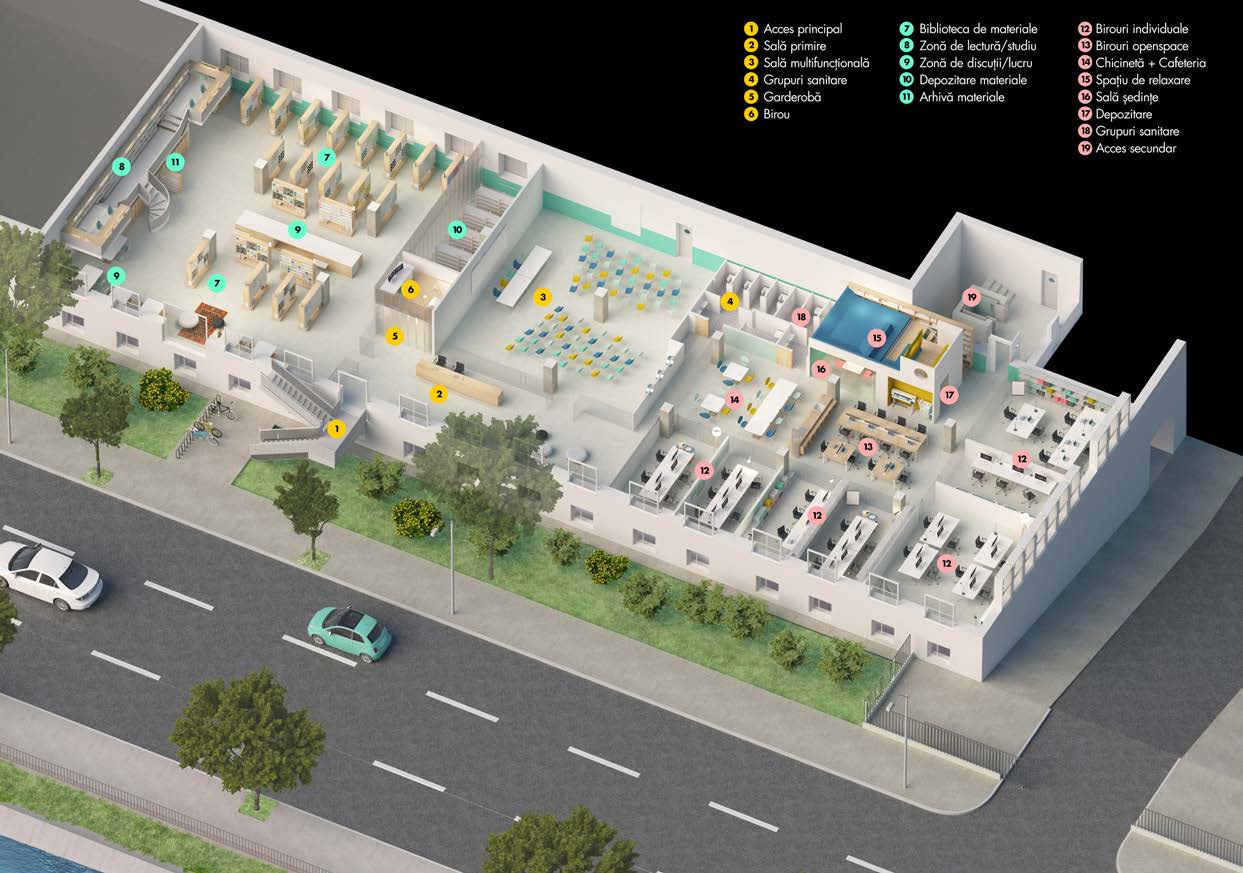
Reconnecting with nature
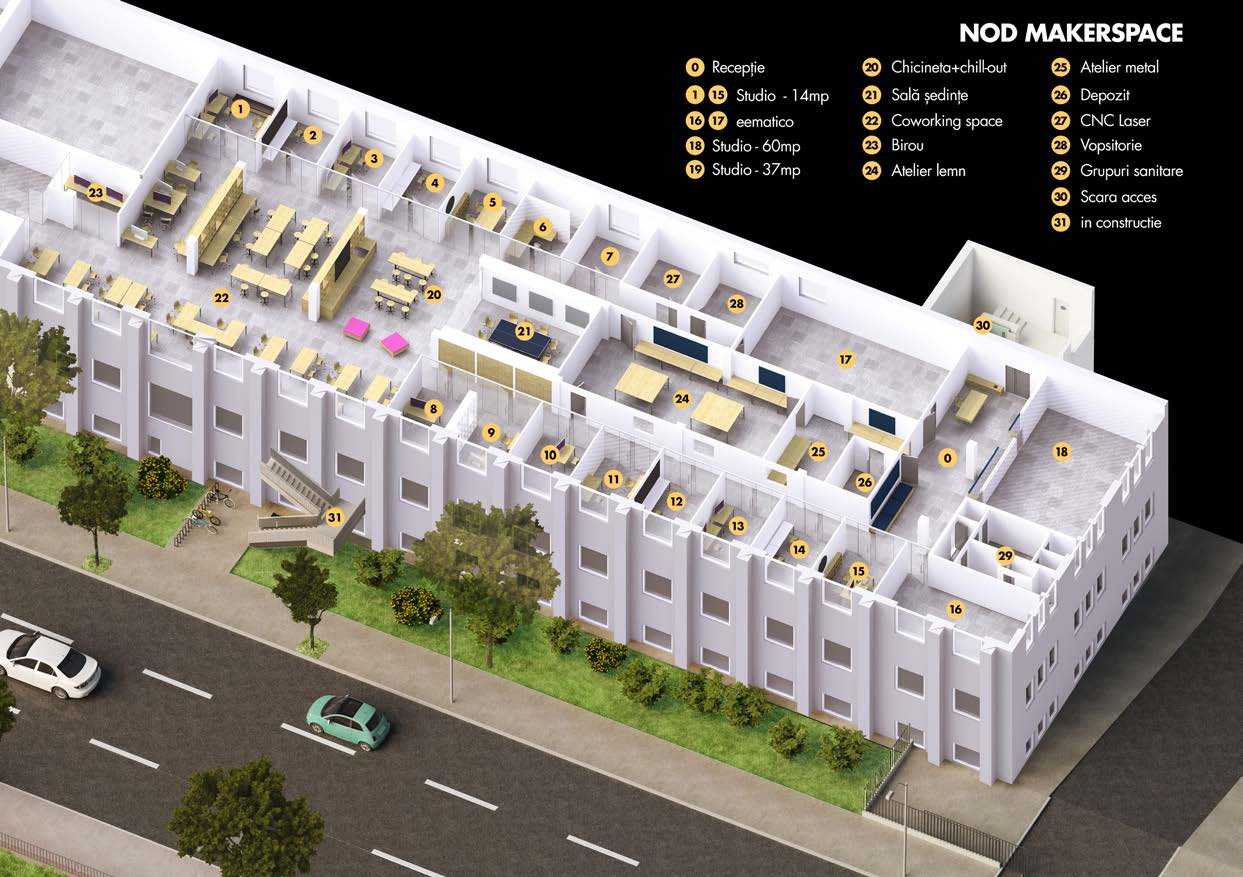
Nod Makerspace
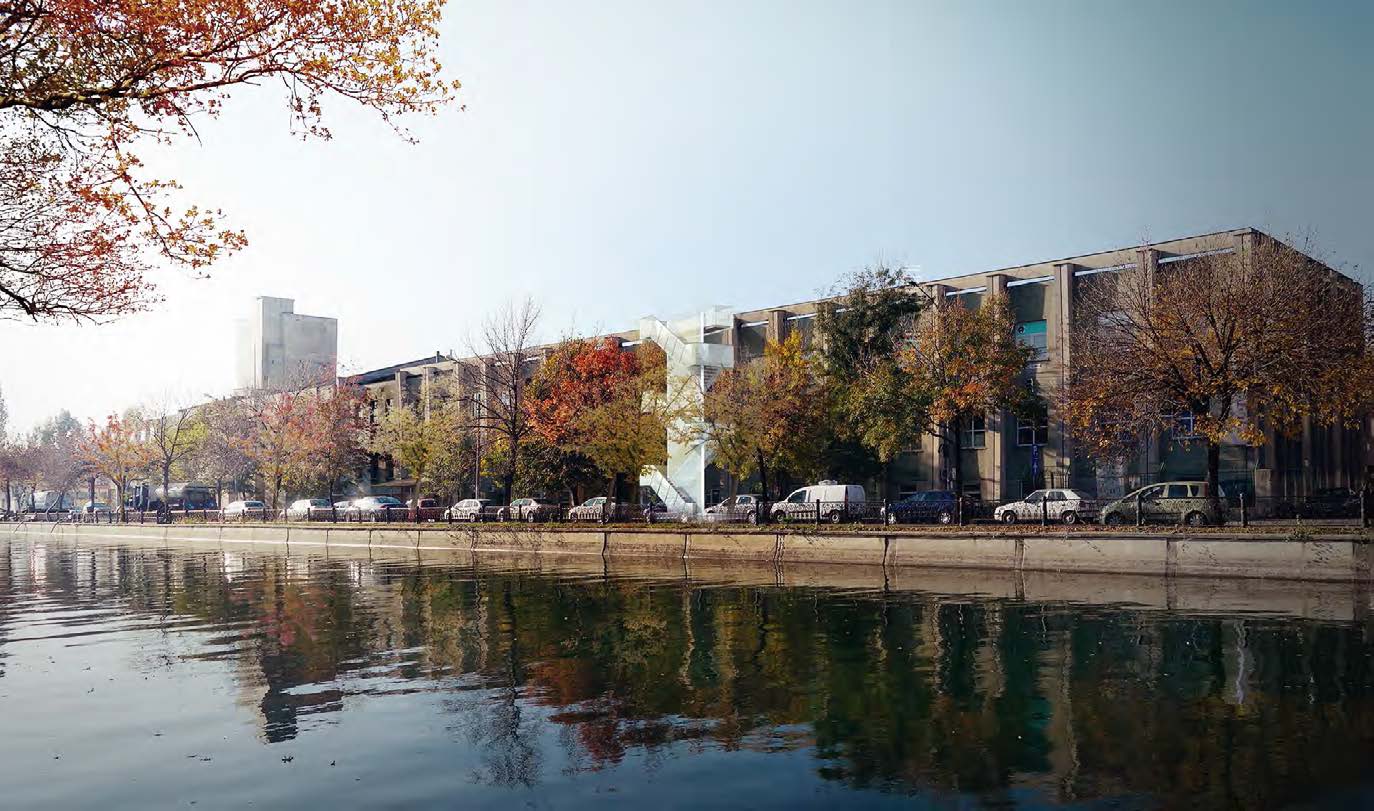
Nod Makerspace – Regenerating Urban Identity Through Creative Collaboration
🚀 Nod Makerspace: Where Creativity Transforms Cities! Housed in a repurposed industrial hall in Bucharest, Nod Makerspace is a thriving hub for designers, makers, innovators, fostering sustainability, inclusion, and urban regeneration. From vocational training for vulnerable communities to reconnecting the city with nature, through hands-on learning, circular design, and collaborative spaces, we empower creatives, students, and entrepreneurs to shape a better future - one prototype at a time! ✨
