Shaping a circular industrial ecosystem and supporting life-cycle thinking
AI for NEB Facades
AI Suggestions for Facades Based on New European Bauhaus Self Assesment Tool
Our project tackles the challenges of sustainability, inclusiveness, and aesthetics in the built environment through a platform inspired by the European Bauhaus initiative (NEB). With an annual funding pool of €120 million, this initiative motivates us, as designers, to create environmentally responsible and socially inclusive designs. Our platform bridges the gap between complex NEB guidelines and practical implementation, offering tools that simplify self-assessment and streamline access to fu
Spain
National
Mainly urban
It refers to other types of transformations (soft investment)
Prototype level
No
No
As an individual partnership with other persons/organisation(s)
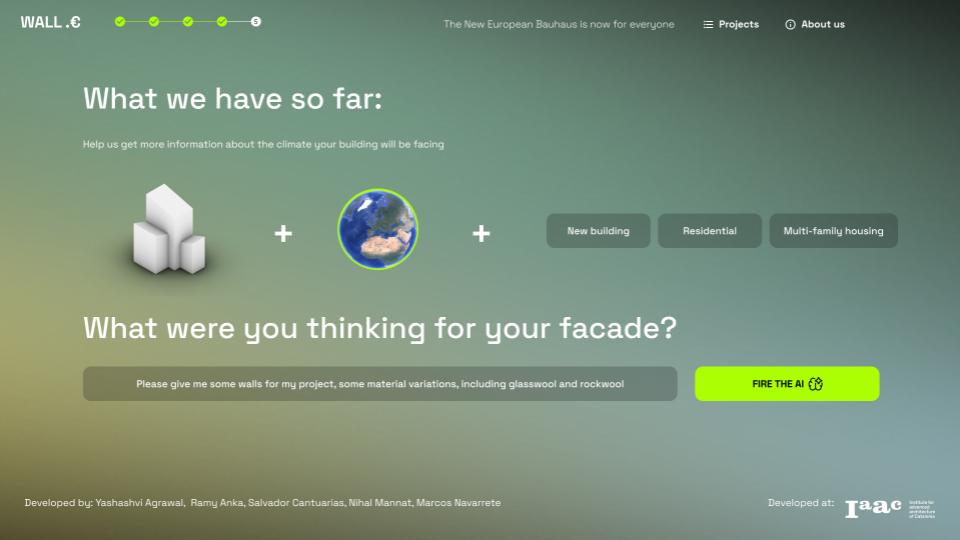
AI Suggestions for Façades Based on Environmental Guidelines is an online platform that helps architects design sustainable facades by providing data-driven material recommendations. Developed at IAAC’s Master in AI for Architecture and the Built Environment, the tool translates New European Bauhaus (NEB) guidelines into a machine-readable format, allowing architects to align projects with sustainability goals.
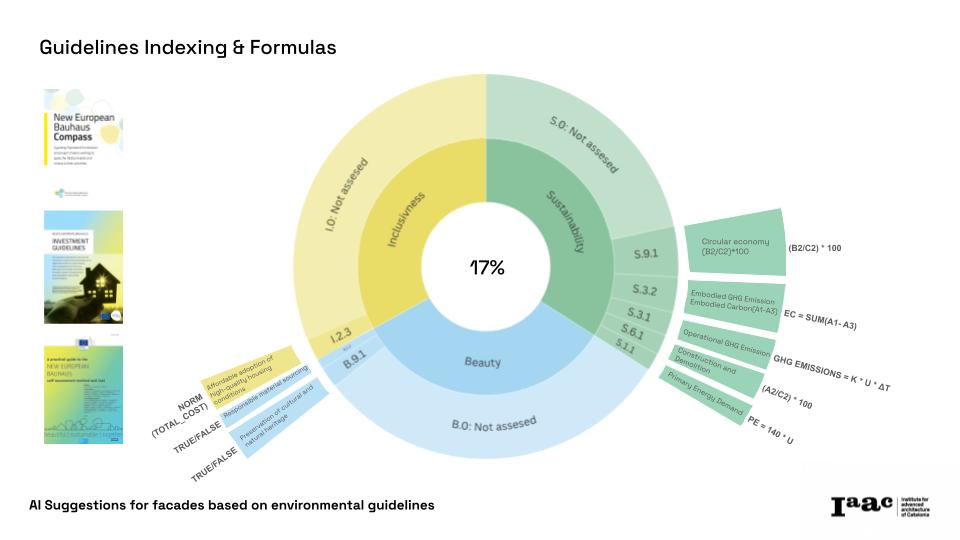
By focusing on façade design—responsible for 17% of NEB’s sustainability impact—the platform optimizes carbon reduction, material efficiency, and energy performance in early design phases, where impact is greatest. It integrates detailed material datasets, including those from the Building Transparency Organization, and employs an advanced graph database to establish semantic relationships between materials, performance metrics, and design criteria.
Using generative AI, the system translates natural language queries into actionable recommendations, helping architects evaluate embodied carbon, thermal insulation, and cost optimization while keeping final design decisions in human hands.
