rainwater management.
4. Social Inclusion and Community-Centered Approach
• The initiative integrates a participatory approach, involving citizens in the co-design of public spaces.
• The project aims to strengthen the sense of community through the creation of shared spaces for different age groups and social categories.
The project enhances the relationship between city and countryside, with spaces reflecting the history and morphology of the territory.
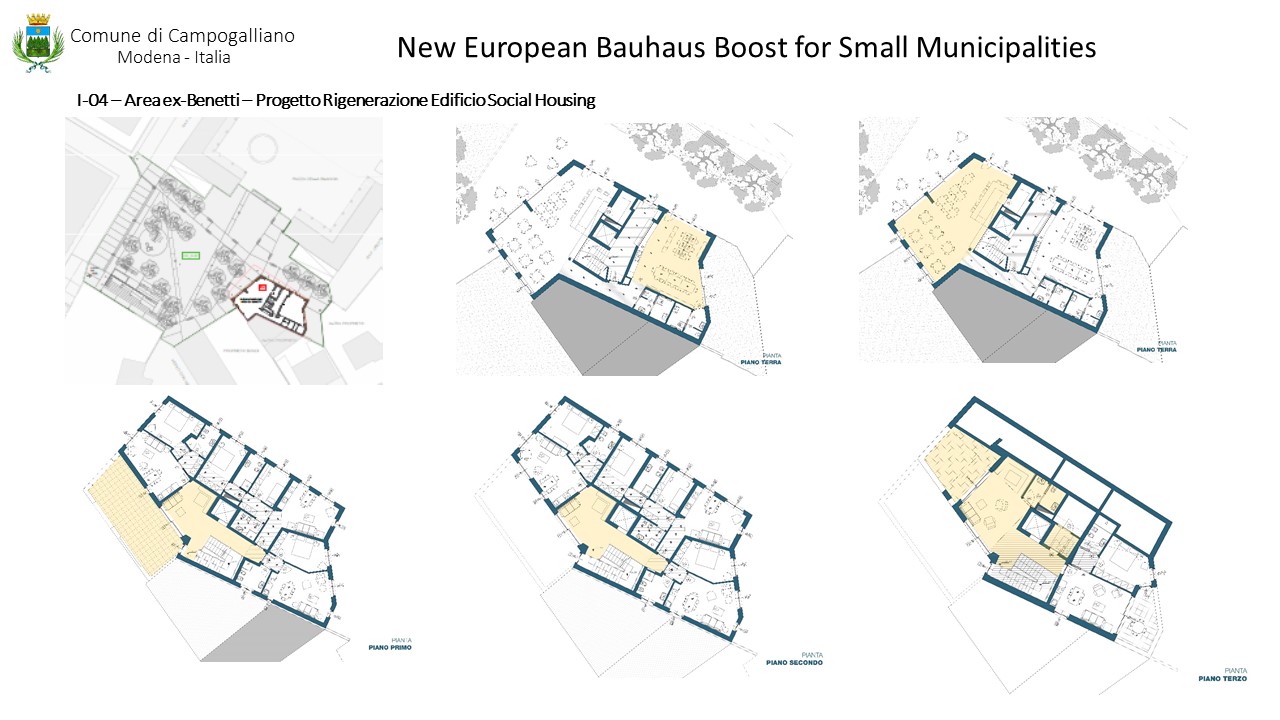
The new building for the Senior Center and social residences will use materials and colors in harmony with the existing urban setting, creating a welcoming environment.