Romania
Local
Bucharest
Mainly urban
It refers to a physical transformation of the built environment (hard investment)
Yes
2025-01-01
Yes
ERASMUS
No
No
As a representative of an organisation
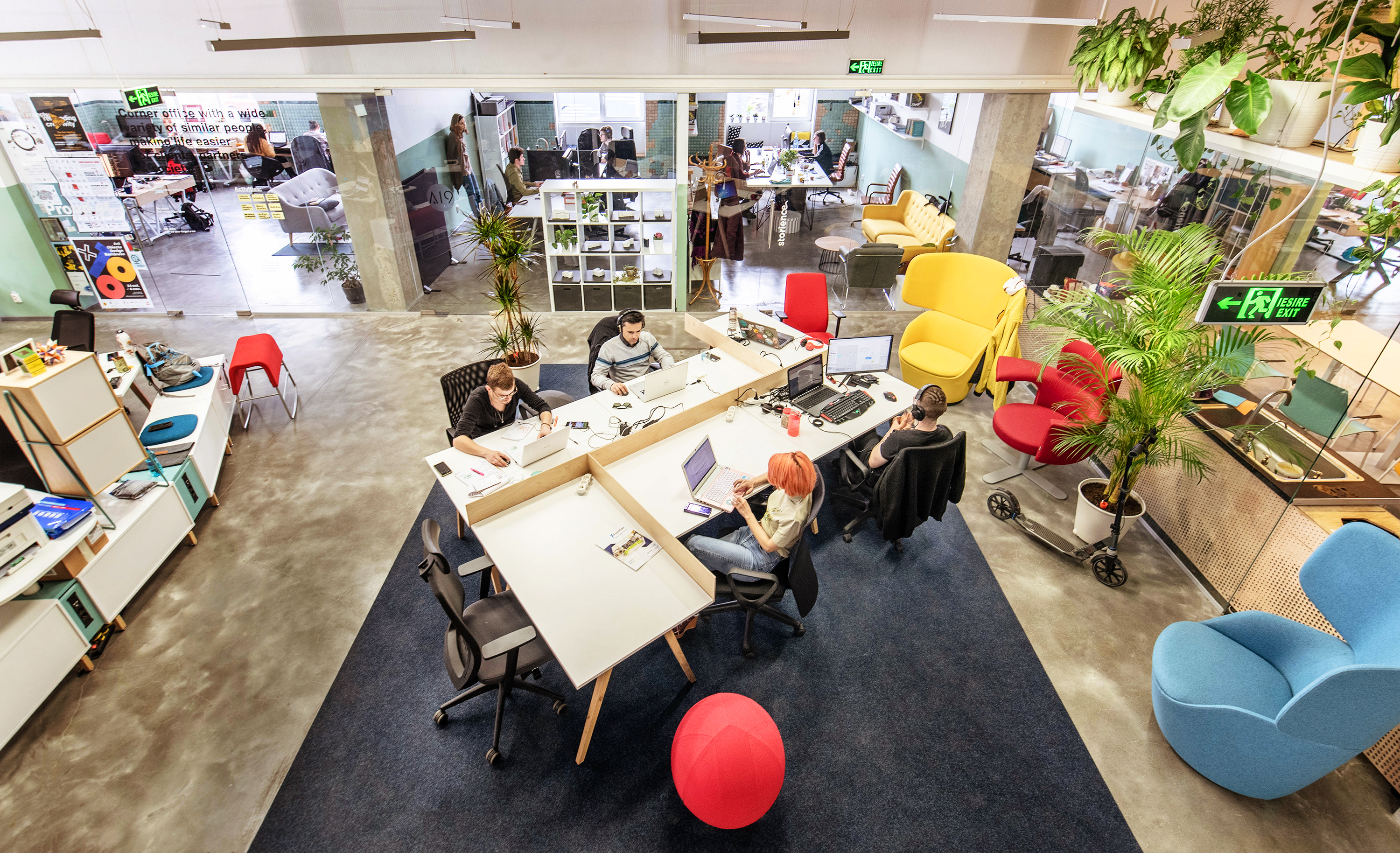
Nod Makerspace is a hybrid cultural-creative hub recognized for catalysing urban regeneration, creative entrepreneurship, &social inclusion. Located in a repurposed 2200sqm industrial hall on the riverside, Nod stands for co-creation, sustainability, and resilience, reconnecting people with their craft, their city, & to each other, reinforcing a sense of belonging in Bucharest’s creative ecosystem.