The user-friendly interface ensures accessibility for a broad range of users, from large firms to independent architects. It supports both new constructions and retrofits, addressing sustainable urban development and improving the existing built fabric.
Future plans include integrating real-world industry datasets and advancing AI models to enhance material selection and sustainability analyses. By democratizing access to sustainability tools, the project empowers designers to implement eco-conscious solutions, setting a new benchmark for sustainable architecture.
By focusing on façade design—responsible for 17% of NEB’s sustainability impact—the platform optimizes carbon reduction, material efficiency, and energy performance in early design phases, where impact is greatest. It integrates detailed material datasets, including those from the Building Transparency Organization, and employs an advanced graph database to establish semantic relationships between materials, performance metrics, and design criteria.
Using generative AI, the system translates natural language queries into actionable recommendations, helping architects evaluate embodied carbon, thermal insulation, and cost optimization while keeping final design decisions in human hands.
The user-friendly interface ensures accessibility for a broad range of users, from large firms to independent architects. It supports both new constructions and retrofits, addressing sustainable urban development and improving the existing built fabric.
Future plans include integrating real-world industry datasets and advancing AI models to enhance material selection and sustainability analyses. By democratizing access to sustainability tools, the project empowers designers to implement eco-conscious solutions, setting a new benchmark for sustainable architecture.
NEB Self-assessment Tool
Generative Artificial Intelligence
Façade Optimization
Life Cycle Analysis
Decarbonization
Our project is a product research initiative within academia, specifically in a Master’s program in Artificial Intelligence for Architecture and the Built Environment. "AI Suggestions for Facades Based on Environmental Guidelines" is a transformative tool aimed at embedding sustainability into architectural design from the outset. By focusing on façades—key components responsible for 17% of the NEB sustainability impact—we address carbon reduction, energy efficiency, and material sustainability. Using advanced AI, our platform transforms complex NEB guidelines into accessible and actionable insights for designers.
We integrate robust datasets, including material performance data from the Building Transparency Organization, to help users evaluate materials based on embodied carbon, recyclability, and durability. By offering AI-driven recommendations, designers can make informed decisions aligned with environmental goals, minimizing resource depletion and carbon emissions.
The platform also promotes life-cycle thinking, encouraging designers to consider long-term environmental impacts during the conceptual phase. Our innovative system bridges the gap between sustainability principles and practical implementation, exemplifying how technology can drive the NEB vision.
Targets regarding sustainability:
For the NEB: To operationalize sustainability by translating guidelines into practical tools, fostering adoption among diverse users.
For designers: To provide an intuitive, efficient system that integrates sustainability into design decisions seamlessly.
For end-users: To live in eco-conscious environments designed with health, comfort, and resource conservation in mind.
We integrate robust datasets, including material performance data from the Building Transparency Organization, to help users evaluate materials based on embodied carbon, recyclability, and durability. By offering AI-driven recommendations, designers can make informed decisions aligned with environmental goals, minimizing resource depletion and carbon emissions.
The platform also promotes life-cycle thinking, encouraging designers to consider long-term environmental impacts during the conceptual phase. Our innovative system bridges the gap between sustainability principles and practical implementation, exemplifying how technology can drive the NEB vision.
Targets regarding sustainability:
For the NEB: To operationalize sustainability by translating guidelines into practical tools, fostering adoption among diverse users.
For designers: To provide an intuitive, efficient system that integrates sustainability into design decisions seamlessly.
For end-users: To live in eco-conscious environments designed with health, comfort, and resource conservation in mind.
Our project differentiates between the overall platform and the AI-powered façade tool.
The project aligns with the New European Bauhaus aesthetic principles—welcoming, colorful, and vibrant. It bridges the gap between untrained designers and complex sustainability tools like Life Cycle Analysis (LCA) and AI-powered façade design.
By adopting a futuristic yet accessible UX/UI design, the platform offers intuitive user guidance through simple steps and AI-driven suggestions, demonstrating complex environmental concepts in an easy-to-understand format.
While aesthetics are not the primary focus of the AI tool, it empowers designers to make sustainable choices without compromising their creative vision. The tool evaluates key NEB criteria, such as:
Responsible Material Sourcing (B.2.2)
Preservation of Cultural & Natural Heritage (B.9.1)
Using generative AI, the system provides tailored suggestions for façade designs that balance:
Embodied Carbon - Aesthetic Considerations - Thermal Insulation - Cost Efficiency. Designers retain full creative control while simplifying compliance with NEB guidelines.
The tool supports both new construction and renovation projects, recognizing the importance of retrofitting Europe’s existing building stock while aligning with emerging sustainable aesthetic trends.
Targets regarding aesthetics:
For the NEB Team: To demonstrate that aesthetic design and sustainability can coexist within AI-driven NEB self-assessment tools.
For Designers: To inspire creativity and sustainability through an accessible, user-friendly AI system, available to all designers, regardless of expertise.
The project aligns with the New European Bauhaus aesthetic principles—welcoming, colorful, and vibrant. It bridges the gap between untrained designers and complex sustainability tools like Life Cycle Analysis (LCA) and AI-powered façade design.