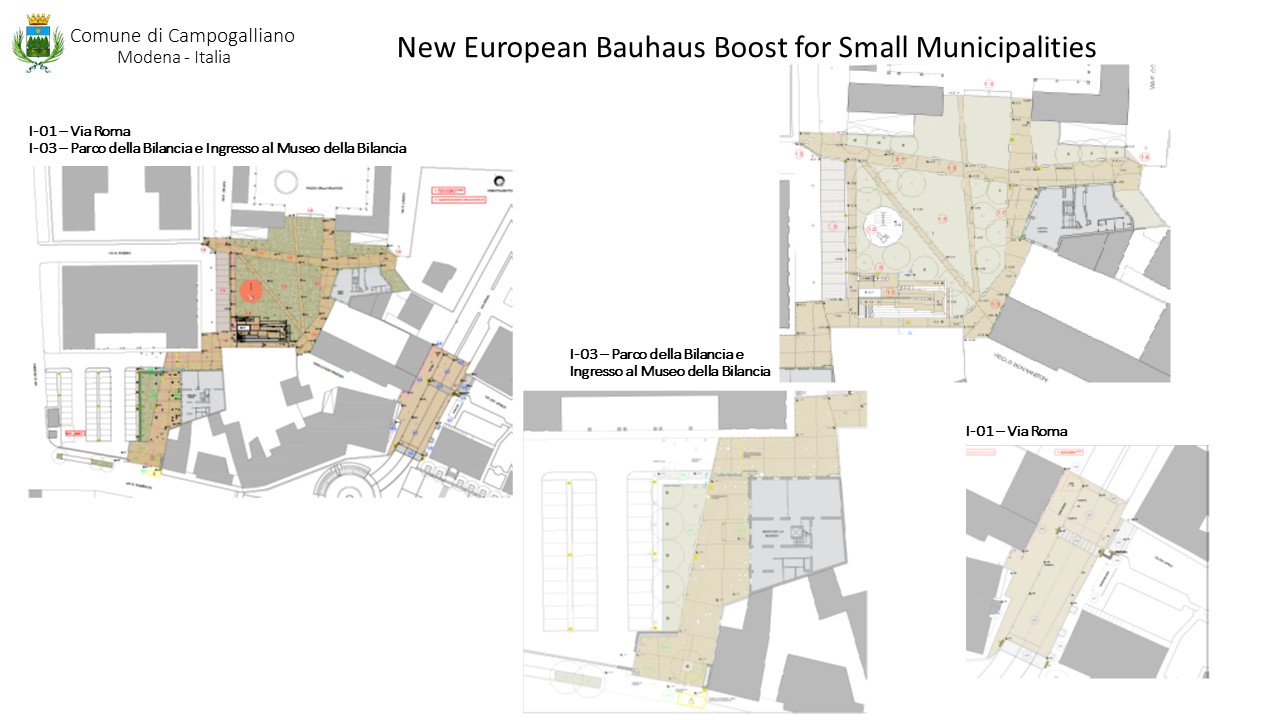
The interventions in Parco della Bilancia and Piazza della Bilancia aim to restore architectural quality, improving pavements, lighting, and urban furnishings.
The project fosters social interaction and a sense of belonging through spaces designed to encourage meetings and dialogue.
The use of natural materials and regenerated green areas creates a sense of well-being and relaxation for citizens.
Improved accessibility and pedestrian/cycling mobility contribute to a smoother and more enjoyable urban experience.
The project includes a diffused museum route, enhancing the "Museo della Bilancia" and connecting it to the urban fabric through installations and interactive elements.
Cultural events and outdoor activities, such as cinema under the stars and street exhibitions, will make public spaces more lively and engaging.
The restoration of historic spaces and their contemporary reinterpretation strengthen the area's identity, balancing past and future.
The new building for the Senior Center and social residences will use materials and colors in harmony with the existing urban setting, creating a welcoming environment.
The interventions in Parco della Bilancia and Piazza della Bilancia aim to restore architectural quality, improving pavements, lighting, and urban furnishings.
The project fosters social interaction and a sense of belonging through spaces designed to encourage meetings and dialogue.
The use of natural materials and regenerated green areas creates a sense of well-being and relaxation for citizens.
Improved accessibility and pedestrian/cycling mobility contribute to a smoother and more enjoyable urban experience.
The project includes a diffused museum route, enhancing the "Museo della Bilancia" and connecting it to the urban fabric through installations and interactive elements.
Cultural events and outdoor activities, such as cinema under the stars and street exhibitions, will make public spaces more lively and engaging.
The restoration of historic spaces and their contemporary reinterpretation strengthen the area's identity, balancing past and future.
The urban regeneration initiative in Campogalliano aims to create accessible, inclusive, and socially equitable spaces by integrating solutions for mobility, accessibility, and community engagement, through the following measures:
• Elimination of architectural barriers: Every space will be accessible to people with reduced mobility through obstacle-free pathways, raised crossings, and access ramps.
• Sustainable mobility: The project includes pedestrian and cycling paths connected to the urban center and public transport, making movement easier for everyone.