Target Groups
✅ Creative professionals & entrepreneurs – Designers, architects, makers, and engineers
✅ Students & young professionals – Access to hands-on learning, prototyping tools, mentorship and incubators
✅ Vulnerable groups – Free vocational & digital fab trainings
✅ Local communities & citizens – Public engagement through urban interventions, workshops, and participatory design projects.
Specific Objectives & Achieved Outcomes for its 10th anniversary
1. Adaptive Reuse & Urban Regeneration
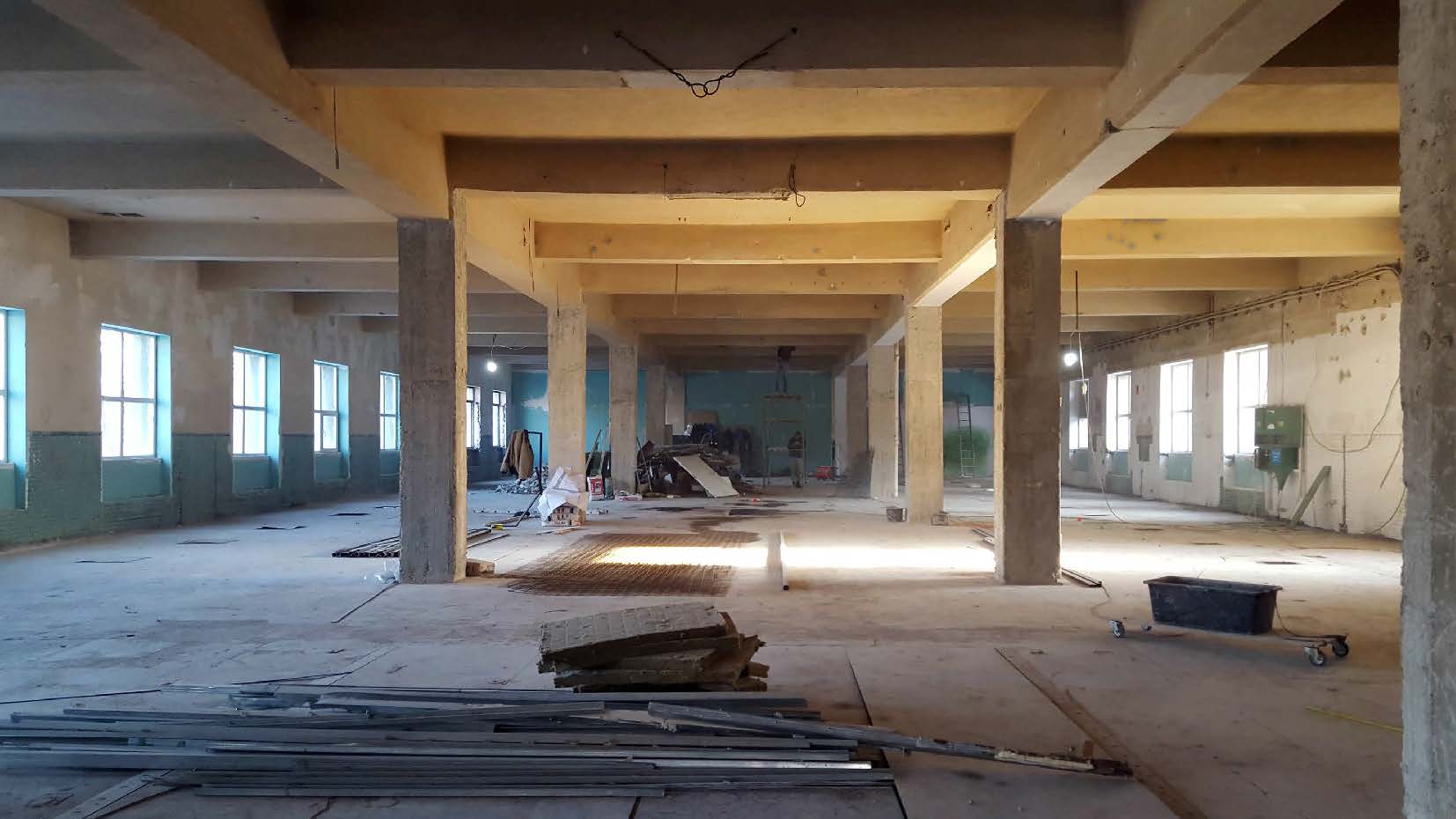
✅ Transformed an abandoned industrial hall into a thriving creative ecosystem, proving the impact of bottom-up urban renewal.
✅ Revitalized public space through Dâmbovița Apă Dulce, engaging 20,000+ citizens in yearly public events, art installations, &environmental activism.
2. Social Inclusion & Skills Development
✅ 350+ individuals trained in 2024 (Solidarity FabLab), equipping Neets with employable technical skills.
✅ 500+ workshops and events, fostering collaboration between disciplines&generations.
✅ 120+ active members hosted by the hub
3. Supporting Innovation & Circular Economy
✅ 40+ creative businesses incubated through Arhitecții Inovării and Consolidate, helping startups thrive.
✅ Expanded the Materials Library, giving access to sustainable materials&circular design solutions.
Thus, Nod Makerspace is a model for repurposing urban spaces into collaborative, people-centered environments. Through adaptive reuse, education, and creativity, Nod strengthens civic engagement, economic resilience, &urban belonging, offering a replicable model for cities
Target Groups
✅ Creative professionals & entrepreneurs – Designers, architects, makers, and engineers
✅ Students & young professionals – Access to hands-on learning, prototyping tools, mentorship and incubators
✅ Vulnerable groups – Free vocational & digital fab trainings
✅ Local communities & citizens – Public engagement through urban interventions, workshops, and participatory design projects.
Specific Objectives & Achieved Outcomes for its 10th anniversary
1. Adaptive Reuse & Urban Regeneration
✅ Transformed an abandoned industrial hall into a thriving creative ecosystem, proving the impact of bottom-up urban renewal.
✅ Revitalized public space through Dâmbovița Apă Dulce, engaging 20,000+ citizens in yearly public events, art installations, &environmental activism.
2. Social Inclusion & Skills Development
✅ 350+ individuals trained in 2024 (Solidarity FabLab), equipping Neets with employable technical skills.
✅ 500+ workshops and events, fostering collaboration between disciplines&generations.
✅ 120+ active members hosted by the hub
3. Supporting Innovation & Circular Economy
✅ 40+ creative businesses incubated through Arhitecții Inovării and Consolidate, helping startups thrive.
✅ Expanded the Materials Library, giving access to sustainable materials&circular design solutions.
Thus, Nod Makerspace is a model for repurposing urban spaces into collaborative, people-centered environments. Through adaptive reuse, education, and creativity, Nod strengthens civic engagement, economic resilience, &urban belonging, offering a replicable model for cities
Aesthetics & Adaptive Reuse – Transforming a former industrial hall into a vibrant cultural hub.
Innovation & Lifelong Learning – Bridging craftsmanship, digital fabrication, and creative entrepreneurship.