By adopting a futuristic yet accessible UX/UI design, the platform offers intuitive user guidance through simple steps and AI-driven suggestions, demonstrating complex environmental concepts in an easy-to-understand format.
While aesthetics are not the primary focus of the AI tool, it empowers designers to make sustainable choices without compromising their creative vision. The tool evaluates key NEB criteria, such as:
Responsible Material Sourcing (B.2.2)
Preservation of Cultural & Natural Heritage (B.9.1)
Using generative AI, the system provides tailored suggestions for façade designs that balance:
Embodied Carbon - Aesthetic Considerations - Thermal Insulation - Cost Efficiency. Designers retain full creative control while simplifying compliance with NEB guidelines.
The tool supports both new construction and renovation projects, recognizing the importance of retrofitting Europe’s existing building stock while aligning with emerging sustainable aesthetic trends.
Targets regarding aesthetics:
For the NEB Team: To demonstrate that aesthetic design and sustainability can coexist within AI-driven NEB self-assessment tools.
For Designers: To inspire creativity and sustainability through an accessible, user-friendly AI system, available to all designers, regardless of expertise.
We differentiate between the complete project and the AI Suggestions tool for Facades. We consider our project inclusive because its main goal is to make Life Cycle Analysis easier and democratize it for all kinds of users—not just large firms with the resources to invest in consultation services. By generating a suggestions tool based on the New European Bauhaus, we aim to cover all European countries while also developing a methodology that can be applied globally and to any kind of project.
The façade approach is the quickest way to achieve significant impact on building-embodied carbon and sustainability implications in the early design phase, ensuring that it does not result in unnecessary time or resource investments, which might discourage small practices from using it.
The Façade Designing Tool specifically promotes the affordable adoption of high-quality housing conditions (I.2.3). If we can suggest façades that follow NEB guidelines while remaining affordable and accessible, we will be actively advancing inclusivity.
Inclusivity underpins our project’s design and application. By transforming complex NEB guidelines into user-friendly tools, we democratize access to sustainable design knowledge, ensuring that designers at all levels—from large firms to independent practitioners—can seamlessly adopt sustainable practices.
Our platform prioritizes affordability, making cutting-edge tools accessible to smaller firms and underserved communities.
Targets regarding inclusion:
For the NEB: To bridge the gap between complex sustainability regulations and practical, accessible design solutions, empowering diverse designers to create NEB-guided designs.
For Designers: To simplify the adoption of inclusive practices while ensuring affordability, giving all designers equal opportunities.
The façade approach is the quickest way to achieve significant impact on building-embodied carbon and sustainability implications in the early design phase, ensuring that it does not result in unnecessary time or resource investments, which might discourage small practices from using it.
The Façade Designing Tool specifically promotes the affordable adoption of high-quality housing conditions (I.2.3). If we can suggest façades that follow NEB guidelines while remaining affordable and accessible, we will be actively advancing inclusivity.
Inclusivity underpins our project’s design and application. By transforming complex NEB guidelines into user-friendly tools, we democratize access to sustainable design knowledge, ensuring that designers at all levels—from large firms to independent practitioners—can seamlessly adopt sustainable practices.
Our platform prioritizes affordability, making cutting-edge tools accessible to smaller firms and underserved communities.
Targets regarding inclusion:
For the NEB: To bridge the gap between complex sustainability regulations and practical, accessible design solutions, empowering diverse designers to create NEB-guided designs.
For Designers: To simplify the adoption of inclusive practices while ensuring affordability, giving all designers equal opportunities.
Our approach to designing this tool involved research among architectural façade designers and users of Life Cycle Analysis (LCA) software, applying product design methods, including User Experience (UX) and User Interface (UI) design. This ensures the tool is accessible to all users, not just sustainability experts.
Although co-design does not apply in the same way to this kind of platform/product design, the aim was to include multiple different views and experts in the development.
While our primary audience is designers, citizens indirectly benefit from the improved architectural outcomes. Our platform enhances sustainability and decarbonization in the built environment, positively impacting communities and advocating for architects’ roles in driving industry-wide change.
Through our user-centered design approach, we aim to bridge the gap between sustainability regulations and their practical application, ensuring that environmental principles become a standard part of the design process. By providing intuitive AI-driven suggestions, we empower architects and designers to make informed decisions that lead to more sustainable, inclusive, and aesthetically pleasing urban environments.
Although co-design does not apply in the same way to this kind of platform/product design, the aim was to include multiple different views and experts in the development.
While our primary audience is designers, citizens indirectly benefit from the improved architectural outcomes. Our platform enhances sustainability and decarbonization in the built environment, positively impacting communities and advocating for architects’ roles in driving industry-wide change.
Through our user-centered design approach, we aim to bridge the gap between sustainability regulations and their practical application, ensuring that environmental principles become a standard part of the design process. By providing intuitive AI-driven suggestions, we empower architects and designers to make informed decisions that lead to more sustainable, inclusive, and aesthetically pleasing urban environments.