• Inclusive public transport: Bus stops will be upgraded with clear and accessible signage, facilitating public transport use for elderly people and individuals with disabilities.
• Diffused square and relational spaces: The diffused square concept envisions a network of interconnected public spaces that encourage social interaction across different population groups.
• Gathering places for all ages: The Senior Center and Social Residences are designed to promote intergenerational interaction, creating opportunities for engagement between young and elderly people.
• Accessible green spaces: Parco della Bilancia will be redesigned with rest areas, inclusive playgrounds, and sensory pathways, enhancing the quality of life for people of all ages.
• Co-design with the community: The initiative has been developed through the active involvement of citizens, associations, and institutions, ensuring that local needs are integrated into the project.
• Economic and social revitalization: by improving infrastructure and creating new commercial spaces, the project promotes inclusive economic growth with opportunities for all.
• Diffused museum and cultural enhancement: integrating the Museo della Bilancia into the urban context allows everyone to experience accessible and engaging cultural activities.
• Elimination of architectural barriers: Every space will be accessible to people with reduced mobility through obstacle-free pathways, raised crossings, and access ramps.
• Sustainable mobility: The project includes pedestrian and cycling paths connected to the urban center and public transport, making movement easier for everyone.
• Inclusive public transport: Bus stops will be upgraded with clear and accessible signage, facilitating public transport use for elderly people and individuals with disabilities.
• Diffused square and relational spaces: The diffused square concept envisions a network of interconnected public spaces that encourage social interaction across different population groups.
• Gathering places for all ages: The Senior Center and Social Residences are designed to promote intergenerational interaction, creating opportunities for engagement between young and elderly people.
• Accessible green spaces: Parco della Bilancia will be redesigned with rest areas, inclusive playgrounds, and sensory pathways, enhancing the quality of life for people of all ages.
• Co-design with the community: The initiative has been developed through the active involvement of citizens, associations, and institutions, ensuring that local needs are integrated into the project.
• Economic and social revitalization: by improving infrastructure and creating new commercial spaces, the project promotes inclusive economic growth with opportunities for all.
• Diffused museum and cultural enhancement: integrating the Museo della Bilancia into the urban context allows everyone to experience accessible and engaging cultural activities.
The involvement of citizens and civil society in the urban regeneration initiative follows a structured and participatory approach designed to maximize engagement and impact. Here’s how:
1. Social and Collaborative Housing
The initiative includes the development of social housing, not only as an affordable residential service but as an innovative living model based on sharing and social participation.
A key focus is on addressing the lack of modern housing structures that provide collective socio-health services, encouraging interaction among different generations and cultural groups.
2. Public Consultations and Participatory Governance
The local administration of Campogalliano has organized meetings and working groups to ensure that citizens and interested entities can participate actively in shaping the strategy.
These discussions take place before the executive planning phase, allowing for citizen input and adaptation of strategies.
3. Community-Driven Initiatives and Events
The strategy promotes initiatives such as cultural events, agricultural and food heritage promotions, and intergenerational knowledge exchange.
Elderly citizens are actively involved in transmitting local traditions, reinforcing a collective memory to preserve cultural identity.
A contest for artistic installations in Parco della Bilancia and educational programs linked to local history and environment are planned.
4.Sustainable and Inclusive Urban Development
The strategy includes enhancing public green spaces, planting trees, and improving urban accessibility to promote well-being and social interaction.
5.Impact of Citizen Participation
Increased social cohesion by creating dynamic spaces for interaction.
Improved sense of community ownership, as citizens become active contributors rather than passive beneficiaries of urban changes.
1. Social and Collaborative Housing
The initiative includes the development of social housing, not only as an affordable residential service but as an innovative living model based on sharing and social participation.
A key focus is on addressing the lack of modern housing structures that provide collective socio-health services, encouraging interaction among different generations and cultural groups.
2. Public Consultations and Participatory Governance
The local administration of Campogalliano has organized meetings and working groups to ensure that citizens and interested entities can participate actively in shaping the strategy.
These discussions take place before the executive planning phase, allowing for citizen input and adaptation of strategies.
3. Community-Driven Initiatives and Events
The strategy promotes initiatives such as cultural events, agricultural and food heritage promotions, and intergenerational knowledge exchange.