Sustainable System – Fostering circular design, resource efficiency, and long-term resilience.
Social Inclusion – Supporting vulnerable communities through education and skill-building.
Urban nature & Community Engagement – Reconnecting people with their environment and the Dâmbovița River, Co-creation, participatory urbanism, and collaborative learning.
Nod Makerspace is built on a sustainable ecosystem model, integrating adaptive reuse, circular design, and responsible resource management to create a lasting impact on the creative industries and urban environment. Key Sustainability Objectives:
✅ 1. Adaptive Reuse & Circular Economy
Nod repurposed a former industrial hall into a thriving creative hub, avoiding demolition and reducing material waste. Through the makerspace, the project promotes resource efficiency. The space is designed for flexibility and longevity, ensuring minimal waste generation and efficient use of shared resources.
✅ 2. Energy Efficiency & Green Practices
The space is equipped with natural lighting, LED lighting, and energy-efficient systems, reducing its carbon footprint. Nod supports sustainable fabrication methods, integrating digital prototyping and precision design to minimize excess material use.
✅ 3. Social Sustainability & Inclusion
Programs like Solidarity FabLab provide free vocational training for vulnerable groups, ensuring economic empowerment and skill-building.
Nod fosters an inclusive ecosystem where young creatives, entrepreneurs, and underserved communities collaborate in an accessible and affordable space.
✅ 4. Reconnecting with Nature
Through Dâmbovița Apă Dulce programme, Nod engages the public in riverfront revitalization, urban gardening, and environmental awareness initiatives.
The hub integrates nature-based design principles, encouraging users to adopt sustainable urban solutions.
Exemplary Impact & Replicability
Nod Makerspace serves as a model for urban regeneration, showing how industrial heritage sites can be transformed into sustainable, participatory, and creative spaces. Its bottom-up development, long-term resilience, and commitment to continuous learning make it an exemplary project in sustainability, adaptable to other cities and underutilized spaces across Europe.
✅ 1. Adaptive Reuse & Circular Economy
Nod repurposed a former industrial hall into a thriving creative hub, avoiding demolition and reducing material waste. Through the makerspace, the project promotes resource efficiency. The space is designed for flexibility and longevity, ensuring minimal waste generation and efficient use of shared resources.
✅ 2. Energy Efficiency & Green Practices
The space is equipped with natural lighting, LED lighting, and energy-efficient systems, reducing its carbon footprint. Nod supports sustainable fabrication methods, integrating digital prototyping and precision design to minimize excess material use.
✅ 3. Social Sustainability & Inclusion
Programs like Solidarity FabLab provide free vocational training for vulnerable groups, ensuring economic empowerment and skill-building.
Nod fosters an inclusive ecosystem where young creatives, entrepreneurs, and underserved communities collaborate in an accessible and affordable space.
✅ 4. Reconnecting with Nature
Through Dâmbovița Apă Dulce programme, Nod engages the public in riverfront revitalization, urban gardening, and environmental awareness initiatives.
The hub integrates nature-based design principles, encouraging users to adopt sustainable urban solutions.
Exemplary Impact & Replicability
Nod Makerspace serves as a model for urban regeneration, showing how industrial heritage sites can be transformed into sustainable, participatory, and creative spaces. Its bottom-up development, long-term resilience, and commitment to continuous learning make it an exemplary project in sustainability, adaptable to other cities and underutilized spaces across Europe.
Nod Makerspace is a living example of how design, culture, and adaptive reuse can transform an underutilized industrial site into a vibrant, inspiring space for creativity and collaboration. By blending functional design, cultural heritage, and community participation, Nod fosters an environment where aesthetics enhance both experience and purpose. Key Aesthetic & Cultural Objectives:
1. Adaptive Reuse & Industrial Heritage Revitalization. Housed in a former cotton factory, Nod preserves architectural authenticity while integrating modern, sustainable interventions. The transformation of the space has been collaborative, with designers, architects, and makers actively shaping its aesthetic identity through a bottom-up approach.
2. Design for Creativity & Well-being. The space is modular and dynamic, fostering interaction and multidisciplinary exchanges. It includes open workspaces, fabrication labs, event areas, and green relaxation zones, ensuring an optimal creative environment.
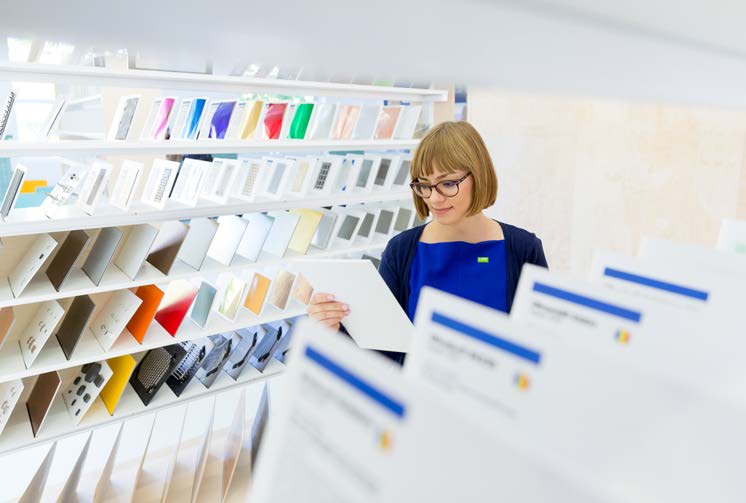
The Materials Library acts as a tactile and visual archive, inspiring through material exploration and experimentation.
3. Cultural Impact & Community Identity. Nod serves as a hub for events, exhibitions, and urban interventions, strengthening the connection between people and place. Programs like Dâmbovița Apă Dulce reconnect the community with the river, using art, design, and participatory projects to reimagine urban spaces.
Through programs such as Solidarity FabLab, the space democratizes access to design and craftsmanship, ensuring that aesthetics are inclusive and meaningful.
Exemplary Impact & Replicability
Nod Makerspace proves that aesthetics go beyond appearance—they shape experiences, emotions, and community identity. By fostering participation, preserving heritage, it is a model for rethinking post-industrial spaces as creative, sustainable, and socially engaging environments. Scalable, adaptable, it offers a blueprint for urban regeneration through culture and design
1. Adaptive Reuse & Industrial Heritage Revitalization. Housed in a former cotton factory, Nod preserves architectural authenticity while integrating modern, sustainable interventions. The transformation of the space has been collaborative, with designers, architects, and makers actively shaping its aesthetic identity through a bottom-up approach.
2. Design for Creativity & Well-being. The space is modular and dynamic, fostering interaction and multidisciplinary exchanges. It includes open workspaces, fabrication labs, event areas, and green relaxation zones, ensuring an optimal creative environment.
The Materials Library acts as a tactile and visual archive, inspiring through material exploration and experimentation.
3. Cultural Impact & Community Identity. Nod serves as a hub for events, exhibitions, and urban interventions, strengthening the connection between people and place. Programs like Dâmbovița Apă Dulce reconnect the community with the river, using art, design, and participatory projects to reimagine urban spaces.
Through programs such as Solidarity FabLab, the space democratizes access to design and craftsmanship, ensuring that aesthetics are inclusive and meaningful.