Our project development tried to involve stakeholders across local, regional, national, and European levels, ensuring holistic engagement and multidisciplinary collaboration:
Local: Architects and urban planners who would use our tool to address specific projects and respond to community needs.
Regional and national: The Institute for Advanced Architecture of Catalonia plays a key role as an innovation hub, integrating sustainability in Spain’s architectural landscape, the institution collaborate with sustainability bodies, municipalities and festivals in all scales, and have several project related to NEB initiatives.
European: By aligning with NEB principles, we engage with EU policymakers and funding bodies, demonstrating our commitment to NEB objectives. We actively follow NEB Self-Assessment Tool and NEB Checklist developments, analyzing its weaknesses to enhance our platform. The ultimate goal would be to include the platform capabilities inside whatever New European Bauhaus considered suitable.
This multi-tiered engagement enriches our tool’s capabilities, ensuring that it remains dynamic, responsive, and adaptable to evolving sustainability guidelines. The tool’s knowledge graph database is specifically designed to accommodate the ever-changing nature of NEB guidelines, enabling continuous refinement.
Local: Architects and urban planners who would use our tool to address specific projects and respond to community needs.
Regional and national: The Institute for Advanced Architecture of Catalonia plays a key role as an innovation hub, integrating sustainability in Spain’s architectural landscape, the institution collaborate with sustainability bodies, municipalities and festivals in all scales, and have several project related to NEB initiatives.
European: By aligning with NEB principles, we engage with EU policymakers and funding bodies, demonstrating our commitment to NEB objectives. We actively follow NEB Self-Assessment Tool and NEB Checklist developments, analyzing its weaknesses to enhance our platform. The ultimate goal would be to include the platform capabilities inside whatever New European Bauhaus considered suitable.
This multi-tiered engagement enriches our tool’s capabilities, ensuring that it remains dynamic, responsive, and adaptable to evolving sustainability guidelines. The tool’s knowledge graph database is specifically designed to accommodate the ever-changing nature of NEB guidelines, enabling continuous refinement.
Our project integrates expertise across multiple disciplines, ensuring a comprehensive and innovative approach:
Architecture & Façade Design – Defines the structural and aesthetic aspects of sustainable building envelopes.
Sustainability & Environmental Science – Provides data-driven insights for carbon reduction, material efficiency, and life cycle analysis.
Artificial Intelligence & Data Science – Powers the AI-driven recommendation system and knowledge graph database.
Policy & Regulatory Frameworks – Aligns the tool with European sustainability regulations and ensures compliance with NEB guidelines.
This multidisciplinary collaboration was fostered through frequent cross-disciplinary workshops, allowing experts to exchange knowledge and refine the tool’s functionality. The diversity of perspectives enhanced innovation, usability, and real-world applicability, ensuring our platform could reach both technically robust and practically relevant.
Architecture & Façade Design – Defines the structural and aesthetic aspects of sustainable building envelopes.
Sustainability & Environmental Science – Provides data-driven insights for carbon reduction, material efficiency, and life cycle analysis.
Artificial Intelligence & Data Science – Powers the AI-driven recommendation system and knowledge graph database.
Policy & Regulatory Frameworks – Aligns the tool with European sustainability regulations and ensures compliance with NEB guidelines.
This multidisciplinary collaboration was fostered through frequent cross-disciplinary workshops, allowing experts to exchange knowledge and refine the tool’s functionality. The diversity of perspectives enhanced innovation, usability, and real-world applicability, ensuring our platform could reach both technically robust and practically relevant.
The first differential value of our project is that it is digital, is not located or based anywhere and can be applicable everywhere and with changes in the materials database it can be as local as a real built project. The project is a tool. Unlike traditional tools, which require manual interpretation of sustainability guidelines, our platform revolutionizes the process through AI-driven automation. This:
Saves time, reducing manual work and increasing efficiency.
Minimizes errors, ensuring greater compliance with sustainability principles.
Enhances design outcomes, offering data-backed, optimized suggestions.
Our literature review highlights that existing LCA software is often disconnected from European design guidelines, slow, and expensive due to its reliance on traditional calculations. Our platform overcomes these limitations by applying Artificial Intelligence methods and algorithms, offering a faster, more adaptive solution.