Elderly citizens are actively involved in transmitting local traditions, reinforcing a collective memory to preserve cultural identity.
A contest for artistic installations in Parco della Bilancia and educational programs linked to local history and environment are planned.
4.Sustainable and Inclusive Urban Development
The strategy includes enhancing public green spaces, planting trees, and improving urban accessibility to promote well-being and social interaction.
5.Impact of Citizen Participation
Increased social cohesion by creating dynamic spaces for interaction.
Improved sense of community ownership, as citizens become active contributors rather than passive beneficiaries of urban changes.
The urban regeneration initiative in Campogalliano involved local, regional and nationale stakeholders:
1. Local Level: Municipality of Campogalliano and Citizens
• Municipality of Campogalliano: Project promoter, co-funding body and coordinator, responsible for defining the regeneration strategy and managing execution.
• Citizens and local associations: A participatory approach was adopted, including public meetings and consultations to integrate community needs.
• Economic operators and merchants: The commercial sector’s involvement was crucial for ensuring the economic revitalization of redeveloped areas.
2. Regional Level: Emilia-Romagna Region
• Emilia-Romagna Region: Co-funded the project through the Urban Regeneration Grant DGR 550/2018, supporting interventions to improve urban quality and sustainability.
3. National level: Politecnico di Milano – ABC Department (Architecture, Built Environment, and Construction Engineering):
Before the implementation of the urban regeneration strategy, a partnership agreement was signed between Unione Terre d'Argine ( a supra-municipal body including Municipality of Campogalliano) and the Polytechnic University of Milan, which was commissioned to conduct a research to identify possible supra-municipal territorial strategic lines, which would, however, be able to activate local-scale strategies.
1. Local Level: Municipality of Campogalliano and Citizens
• Municipality of Campogalliano: Project promoter, co-funding body and coordinator, responsible for defining the regeneration strategy and managing execution.
• Citizens and local associations: A participatory approach was adopted, including public meetings and consultations to integrate community needs.
• Economic operators and merchants: The commercial sector’s involvement was crucial for ensuring the economic revitalization of redeveloped areas.
2. Regional Level: Emilia-Romagna Region
• Emilia-Romagna Region: Co-funded the project through the Urban Regeneration Grant DGR 550/2018, supporting interventions to improve urban quality and sustainability.
3. National level: Politecnico di Milano – ABC Department (Architecture, Built Environment, and Construction Engineering):
Before the implementation of the urban regeneration strategy, a partnership agreement was signed between Unione Terre d'Argine ( a supra-municipal body including Municipality of Campogalliano) and the Polytechnic University of Milan, which was commissioned to conduct a research to identify possible supra-municipal territorial strategic lines, which would, however, be able to activate local-scale strategies.
The urban regeneration initiative in Campogalliano integrated various disciplines and fields of knowledge, such as:
1) Architecture and Urban Planning, redefining public spaces, creating new urban connections and encouraging social interaction;
2) Civil and Environmental Engineering, using NZEB (Nearly Zero Energy Building) technologies, eco-friendly materials, and water management strategies;
3) Social, economic and cultural development, actively involving citizens in the co-design of public spaces and promoting cultural events and public activities to enhance spaces and stimulate community participation.
1) Architecture and Urban Planning, redefining public spaces, creating new urban connections and encouraging social interaction;
2) Civil and Environmental Engineering, using NZEB (Nearly Zero Energy Building) technologies, eco-friendly materials, and water management strategies;
3) Social, economic and cultural development, actively involving citizens in the co-design of public spaces and promoting cultural events and public activities to enhance spaces and stimulate community participation.
The initiative introduces innovative solutions such as:
1) New Concept of "Diffused Square" and Urban Centrality:
Instead of a single central square, the project introduces a system of interconnected public spaces, transforming underutilized areas into hubs for social and cultural interaction.
This approach moves beyond the traditional static square model, creating dynamic and flexible spaces adaptable to various collective activities and functions.
2. Advanced Sustainability and NZEB Design
The planned buildings (Senior Center and Social Residences) will follow NZEB (Nearly Zero Energy Building) standards, ensuring a reduced environmental impact.
Introduction of innovative materials and energy-efficient technologies, such as photovoltaic panels, natural ventilation systems, and low-consumption LED lighting.