Exemplary Impact & Replicability
Nod Makerspace proves that aesthetics go beyond appearance—they shape experiences, emotions, and community identity. By fostering participation, preserving heritage, it is a model for rethinking post-industrial spaces as creative, sustainable, and socially engaging environments. Scalable, adaptable, it offers a blueprint for urban regeneration through culture and design
Nod Makerspace is designed as an accessible creative ecosystem, where people from diverse backgrounds, skill levels, and economic means collaborate, learn, and create. By integrating affordability, participatory governance, and design-for-all, Nod fosters a new societal model where creativity&innovation are open to everyone, not just a privileged few. Key Inclusion Objectives:
1. Accessibility & Affordability for All.
Nod operates as an open and flexible workspace, offering affordable access to tools, workshops, and collaborative spaces for students, professionals, and emerging creatives.
The Materials Library offers free access to materials, allowing creators to experiment and innovate.
Through Solidarity FabLab, young people from vulnerable backgrounds receive free vocational training in woodworking, digital fabrication, tailoring, and design, providing real career opportunities.
2. Participatory & Inclusive Governance
Nod was co-designed with its community, allowing members to shape the space, resources, and programming based on their needs.
The hub fosters cross-disciplinary collaboration, connecting designers, engineers, artisans, and entrepreneurs to share knowledge and resources.
3. Design for All: Multigenerational & Multidisciplinary Engagement.
The space includes ergonomic workspaces and universal design principles.
Programs cater to a diverse audience, from students to established professionals, bridging generational and disciplinary gaps.
Initiatives like Dâmbovița Apă Dulce bring communities together in urban co-creation, empowering residents to reclaim public space and foster a shared sense of belonging.
Nod Makerspace demonstrates how affordable access, participatory governance, and design-for-all can empower communities and strengthen social cohesion. By integrating education, entrepreneurship, urban engagement, Nod exemplifies a new, inclusive societal model that can be replicated across cities seeking to democratize innovation&design.
1. Accessibility & Affordability for All.
Nod operates as an open and flexible workspace, offering affordable access to tools, workshops, and collaborative spaces for students, professionals, and emerging creatives.
The Materials Library offers free access to materials, allowing creators to experiment and innovate.
Through Solidarity FabLab, young people from vulnerable backgrounds receive free vocational training in woodworking, digital fabrication, tailoring, and design, providing real career opportunities.
2. Participatory & Inclusive Governance
Nod was co-designed with its community, allowing members to shape the space, resources, and programming based on their needs.
The hub fosters cross-disciplinary collaboration, connecting designers, engineers, artisans, and entrepreneurs to share knowledge and resources.
3. Design for All: Multigenerational & Multidisciplinary Engagement.
The space includes ergonomic workspaces and universal design principles.
Programs cater to a diverse audience, from students to established professionals, bridging generational and disciplinary gaps.
Initiatives like Dâmbovița Apă Dulce bring communities together in urban co-creation, empowering residents to reclaim public space and foster a shared sense of belonging.
Nod Makerspace demonstrates how affordable access, participatory governance, and design-for-all can empower communities and strengthen social cohesion. By integrating education, entrepreneurship, urban engagement, Nod exemplifies a new, inclusive societal model that can be replicated across cities seeking to democratize innovation&design.
Nod Makerspace was built by and for the community, engaging citizens, local creatives, and civil society in every stage—from design and development to governance and programming. This participatory model ensures that Nod reflects real urban needs while fostering a deep sense of ownership and engagement.
1. Co-Creation & Collaborative Space Design
✅ Role: Citizens, makers, and creative professionals co-designed and co-built Nod Makerspace, shaping the space through participatory decision-making and hands-on involvement.
✅ Impact: This bottom-up transformation ensured the space evolved organically, adapting to real user needs and strengthening community belonging.
2. Inclusive Access to Learning & Prototyping Resources
✅ Role: Citizens, students, and young professionals use Nod’s tools, labs, and workshops to develop projects, prototypes, and businesses. Civil society organizations collaborate on educational programs.
✅ Impact: Thousands of individuals have gained technical skills, business support, and access to resources, helping them turn ideas into tangible impact.
3. Social Inclusion Through Free Vocational Programs
✅ Role: Through Solidarity FabLab, civil society and NGOs help NEETs access free training in woodworking, tailoring, engineering, and digital fabrication.
✅ Impact: This has provided concrete career pathways, increasing employment prospects and reducing inequalities.
4. Citizen-Driven Urban Interventions & Public Engagement
✅ Role: Residents participate in Dâmbovița Apă Dulce, co-creating urban activation projects, artistic interventions, and environmental initiatives.
✅ Impact: This has reconnected citizens with the river, strengthened public space activation, and fostered community-led urbanism.
Conclusion
By embedding citizens and civil society in its DNA, Nod Makerspace ensures that its impact is inclusive, responsive, and deeply rooted in community needs—a scalable model for citizen-driven urban transformation.
1. Co-Creation & Collaborative Space Design
✅ Role: Citizens, makers, and creative professionals co-designed and co-built Nod Makerspace, shaping the space through participatory decision-making and hands-on involvement.
✅ Impact: This bottom-up transformation ensured the space evolved organically, adapting to real user needs and strengthening community belonging.
2. Inclusive Access to Learning & Prototyping Resources
✅ Role: Citizens, students, and young professionals use Nod’s tools, labs, and workshops to develop projects, prototypes, and businesses. Civil society organizations collaborate on educational programs.
✅ Impact: Thousands of individuals have gained technical skills, business support, and access to resources, helping them turn ideas into tangible impact.
3. Social Inclusion Through Free Vocational Programs
✅ Role: Through Solidarity FabLab, civil society and NGOs help NEETs access free training in woodworking, tailoring, engineering, and digital fabrication.
✅ Impact: This has provided concrete career pathways, increasing employment prospects and reducing inequalities.
4. Citizen-Driven Urban Interventions & Public Engagement
✅ Role: Residents participate in Dâmbovița Apă Dulce, co-creating urban activation projects, artistic interventions, and environmental initiatives.
✅ Impact: This has reconnected citizens with the river, strengthened public space activation, and fostered community-led urbanism.
Conclusion
By embedding citizens and civil society in its DNA, Nod Makerspace ensures that its impact is inclusive, responsive, and deeply rooted in community needs—a scalable model for citizen-driven urban transformation.
Nod Makerspace thrives through a dynamic, multi-level collaboration involving local communities, local & national institutions, and European funds and networks. This multi-stakeholder approach ensures long-term sustainability, cross-sector innovation, and broad social impact.
1. Local Level: Community & Grassroots Engagement
Role: Local designers, makers, and entrepreneurs co-designed the space, shaping resources, programs, and governance based on their needs.
Impact: This bottom-up transformation fostered community ownership, ensuring sustainability & resilience.
2. Local & National Level: Institutional & Private Sector Partnerships. Role:
Municipal authorities & urban development agencies contribute as stakeholders in Dâmbovița Apă Dulce program.
Universities and technical schools in Bucharest are partners in incubator programs, such as Arhitecții Inovarii and Consolidate.
Private sector partners (e.g., industry leaders, local businesses) contributed to training programs, the materials library, startup incubation and also as stakeholders in Dâmbovița Apă Dulce program. The added Value of these partnerships enabled financial stability, workforce development, and increased accessibility to resources.
3. European Level: Transnational Networks & EU Programs (funding and cross-border knowledge exchange). Role:
Erasmus+ projects enabled adult knowledge exchange&skill transfer.
Innotech Students/Arhitecții Inovării provided grants & incubation for creative entrepreneurs.
International networks (Re:Kreators, the Cooperative CIty, Trans Europe Halle, European Creative Hubs Network, Living spaces) connected Nod to global best practices in urban innovation, adaptive design, and entrepreneurship.
By engaging stakeholders at multiple levels, Nod Makerspace bridges local action with global innovation, making it a scalable model for creative and sustainable urban transformation.