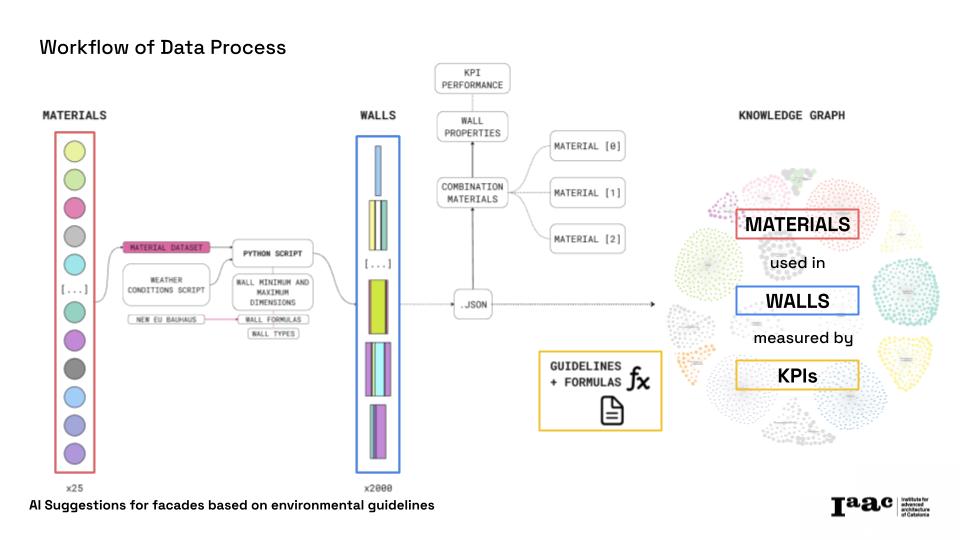
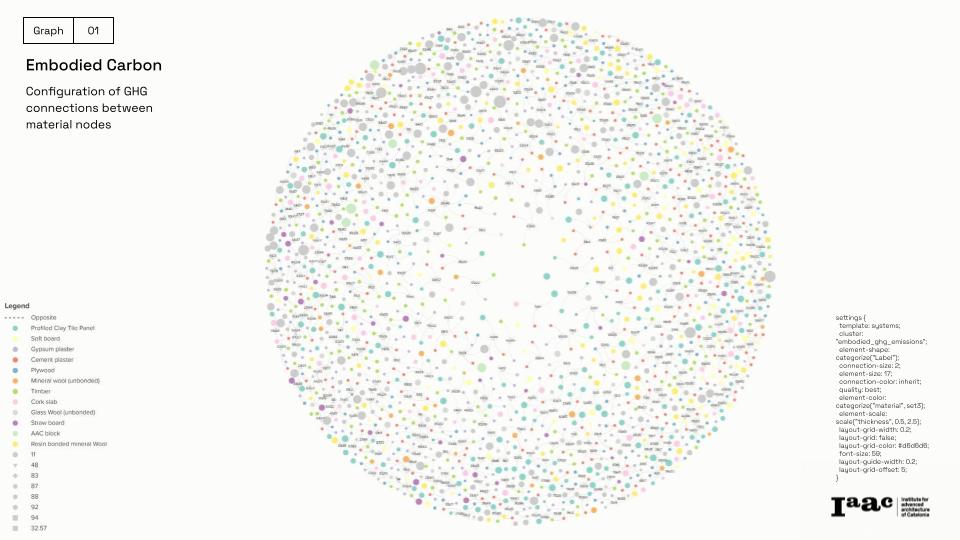
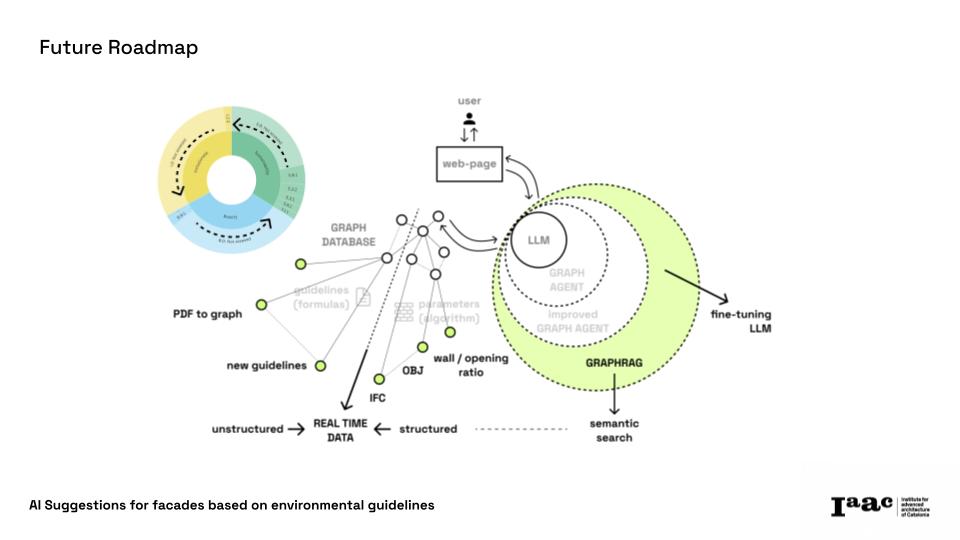
The implementation of a Graph-RAG Model introduces a new way of processing and structuring sustainability knowledge and mix it with the inclusion and aesthetics KPIs. Using Neo4j for knowledge graph modeling, our tool can efficiently analyze complex regulations. Additionally, Large Language Models (LLMs) provide cutting-edge capabilities, making sustainability compliance more intuitive and powerful. The platform can be imagined as a private Chat Gpt-like expert on facades following NEB self-assessment tool.
By leveraging these new technological approaches, our project establishes a new standard in sustainable architecture, making NEB-compliant façade design accessible to all designers, regardless of their expertise in sustainability.