Urban green redevelopment with desealing solutions to improve water management and reduce heat islands.
3. Innovative Accessibility and Mobility
The project eliminates architectural barriers with an integrated system of elevated pedestrian pathways and fully accessible spaces.
It aims to create a slow mobility network, with pedestrian and cycling paths connected to local public transport, promoting safe and sustainable movement.
4. Participatory Governance Model
Active involvement of citizens and local associations in the design process through public meetings and co-design initiatives, ensures that the redevelopment reflects the needs and desires of the community, fostering a sense of ownership and belonging.
1) New Concept of "Diffused Square" and Urban Centrality:
Instead of a single central square, the project introduces a system of interconnected public spaces, transforming underutilized areas into hubs for social and cultural interaction.
This approach moves beyond the traditional static square model, creating dynamic and flexible spaces adaptable to various collective activities and functions.
2. Advanced Sustainability and NZEB Design
The planned buildings (Senior Center and Social Residences) will follow NZEB (Nearly Zero Energy Building) standards, ensuring a reduced environmental impact.
Introduction of innovative materials and energy-efficient technologies, such as photovoltaic panels, natural ventilation systems, and low-consumption LED lighting.
Urban green redevelopment with desealing solutions to improve water management and reduce heat islands.
3. Innovative Accessibility and Mobility
The project eliminates architectural barriers with an integrated system of elevated pedestrian pathways and fully accessible spaces.
It aims to create a slow mobility network, with pedestrian and cycling paths connected to local public transport, promoting safe and sustainable movement.
4. Participatory Governance Model
Active involvement of citizens and local associations in the design process through public meetings and co-design initiatives, ensures that the redevelopment reflects the needs and desires of the community, fostering a sense of ownership and belonging.
The methodology used in the urban regeneration strategy adopted is based on an integrated approach that involves various urban, social, and environmental aspects. Here are the key elements of the methodology adopted:
1) Regeneration Based on Participation:
Active involvement of citizens and local stakeholders in defining interventions.
Public consultation processes to gather input and ensure social consensus.
2)Multi-Dimensional Approach
The urban intervention is not limited to physical redevelopment but includes cultural, social, and environmental actions.
Creation of new urban centralities to overcome spatial fragmentation.
Development of social housing with innovative cohabitation models for self-sufficient elderly people and young residents.
3)Connections and Accessibility
Enhancement of pedestrian and cycling networks to improve sustainable mobility.
Removal of architectural barriers to ensure universal accessibility.
4)Environmental Sustainability and Heritage Valorization
Restoration of historic buildings to reduce land consumption.
Reorganization of public green spaces and marginal areas to make them more usable.
5)Management and Governance
Involvement of local authorities, universities (e.g., Politecnico di Milano), and private entities for funding and management of initiatives.
Sequential planning of interventions with a clear definition of timelines and available financial resources
.
This strategy aims to create a more inclusive, sustainable, and dynamic city, improving the quality of life and social cohesion.
1) Regeneration Based on Participation:
Active involvement of citizens and local stakeholders in defining interventions.
Public consultation processes to gather input and ensure social consensus.
2)Multi-Dimensional Approach
The urban intervention is not limited to physical redevelopment but includes cultural, social, and environmental actions.
Creation of new urban centralities to overcome spatial fragmentation.
Development of social housing with innovative cohabitation models for self-sufficient elderly people and young residents.
3)Connections and Accessibility
Enhancement of pedestrian and cycling networks to improve sustainable mobility.
Removal of architectural barriers to ensure universal accessibility.
4)Environmental Sustainability and Heritage Valorization
Restoration of historic buildings to reduce land consumption.
Reorganization of public green spaces and marginal areas to make them more usable.
5)Management and Governance
Involvement of local authorities, universities (e.g., Politecnico di Milano), and private entities for funding and management of initiatives.
Sequential planning of interventions with a clear definition of timelines and available financial resources
.
This strategy aims to create a more inclusive, sustainable, and dynamic city, improving the quality of life and social cohesion.
The elements that can be replicated to other places and contexts include methodological approaches, governance models, and community-driven processes.
The methodology used in this project involves citizen engagement and participatory governance, ensuring that urban transformations are aligned with community needs.
The social housing model implemented in the project offers an innovative approach to intergenerational living, fostering cohabitation between the elderly and young adults. This model can be adapted in other urban and rural areas to address housing shortages and social isolation.