1. Local Level: Community & Grassroots Engagement
Role: Local designers, makers, and entrepreneurs co-designed the space, shaping resources, programs, and governance based on their needs.
Impact: This bottom-up transformation fostered community ownership, ensuring sustainability & resilience.
2. Local & National Level: Institutional & Private Sector Partnerships. Role:
Municipal authorities & urban development agencies contribute as stakeholders in Dâmbovița Apă Dulce program.
Universities and technical schools in Bucharest are partners in incubator programs, such as Arhitecții Inovarii and Consolidate.
Private sector partners (e.g., industry leaders, local businesses) contributed to training programs, the materials library, startup incubation and also as stakeholders in Dâmbovița Apă Dulce program. The added Value of these partnerships enabled financial stability, workforce development, and increased accessibility to resources.
3. European Level: Transnational Networks & EU Programs (funding and cross-border knowledge exchange). Role:
Erasmus+ projects enabled adult knowledge exchange&skill transfer.
Innotech Students/Arhitecții Inovării provided grants & incubation for creative entrepreneurs.
International networks (Re:Kreators, the Cooperative CIty, Trans Europe Halle, European Creative Hubs Network, Living spaces) connected Nod to global best practices in urban innovation, adaptive design, and entrepreneurship.
By engaging stakeholders at multiple levels, Nod Makerspace bridges local action with global innovation, making it a scalable model for creative and sustainable urban transformation.
Nod Makerspace was designed as a multidisciplinary hub, where architecture, design, engineering, and social innovation converge. By integrating diverse expertise and knowledge fields, the hub fosters collaborative problem-solving, cross-sector learning, and innovation-driven urban transformation. Key Knowledge Fields & Disciplines Involved
1. Architecture & Urban Planning
Adaptive reuse – Architects and urban planners led the transformation of an industrial hall into a creative hub, demonstrating how underutilized spaces can be repurposed sustainably.
Public space activation – Projects like Dâmbovița Apă Dulce involved urban designers in reconnecting the community with the city’s riverfront.
2. Design & Material Innovation
Product & industrial designers engaged in circular economy research, creating sustainable material prototypes showcased in the Materials Library.
3. Engineering & Digital Fabrication
Mechanical & software engineers contributed to the development of open-access prototyping tools
The Solidarity FabLab program combined engineering, woodworking, tailoring and digital fabrication to provide hands-on vocational training for underserved communities.
4. Social Sciences & Education
Community organizers developed inclusive governance models, ensuring the space remains accessible, participatory, and community-driven.
Educators and cultural managers designed workshops, incubators, and mentorship programs that empower individuals to develop creative and entrepreneurial skills.
Added Value of the Interdisciplinary Approach
✅ Enhanced problem-solving
✅ Scalability & replicability – By integrating design, engineering, and social innovation, the Nod model can be adapted to other cities.
✅ A holistic creative ecosystem – The interaction between architects, designers, engineers, and educators ensures a dynamic space where knowledge transfer and innovation thrive.
1. Architecture & Urban Planning
Adaptive reuse – Architects and urban planners led the transformation of an industrial hall into a creative hub, demonstrating how underutilized spaces can be repurposed sustainably.
Public space activation – Projects like Dâmbovița Apă Dulce involved urban designers in reconnecting the community with the city’s riverfront.
2. Design & Material Innovation
Product & industrial designers engaged in circular economy research, creating sustainable material prototypes showcased in the Materials Library.
3. Engineering & Digital Fabrication
Mechanical & software engineers contributed to the development of open-access prototyping tools
The Solidarity FabLab program combined engineering, woodworking, tailoring and digital fabrication to provide hands-on vocational training for underserved communities.
4. Social Sciences & Education
Community organizers developed inclusive governance models, ensuring the space remains accessible, participatory, and community-driven.
Educators and cultural managers designed workshops, incubators, and mentorship programs that empower individuals to develop creative and entrepreneurial skills.
Added Value of the Interdisciplinary Approach
✅ Enhanced problem-solving
✅ Scalability & replicability – By integrating design, engineering, and social innovation, the Nod model can be adapted to other cities.
✅ A holistic creative ecosystem – The interaction between architects, designers, engineers, and educators ensures a dynamic space where knowledge transfer and innovation thrive.
Nod Makerspace sets itself apart from mainstream co-working spaces, incubators, or makerspaces through its hybrid, community-driven, and impact-oriented approach. It is more than a workspace—it is a catalyst for sustainable urban transformation, bringing together design, digital fabrication, circular economy, and social inclusion in an ecosystem.
What Makes Nod Innovative?
1. Adaptive Reuse & Self-Built Model
Unlike conventional creative spaces, Nod was co-designed&co-built by its community in a bottom-up transformation of an industrial hall. This collaborative approach to urban regeneration gives ownership to creatives and makers, ensuring long-term sustainability and engagement.
2. Blending Physical & Educational Infrastructure
While most makerspaces focus on either fabrication or co-working, Nod is a hybrid model, combining state-of-the-art prototyping tools, educational programs for skills development (Solidarity FabLab), public engagement initiatives (Dâmbovița Apă Dulce), business incubators for creative entrepreneurs
This ecosystemic approach ensures a holistic, long-term impact, instead of one-time interventions.
3. Circular Design & Material Innovation
Unlike traditional prototyping spaces, through its Materials Library, the first open-source archive of materials for designers in Romania, Nod supports circular economy solutions, connecting designers, researchers, and industry leaders.
4. Social Innovation & Accessibility
Nod Makerspace is actively bridging social and economic gaps by providing free vocational training for vulnerable groups (Solidarity FabLab)
By offering affordable access to tools, space, and expertise, Nod democratizes innovation, making high-quality design and fabrication accessible to a wider audience.
Nod is a scalable model, being both a workshop and a social&environmental innovation hub. Its model challenges the traditional divide between workspace, education, and urban transformation, making it exemplary.
What Makes Nod Innovative?
1. Adaptive Reuse & Self-Built Model
Unlike conventional creative spaces, Nod was co-designed&co-built by its community in a bottom-up transformation of an industrial hall. This collaborative approach to urban regeneration gives ownership to creatives and makers, ensuring long-term sustainability and engagement.
2. Blending Physical & Educational Infrastructure
While most makerspaces focus on either fabrication or co-working, Nod is a hybrid model, combining state-of-the-art prototyping tools, educational programs for skills development (Solidarity FabLab), public engagement initiatives (Dâmbovița Apă Dulce), business incubators for creative entrepreneurs
This ecosystemic approach ensures a holistic, long-term impact, instead of one-time interventions.
3. Circular Design & Material Innovation
Unlike traditional prototyping spaces, through its Materials Library, the first open-source archive of materials for designers in Romania, Nod supports circular economy solutions, connecting designers, researchers, and industry leaders.
4. Social Innovation & Accessibility
Nod Makerspace is actively bridging social and economic gaps by providing free vocational training for vulnerable groups (Solidarity FabLab)
By offering affordable access to tools, space, and expertise, Nod democratizes innovation, making high-quality design and fabrication accessible to a wider audience.
Nod is a scalable model, being both a workshop and a social&environmental innovation hub. Its model challenges the traditional divide between workspace, education, and urban transformation, making it exemplary.
Nod Makerspace was built on a flexible, participatory, interdisciplinary, and adaptive methodology. Unlike traditional makerspaces or co-working hubs, Nod integrates urban regeneration, hands-on education, and creative entrepreneurship, being now a resilient ecosystem.