Saves time, reducing manual work and increasing efficiency.
Minimizes errors, ensuring greater compliance with sustainability principles.
Enhances design outcomes, offering data-backed, optimized suggestions.
Our literature review highlights that existing LCA software is often disconnected from European design guidelines, slow, and expensive due to its reliance on traditional calculations. Our platform overcomes these limitations by applying Artificial Intelligence methods and algorithms, offering a faster, more adaptive solution.
The implementation of a Graph-RAG Model introduces a new way of processing and structuring sustainability knowledge and mix it with the inclusion and aesthetics KPIs. Using Neo4j for knowledge graph modeling, our tool can efficiently analyze complex regulations. Additionally, Large Language Models (LLMs) provide cutting-edge capabilities, making sustainability compliance more intuitive and powerful. The platform can be imagined as a private Chat Gpt-like expert on facades following NEB self-assessment tool.
By leveraging these new technological approaches, our project establishes a new standard in sustainable architecture, making NEB-compliant façade design accessible to all designers, regardless of their expertise in sustainability.
Our project, AI Suggestions for Façades Based on Environmental Guidelines, helps architects make informed, sustainable design choices using a data-driven approach. By combining computational design, machine learning, and knowledge graphs, we optimize façade materials early in the design process, where carbon reduction has the most significant impact. Our methodology follows three structured phases:
1) AI Integration & Data Curation
We developed a comprehensive dataset integrating structured and unstructured sources:
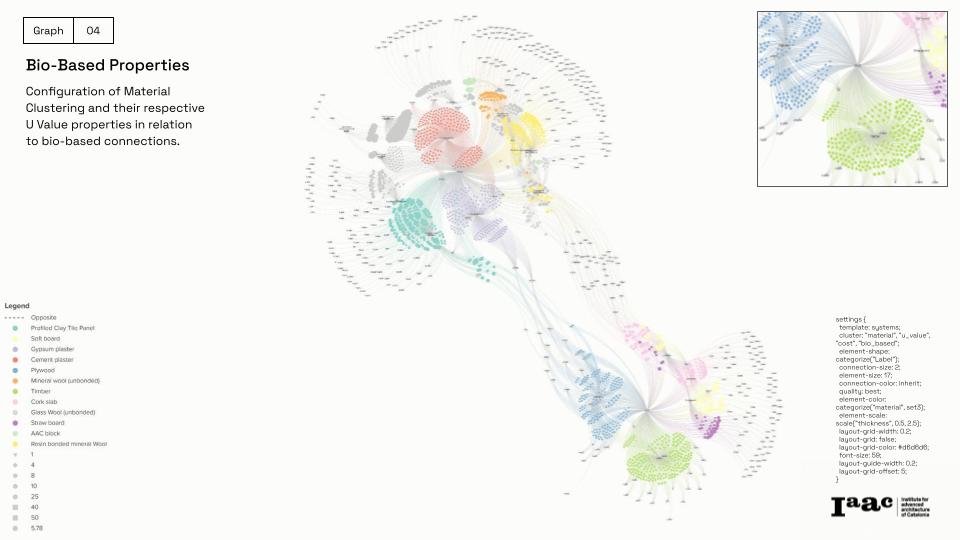
Material Data: Over 27 materials from European Bauhaus guidelines and the Building Transparency Organization, including embodied carbon, insulation, and cost.
NEB Guidelines: Sustainability principles converted into quantitative KPIs for material evaluation.
AI-Powered Analysis: A Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) model assesses façade components and recommends optimized wall assemblies.
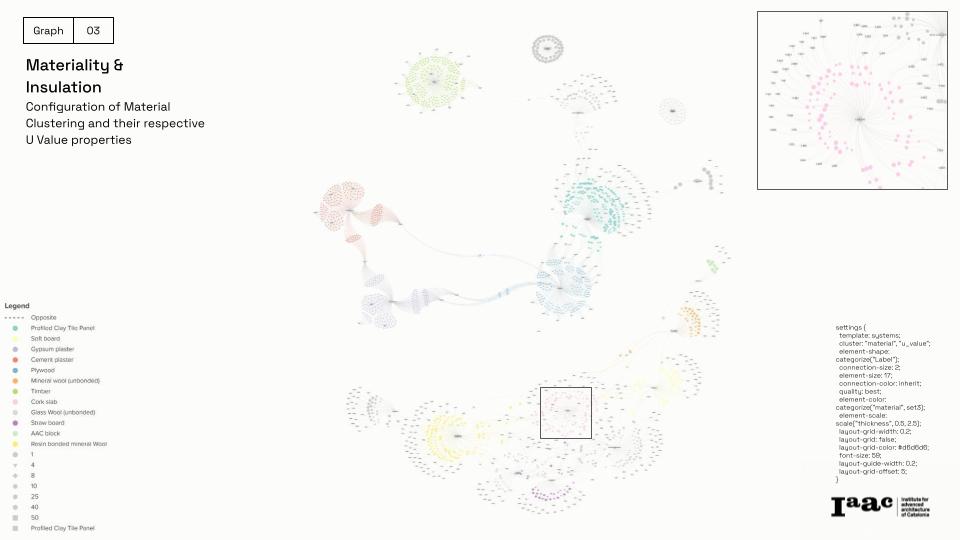
2) Knowledge Graph Development & Performance Scoring
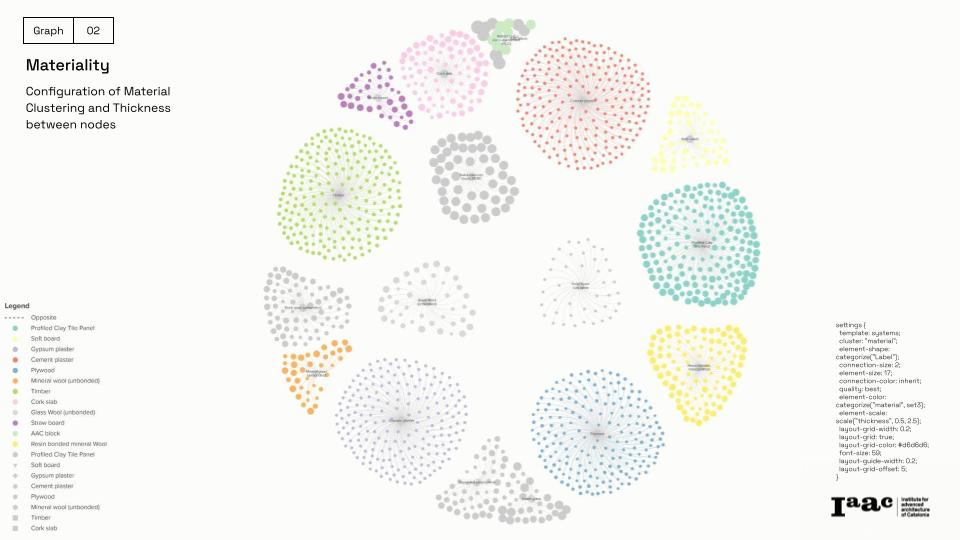
To establish relationships between materials and sustainability factors, we use a graph database with:
Graph-Based Data Modeling: Materials categorized in Neo4J by carbon footprint, thermal resistance, and origin.
Semantic Search & KPI Integration: Intelligent ranking of façade configurations based on performance metrics.
Automated KPI Calculation: A Python-based script generates wall compositions and evaluates energy efficiency and embodied carbon.
3) AI-Powered Query System & User Interface
A user-friendly chatbot translates natural language queries into Cypher searches, making material selection intuitive.
User Workflow:
-3D Model & Location Input: Users upload a façade model and integrate real-time weather data.