The transformation of underutilized spaces, such as the Parco della Bilancia and Piazza della Bilancia, into community hubs, demonstrates how cultural and historical sites can be reintegrated into the urban fabric.
Other municipalities can use this model to preserve cultural heritage while creating dynamic social spaces.
The initiative employs a multi-stakeholder governance model, involving public institutions, private partners, and universities (e.g., Politecnico di Milano) to secure funding and expertise. This framework can be adapted by other regions looking to mobilize local and regional partnerships for sustainable urban development
The methodology used in this project involves citizen engagement and participatory governance, ensuring that urban transformations are aligned with community needs.
The social housing model implemented in the project offers an innovative approach to intergenerational living, fostering cohabitation between the elderly and young adults. This model can be adapted in other urban and rural areas to address housing shortages and social isolation.
The transformation of underutilized spaces, such as the Parco della Bilancia and Piazza della Bilancia, into community hubs, demonstrates how cultural and historical sites can be reintegrated into the urban fabric.
Other municipalities can use this model to preserve cultural heritage while creating dynamic social spaces.
The initiative employs a multi-stakeholder governance model, involving public institutions, private partners, and universities (e.g., Politecnico di Milano) to secure funding and expertise. This framework can be adapted by other regions looking to mobilize local and regional partnerships for sustainable urban development
1. Social Inclusion and Housing Crisis
The initiative addresses the global housing crisis by introducing social housing solutions, particularly for elderly and low-income residents.
It promotes intergenerational and cooperative living models, ensuring that housing is not only affordable but also fosters a sense of community and mutual support
.
2. Climate Change and Environmental Sustainability
To mitigate urban heat islands and combat climate change, the project includes tree planting, creation of green spaces, and revitalization of public parks.
The initiative enhances pedestrian and cycling networks, reducing dependence on cars and lowering carbon emissions, aligning with global sustainability goals
3. Urban Connectivity and Public Space Redesign
By eliminating architectural barriers and improving public space accessibility, the initiative ensures that urban areas are inclusive and user-friendly for people with disabilities.
The "distributed centrality" approach creates multiple connected urban hubs rather than relying on a single central square, making public spaces safer and more dynamic
.
4. Preservation of Cultural Heritage and Community Engagement
The initiative protects local cultural identity by restoring historic buildings and promoting community-driven cultural activities, such as heritage festivals and artistic installations.
It fosters collective memory and social cohesion, strengthening citizens' connection to their urban environment
.
The initiative addresses the global housing crisis by introducing social housing solutions, particularly for elderly and low-income residents.
It promotes intergenerational and cooperative living models, ensuring that housing is not only affordable but also fosters a sense of community and mutual support
.
2. Climate Change and Environmental Sustainability
To mitigate urban heat islands and combat climate change, the project includes tree planting, creation of green spaces, and revitalization of public parks.
The initiative enhances pedestrian and cycling networks, reducing dependence on cars and lowering carbon emissions, aligning with global sustainability goals
3. Urban Connectivity and Public Space Redesign
By eliminating architectural barriers and improving public space accessibility, the initiative ensures that urban areas are inclusive and user-friendly for people with disabilities.
The "distributed centrality" approach creates multiple connected urban hubs rather than relying on a single central square, making public spaces safer and more dynamic
.
4. Preservation of Cultural Heritage and Community Engagement
The initiative protects local cultural identity by restoring historic buildings and promoting community-driven cultural activities, such as heritage festivals and artistic installations.
It fosters collective memory and social cohesion, strengthening citizens' connection to their urban environment
.
The next steps planned for further development and implementation of the initiative are:
• Impact monitoring to evaluate space usage, quality of life, and social interaction in regenerated areas.
• Organization of cultural events and outdoor activities, such as "cinema under the stars" and street exhibitions
• Continuous project updates based on community feedback and emerging needs.
• Involvement of local and European partners for future implementations and potential international funding opportunities.
• Impact monitoring to evaluate space usage, quality of life, and social interaction in regenerated areas.
• Organization of cultural events and outdoor activities, such as "cinema under the stars" and street exhibitions
• Continuous project updates based on community feedback and emerging needs.
• Involvement of local and European partners for future implementations and potential international funding opportunities.