Key Methodological Pillars:
1. Bottom-Up, Participatory Development. Nod was co-designed and co-built by its community, following an iterative prototyping approach over several years. The space was transformed gradually, using limited resources and collaborative efforts, proving that high-impact projects can emerge from grassroots initiatives. This approach ensures long-term community engagement, giving users a sense of ownership and responsibility.
2. Interdisciplinary & Ecosystem-Based Thinking. Nod integrates expertise from architecture, design, engineering, social sciences, and entrepreneurship, fostering cross-sector collaboration. Programs like Solidarity FabLab combine technical training with social inclusion, offering vocational education to NEETs
3. Experimental & Scalable Model
Nod operates as a living lab, where new ideas, tools, and business models are tested and refined in real-world conditions.
By incubating creative businesses&social enterprises, Nod provides a pathway from learning to entrepreneurship, ensuring sustainability beyond grants or funding cycles.
4. Community-Centered Urban Impact
Nod fosters collaborative urban interventions, such as Dâmbovița Apă Dulce, reconnecting people with their city through design, public events, and participatory urbanism.
Open workshops, hackathons, and mentorship programs ensure that knowledge and resources are accessible to all, strengthening inclusivity and civic engagement.
By blending adaptive reuse, circular design, and social innovation, Nod offers a scalable model for creative hubs worldwide, redefining how cities can foster creative, sustainable, and inclusive communities.
Key Methodological Pillars:
1. Bottom-Up, Participatory Development. Nod was co-designed and co-built by its community, following an iterative prototyping approach over several years. The space was transformed gradually, using limited resources and collaborative efforts, proving that high-impact projects can emerge from grassroots initiatives. This approach ensures long-term community engagement, giving users a sense of ownership and responsibility.
2. Interdisciplinary & Ecosystem-Based Thinking. Nod integrates expertise from architecture, design, engineering, social sciences, and entrepreneurship, fostering cross-sector collaboration. Programs like Solidarity FabLab combine technical training with social inclusion, offering vocational education to NEETs
3. Experimental & Scalable Model
Nod operates as a living lab, where new ideas, tools, and business models are tested and refined in real-world conditions.
By incubating creative businesses&social enterprises, Nod provides a pathway from learning to entrepreneurship, ensuring sustainability beyond grants or funding cycles.
4. Community-Centered Urban Impact
Nod fosters collaborative urban interventions, such as Dâmbovița Apă Dulce, reconnecting people with their city through design, public events, and participatory urbanism.
Open workshops, hackathons, and mentorship programs ensure that knowledge and resources are accessible to all, strengthening inclusivity and civic engagement.
By blending adaptive reuse, circular design, and social innovation, Nod offers a scalable model for creative hubs worldwide, redefining how cities can foster creative, sustainable, and inclusive communities.
Nod Makerspace is a highly adaptable model that can be replicated in different cities, communities, and socio-economic contexts, offering a sustainable approach to urban regeneration, creative entrepreneurship, and inclusive education.
1. Adaptive Reuse & Community-Led Urban Regeneration
Nod demonstrates how underutilized industrial spaces can be repurposed into creative hubs through bottom-up participation. This model can be replicated in other cities with abandoned factories, warehouses, or civil buildings, fostering cultural preservation and economic revitalization.
2. Hybrid Makerspace & Learning Hub Model
Unlike conventional makerspaces, Nod integrates education, business incubation, and public engagement, making it financially sustainable and community-driven. This model can be transferred to other regions through partnerships with universities, municipalities, and cultural organizations.
3. Solidarity FabLab: Nod’s free vocational programs in woodworking, digital fabrication, and tailoring for vulnerable communities can be adapted to different industries and locations, addressing youth unemployment and social exclusion.
4. The Materials Library connects designers with sustainable materials and circular economy solutions. This concept can be expanded globally, creating localized archives of regional resources to support eco-friendly design and responsible production.
5. Public Space Activation & Community Engagement
Projects like Dâmbovița Apă Dulce demonstrate how public spaces can be revitalized through design and participatory urbanism. This model can be implemented in other cities, reconnecting people with rivers, green spaces, or underused urban areas.
Conclusion: A Blueprint for Sustainable Creative Hubs
By combining adaptive reuse, education, circular design, and community engagement, Nod Makerspace provides a scalable and transferable model for cities seeking to foster inclusive and sustainable creative ecosystems.
1. Adaptive Reuse & Community-Led Urban Regeneration
Nod demonstrates how underutilized industrial spaces can be repurposed into creative hubs through bottom-up participation. This model can be replicated in other cities with abandoned factories, warehouses, or civil buildings, fostering cultural preservation and economic revitalization.
2. Hybrid Makerspace & Learning Hub Model
Unlike conventional makerspaces, Nod integrates education, business incubation, and public engagement, making it financially sustainable and community-driven. This model can be transferred to other regions through partnerships with universities, municipalities, and cultural organizations.
3. Solidarity FabLab: Nod’s free vocational programs in woodworking, digital fabrication, and tailoring for vulnerable communities can be adapted to different industries and locations, addressing youth unemployment and social exclusion.
4. The Materials Library connects designers with sustainable materials and circular economy solutions. This concept can be expanded globally, creating localized archives of regional resources to support eco-friendly design and responsible production.
5. Public Space Activation & Community Engagement
Projects like Dâmbovița Apă Dulce demonstrate how public spaces can be revitalized through design and participatory urbanism. This model can be implemented in other cities, reconnecting people with rivers, green spaces, or underused urban areas.
Conclusion: A Blueprint for Sustainable Creative Hubs
By combining adaptive reuse, education, circular design, and community engagement, Nod Makerspace provides a scalable and transferable model for cities seeking to foster inclusive and sustainable creative ecosystems.
Addressing Global Challenges with Local Solutions
Nod Makerspace tackles climate change, social inequality, urban decline, and the future of work through sustainable design, vocational education, and adaptive reuse, offering scalable, community-driven solutions for resilient cities.
1. Climate Change & Resource Scarcity → Circular Design & Adaptive Reuse
Nod transformed a former industrial hall into a creative hub, reducing material waste and urban sprawl. The Materials Library promotes sustainable materials and circular economy principles, enabling designers to innovate with eco-friendly alternatives.
2. Social Inequality & Workforce Development → Inclusive Vocational Training
Through Solidarity FabLab, Nod offers free hands-on training in woodworking, tailoring, engineering, and digital fabrication, equipping vulnerable groups with marketable skills. This model can be replicated globally to empower disadvantaged communities.
3. Urban Decline & Loss of Public Spaces → Community-Driven Urban Regeneration
The Dâmbovița Apă Dulce project reconnects citizens with urban nature through participatory tactical urbanism, art, and community engagement. This model can help other cities revitalize public spaces sustainably.
4. Creative Industry Challenges → Supporting Local Entrepreneurs & Startups
Nod provides affordable access to prototyping tools, mentorship, and incubation programs, fostering sustainable creative businesses like Arhitecții Inovării and Consolidate to help local talent thrive.
5. Globalization & Loss of Identity → Strengthening Local Belonging
By blending traditional crafts with modern digital fabrication, Nod fosters a unique cultural identity, ensuring that local creativity remains a core element of urban development.
Conclusion
By addressing global challenges with local solutions, Nod Makerspace offers a replicable, scalable model for building inclusive, sustainable, and creative communities worldwide.
Nod Makerspace tackles climate change, social inequality, urban decline, and the future of work through sustainable design, vocational education, and adaptive reuse, offering scalable, community-driven solutions for resilient cities.
1. Climate Change & Resource Scarcity → Circular Design & Adaptive Reuse
Nod transformed a former industrial hall into a creative hub, reducing material waste and urban sprawl. The Materials Library promotes sustainable materials and circular economy principles, enabling designers to innovate with eco-friendly alternatives.