-Building Typology & Wall Selection: AI suggests optimized walls based on design style and technology.
-Performance Evaluation: Each wall section receives a KPI score aligned with NEB guidelines.
-AI Querying: Users define design constraints.
1) AI Integration & Data Curation
We developed a comprehensive dataset integrating structured and unstructured sources:
Material Data: Over 27 materials from European Bauhaus guidelines and the Building Transparency Organization, including embodied carbon, insulation, and cost.
NEB Guidelines: Sustainability principles converted into quantitative KPIs for material evaluation.
AI-Powered Analysis: A Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) model assesses façade components and recommends optimized wall assemblies.
2) Knowledge Graph Development & Performance Scoring
To establish relationships between materials and sustainability factors, we use a graph database with:
Graph-Based Data Modeling: Materials categorized in Neo4J by carbon footprint, thermal resistance, and origin.
Semantic Search & KPI Integration: Intelligent ranking of façade configurations based on performance metrics.
Automated KPI Calculation: A Python-based script generates wall compositions and evaluates energy efficiency and embodied carbon.
3) AI-Powered Query System & User Interface
A user-friendly chatbot translates natural language queries into Cypher searches, making material selection intuitive.
User Workflow:
-3D Model & Location Input: Users upload a façade model and integrate real-time weather data.
-Building Typology & Wall Selection: AI suggests optimized walls based on design style and technology.
-Performance Evaluation: Each wall section receives a KPI score aligned with NEB guidelines.
-AI Querying: Users define design constraints.
Our project is designed for maximum transferability and replicability, ensuring that sustainable design tools are accessible to a wide range of users across different regions and industries. As an open-source, AI-driven research initiative, we aim to democratize Life Cycle Analysis (LCA) and make sustainability assessments available to all designers, eliminating the need for expensive expert consultation.
Key Aspects of Replicability:
Modular AI and Graph-Based Methodology: Our Graph-RAG model can be expanded beyond facade design to other building elements (e.g., structural materials, interiors) or even urban planning and infrastructure projects.
Adaptable to Different Regions: The system can integrate local material datasets to align with different geographical and regulatory contexts, making it applicable across European regions and beyond.
Scalable Across Design Industries: While initially tailored for facade selection, the AI-powered recommendation system can be applied to product design, furniture selection, and industrial design, supporting a broad spectrum of sustainability-focused industries.
User-Friendly and Open Access: The intuitive chatbot interface ensures accessibility for designers with varied expertise levels, from large firms to independent architects.