2. Social Inequality & Workforce Development → Inclusive Vocational Training
Through Solidarity FabLab, Nod offers free hands-on training in woodworking, tailoring, engineering, and digital fabrication, equipping vulnerable groups with marketable skills. This model can be replicated globally to empower disadvantaged communities.
3. Urban Decline & Loss of Public Spaces → Community-Driven Urban Regeneration
The Dâmbovița Apă Dulce project reconnects citizens with urban nature through participatory tactical urbanism, art, and community engagement. This model can help other cities revitalize public spaces sustainably.
4. Creative Industry Challenges → Supporting Local Entrepreneurs & Startups
Nod provides affordable access to prototyping tools, mentorship, and incubation programs, fostering sustainable creative businesses like Arhitecții Inovării and Consolidate to help local talent thrive.
5. Globalization & Loss of Identity → Strengthening Local Belonging
By blending traditional crafts with modern digital fabrication, Nod fosters a unique cultural identity, ensuring that local creativity remains a core element of urban development.
Conclusion
By addressing global challenges with local solutions, Nod Makerspace offers a replicable, scalable model for building inclusive, sustainable, and creative communities worldwide.
Nod Makerspace has become a key driver of urban transformation, fostering community engagement, creative entrepreneurship, and inclusive learning. Through its collaborative, sustainable, and interdisciplinary approach, Nod has reconnected people with their city, their craft, & each other, contributing to a stronger sense of belonging in Bucharest & beyond.
1. Social & Community Impact
✅ Hosting a continuos no. of 120+ active members (designers, makers, architects, engineers) to collaborate, learn, and innovate within a self-sustaining creative ecosystem.
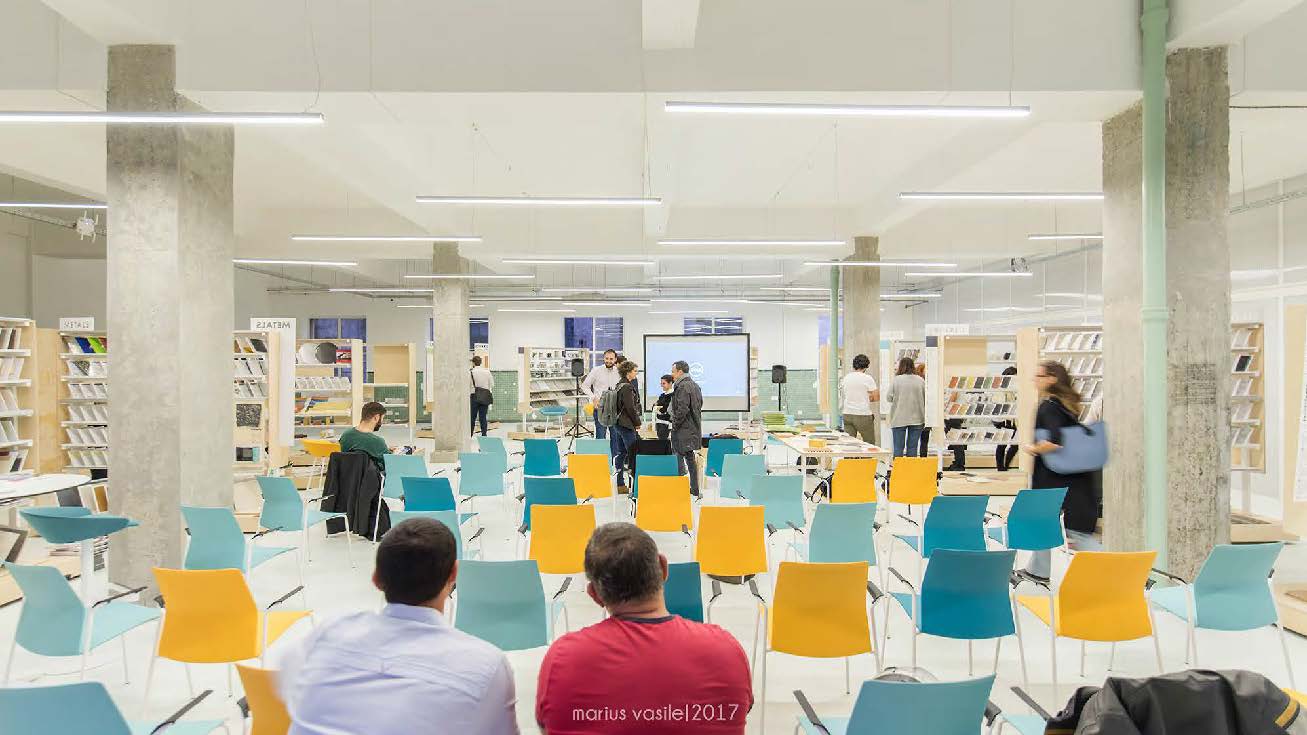
✅ Hosted over 500 events, workshops, and exhibitions
✅ Dâmbovița Delivery reactivated urban space through cultural interventions, public design projects, and environmental awareness campaigns, reconnecting over 20,000 participants with the city’s river in September 2024.
2. Educational & Economic Impact
✅ Trained over 350+ individuals through Solidarity FabLab, offering free vocational courses for NEETs.
✅ Supported 40+ startups & creative entrepreneurs through incubation programs such as Bursa de Makeri, Arhitecții Inovării and Consolidate, fostering sustainable businesses in design, architecture, and social impact sectors.
✅ Reenabled the Materials Library—Romania’s first open-source archive of sustainable materials, for students, designers, & researchers.
3. Urban & Cultural Regeneration Impact
✅ Revitalized 2200 sqm underutilized industrial hall, transforming it into a vibrant cultural-creative hub, setting an exemplary model for adaptive reuse.
✅ Partnered with urban planners & civil society to implement co-creation processes for more inclusive, accessible, and people-centered urban spaces.
[Source: 2024 Activity Report]
In conclusion, Nod Makerspace proves that creative infrastructure fosters social cohesion, economic development, and urban regeneration. Its model can be replicated in cities looking to strengthen community bonds, activate public spaces, and promote sustainable inno
1. Social & Community Impact
✅ Hosting a continuos no. of 120+ active members (designers, makers, architects, engineers) to collaborate, learn, and innovate within a self-sustaining creative ecosystem.
✅ Hosted over 500 events, workshops, and exhibitions
✅ Dâmbovița Delivery reactivated urban space through cultural interventions, public design projects, and environmental awareness campaigns, reconnecting over 20,000 participants with the city’s river in September 2024.
2. Educational & Economic Impact
✅ Trained over 350+ individuals through Solidarity FabLab, offering free vocational courses for NEETs.
✅ Supported 40+ startups & creative entrepreneurs through incubation programs such as Bursa de Makeri, Arhitecții Inovării and Consolidate, fostering sustainable businesses in design, architecture, and social impact sectors.
✅ Reenabled the Materials Library—Romania’s first open-source archive of sustainable materials, for students, designers, & researchers.
3. Urban & Cultural Regeneration Impact
✅ Revitalized 2200 sqm underutilized industrial hall, transforming it into a vibrant cultural-creative hub, setting an exemplary model for adaptive reuse.
✅ Partnered with urban planners & civil society to implement co-creation processes for more inclusive, accessible, and people-centered urban spaces.
[Source: 2024 Activity Report]
In conclusion, Nod Makerspace proves that creative infrastructure fosters social cohesion, economic development, and urban regeneration. Its model can be replicated in cities looking to strengthen community bonds, activate public spaces, and promote sustainable inno