Key Aspects of Replicability:
Modular AI and Graph-Based Methodology: Our Graph-RAG model can be expanded beyond facade design to other building elements (e.g., structural materials, interiors) or even urban planning and infrastructure projects.
Adaptable to Different Regions: The system can integrate local material datasets to align with different geographical and regulatory contexts, making it applicable across European regions and beyond.
Scalable Across Design Industries: While initially tailored for facade selection, the AI-powered recommendation system can be applied to product design, furniture selection, and industrial design, supporting a broad spectrum of sustainability-focused industries.
User-Friendly and Open Access: The intuitive chatbot interface ensures accessibility for designers with varied expertise levels, from large firms to independent architects.
The Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC) industry is responsible for 39% of global carbon emissions (Source: World Green Building Council). While this is a global issue, research shows that early design decisions have the greatest impact on a project’s decarbonization potential.
Our platform takes a localized approach by focusing on façades, which are critical in both new buildings and renovations. Although our tool does not cover the entire NEB framework, we identified façades as the most effective entry point for achieving carbon reduction, aesthetic improvements, and cost optimization.
Through our AI-powered façade suggestions, we empower designers to:
Optimize material choices to lower embodied carbon.
Enhance energy efficiency through better thermal insulation.
Balance sustainability with aesthetics to maintain design integrity, keeping the decision in the designer’s hand, only giving AI powered suggestions.
Ensure cost-effectiveness, making sustainable solutions more financially viable.
By addressing sustainability at the façade level, we create a scalable solution that can be adapted across diverse architectural projects and local contexts. Our platform contributes to global climate action while respecting regional architectural identities and economic constraints by integrating different materials searched locally.
Our platform takes a localized approach by focusing on façades, which are critical in both new buildings and renovations. Although our tool does not cover the entire NEB framework, we identified façades as the most effective entry point for achieving carbon reduction, aesthetic improvements, and cost optimization.
Through our AI-powered façade suggestions, we empower designers to:
Optimize material choices to lower embodied carbon.
Enhance energy efficiency through better thermal insulation.
Balance sustainability with aesthetics to maintain design integrity, keeping the decision in the designer’s hand, only giving AI powered suggestions.
Ensure cost-effectiveness, making sustainable solutions more financially viable.
By addressing sustainability at the façade level, we create a scalable solution that can be adapted across diverse architectural projects and local contexts. Our platform contributes to global climate action while respecting regional architectural identities and economic constraints by integrating different materials searched locally.
Our year-long development roadmap outlines the transformation of an innovative architectural AI concept into a market-ready solution. The implementation is structured into distinct phases, each representing a critical step in revolutionizing sustainable architectural design.
1: AI Architecture & Knowledge Framework
The first quarter focuses on building the AI's core architecture, including developing advanced algorithms, refining data collection methods, and establishing a structured knowledge framework. The AI is trained on European architectural standards, ensuring compliance with modern design principles and sustainability requirements.
2: User Interface & System Integration
The second quarter shifts to developing the architect’s interface, creating an intuitive, professional-grade platform that seamlessly integrates into existing design workflows. A rigorous testing protocol guarantees system stability and reliability, laying the foundation for real-world adoption.
3: Beta Testing & Industry Collaboration
Quarter three initiates strategic partnerships with leading architectural firms. Through extensive beta testing, we assess system performance in professional settings, gathering real-world feedback to refine features and optimize functionality based on industry needs.
4: Refinement & Market Preparation
The fourth quarter focuses on technical optimization and industry engagement. We conduct performance assessments, implement enhancements, and initiate strategic marketing efforts to establish our presence within the architectural community.
Final Phase: Market Launch & NEB Alignment
The culmination of our development journey occurs with the official market launch. This phase includes targeted partnership initiatives, with an ideal scenario involving collaboration with the New European Bauhaus (NEB) to maximize impact and adoption.
1: AI Architecture & Knowledge Framework
The first quarter focuses on building the AI's core architecture, including developing advanced algorithms, refining data collection methods, and establishing a structured knowledge framework. The AI is trained on European architectural standards, ensuring compliance with modern design principles and sustainability requirements.
2: User Interface & System Integration
The second quarter shifts to developing the architect’s interface, creating an intuitive, professional-grade platform that seamlessly integrates into existing design workflows. A rigorous testing protocol guarantees system stability and reliability, laying the foundation for real-world adoption.
3: Beta Testing & Industry Collaboration
Quarter three initiates strategic partnerships with leading architectural firms. Through extensive beta testing, we assess system performance in professional settings, gathering real-world feedback to refine features and optimize functionality based on industry needs.
4: Refinement & Market Preparation
The fourth quarter focuses on technical optimization and industry engagement. We conduct performance assessments, implement enhancements, and initiate strategic marketing efforts to establish our presence within the architectural community.
Final Phase: Market Launch & NEB Alignment
The culmination of our development journey occurs with the official market launch. This phase includes targeted partnership initiatives, with an ideal scenario involving collaboration with the New European Bauhaus (NEB) to maximize impact and adoption.